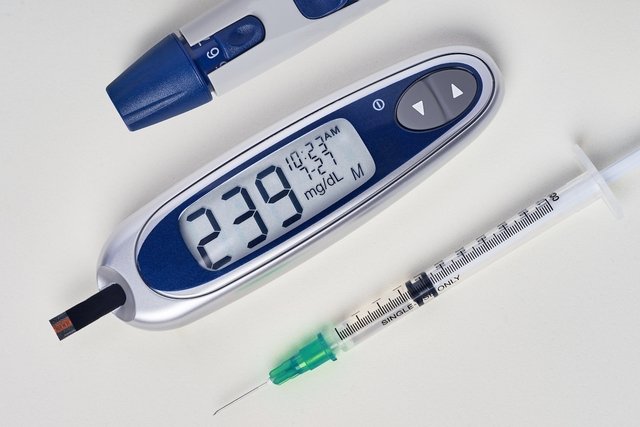
To control diabetes it is necessary to undergo a change in lifestyle, such as stopping smoking, maintaining a healthy and as natural diet as possible, low in sweets and carbohydrates in general, such as bread, rice or pasta, in addition to avoiding alcoholic beverages and practice physical activity regularly.
Furthermore, it is very important that all medical indications regarding treatment, which may involve medication, insulin and monitoring of blood sugar levels, are carried out at the correct times and in the manner indicated.
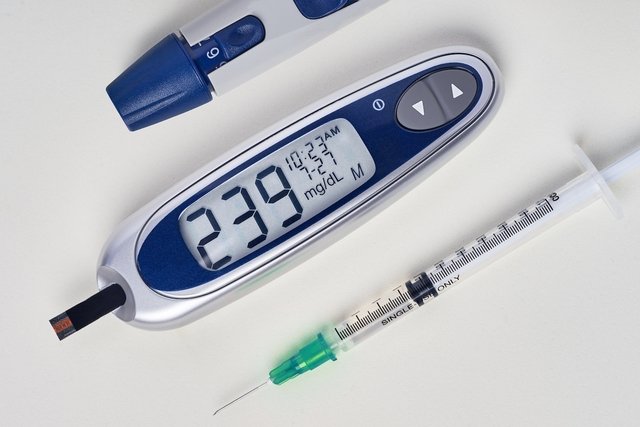
Some tips to help control diabetes, keeping values below 130 mg/dl on an empty stomach and below 180 mg/dl after meals, can be:
1. Record blood sugar values
Recording on paper the blood glucose values checked by the glucometer before and after meals can help in observing which foods can be consumed without causing risks and which should be avoided, and thus adapt the treatment so that it is effective and reduces the risks that uncontrolled diabetes can bring to health.
2. Reduce the consumption of certain fruits alone
Consuming fruits with high levels of carbohydrates, such as persimmon, figs, conde fruit, papaya and dried fruits, can increase the possibility of glycemic peaks, thus deregulating diabetes, which is why it is recommended to eat fruits that are richer in fiber, such as strawberries, melon and avocado. Check out the list of fruits that are recommended for diabetics.
3. Avoid eating sweets
Sweets can raise blood sugar levels as they are quickly absorbed foods, disrupting diabetes and increasing the risk of complications from the disease. Therefore, whenever possible, it is recommended to avoid eating sweets or when eating, it should be after a salty meal.
See with nutritionist Tatiana Zanin how to avoid eating sweets:
4. Reduce alcohol consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia for diabetics, due to overload on the liver, which is responsible for regulating blood sugar, and in this case, it will also metabolize alcohol. See what is the safe amount of alcohol for diabetics to consume.
5. Don’t go more than 3 hours without eating
When a diabetic goes more than 3 hours without eating, there is a great possibility of diabetes becoming unregulated and hypoglycemia occurring, which can lead to loss of consciousness and in more serious cases lead to a state of coma. See other symptoms of hypoglycemia and learn how to identify them.
6. Maintain ideal weight
Maintaining the ideal weight for age, sex and height is very important to be able to effectively regulate blood glucose, as people with diabetes and who are overweight or obese, with a body mass index (BMI) equal to or greater than 25kg/m² , may have impaired glycemic control, due to the decrease in glucose uptake by insulin, in addition to presenting greater risks for heart disease and stroke.
7. Eliminate cigarette use
Nicotine, the main component of cigarettes, can interfere with blood glucose levels, making it difficult to control diabetes. Furthermore, eliminating or reducing the use of cigarettes can bring numerous health benefits, because when nicotine is eliminated from the body , reduces the risk of retinopathy, heart disease and brain damage, all complications of diabetes that are related to smoking. Check out what home remedies can help you quit smoking.
8. Control blood pressure
Blood pressure and diabetes are closely linked, because over the years, diabetes makes the body’s arteries stiffer, and if blood pressure is not controlled, the chances of developing high blood pressure can increase, which increases the possibility of cerebrovascular accident (CVA).
9. Avoid some types of medications
Medications that can potentially harm the pancreas deregulate insulin levels, which are produced by this organ. This prevents sugar from being taken into the cells, causing it to remain in the bloodstream and uncontrollable diabetes.
Therefore, the following medications should be avoided:
- Amoxicillin;
- Clavulanate;
- Chlorpromazine;
- Azithromycin;
- Isoniazid;
- Paracetamol;
- Codeine;
- Mesalazine;
- Simvastatin;
- Furosemide;
- Enalapril;
- Methyldopa;
- Amiodarone;
- Azatioprina:
- Lamivudine;
- Losartan.
Therefore, if it is necessary to undergo any treatment involving these medications, the responsible doctor must know about the diabetes, whether it is controlled or not and how many years the person has lived with this condition, so that an assessment can be made as to whether it really is safe. use medicines.
10. Practice regular physical activity
Regular physical exercise helps control diabetes because it reduces fat levels in the blood, controls weight, improves blood circulation, and also helps the heart to pump blood more adequately.
How to control hypoglycemia
To control hypoglycemia that appears when blood sugar drops excessively, falling below 70 mg/dl, it is necessary to give the person sugar water or a glass of orange juice, for example. These foods will make your sugar rise and you will feel better. Understand what else can be done in cases of hypoglycemia.
How to control hyperglycemia
To control hyperglycemia, which is excess sugar in the blood, it is necessary to give the person the medication prescribed by the doctor to regulate the amount of sugar in the blood. It is still recommended to prevent blood sugar from rising again by reducing or eliminating sweets, such as cakes, soft drinks, puddings or ice cream from your diet and practicing physical activity, such as walking after meals. Know what should be done if hyperglycemia develops.
Nutritionist Tatiana Zanin explains more about how to follow a diet to control diabetes in the following video: