I always wanted to know what this thing is invert sugar that you saw, perhaps, on packaging or recipes. It’s simple and complicated at the same time.
What is invert sugar?
In a very simple way: a syrup (or syrup) made from water, glucose, fructose and may have a little sucrose also, the common sugar.
Sim, just that and nothing more.
Now the explanation of the name is well big head. Involves polarized light, rotation angle, optical activity e optical isomerism. They could have called it Liquid sugar? They could, but nooo. It had to be complicated!
To get there, we need to understand how the production of invert sugar.
How is invert sugar made?
It is made from a common sugar syrup (sucrose) and to turn into invert sugar there are a few ways:
- with use of difficult (invertase);
- with addition of acid (cream of tartar, citric or hydrochloric acid);
- together with cookingthat is, you have to put heat also.
All this to break the sugar (sucrose) which is formed by the union of glucose e fructose that are simple sugars.
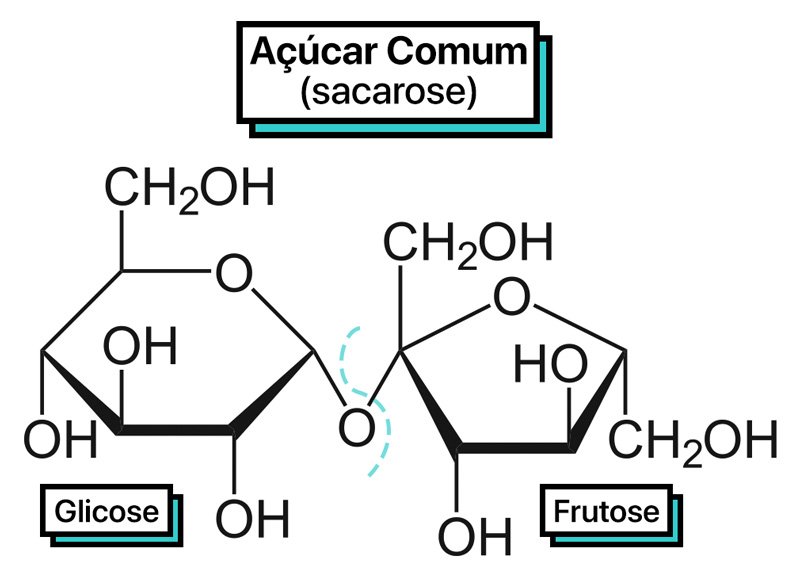
The enzyme breaks the bond between glucose it’s at fructose that form the sucrose molecule. The method that uses acid and cooking has the same function, just through a different mechanism.
On the internet, you can find tutorials that teach to do at home…the detail is: you won’t be sure the proportion of sugars present in the syrup made, there will be a mixture of sucrose, glucose and fructose. And differences in their quantity can influence the functions that invert sugar has.
Inverted sugar and polarized light
When passing a special light (polarized light) by common sugar syrup (sucrose), the light deviates to the right.
And by doing the same, moving on to special light by the fur invert sugar (glucose and fructose syrup), the light deviates to the left. In other words, there was a “inversion” in the direction of the light and thus giving rise to the name.
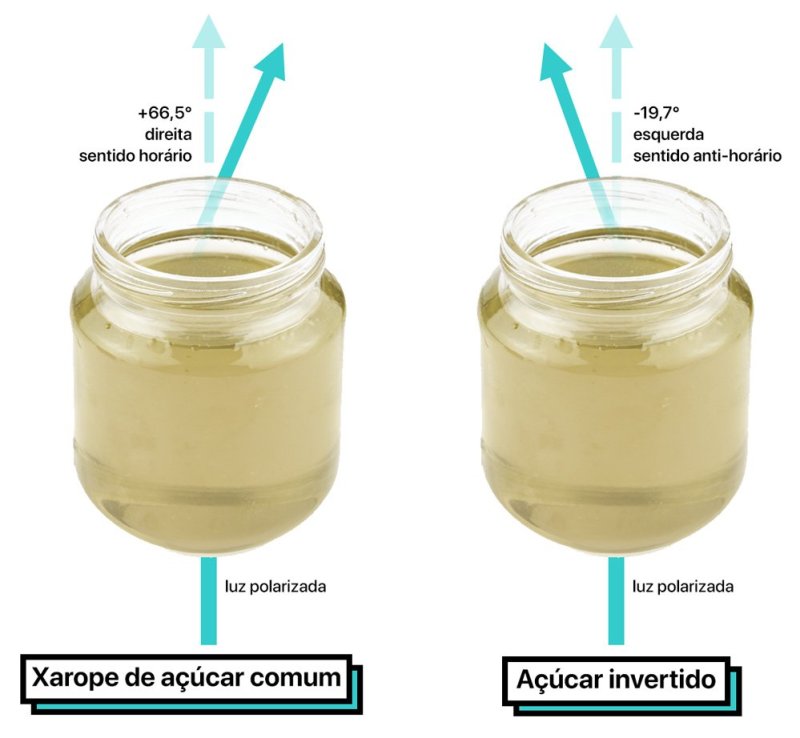
This change in direction is due to differences in chemical properties (e structural) of the sugars involved.
- Ordinary sugar syrup (sucrose) has rotation angle +66.5 (clockwise, right)
- Invert Sugar has a rotation angle of -19.7° (counterclockwise, left).
What is invert sugar for and functions?
O invert sugar is most used in business (bakery, confectionery) and industry. It could be used at home too, but it is not that common and not sold in any store.

The basic functions of invert sugar:
- substitute for sugar (it’s slightly sweeter)
- food source for fermentos
- assists in consistency e textura
- control in crystallization do sugar e água
- retention of umidade
- favors the reaction of Maillard
A amount used from invert sugar It depends on the recipe and what the main objective of its use, is being used to Modify what characteristic of the recipe.
Two substitutes The most common and easiest to find are mel (technically, it is a natural invert sugar because of the composition) and liquid glucose (sold in a confectionery store). In the case of honey, depending on the quantity you can add flavor in the recipe.
One syrup (or syrup) made from water, glucose, fructose and may have a little sucrose also, the common sugar. Sim, just that and nothing more.
Now the explanation of the name is well big head. Involves polarized light, rotation angle, optical activity e optical isomerism. They could have called it Liquid sugar? They could, but nooo. It had to be complicated!
To get there, we need to understand how the production of invert sugar.
Now the explanation of the name is well big head. Involves polarized light, rotation angle, optical activity e optical isomerism. They could have called it Liquid sugar? They could, but nooo. It had to be complicated!
To get there, we need to understand how the production of invert sugar.
It is made from a common sugar syrup (sucrose) and to turn into invert sugar There are a few ways: using difficult (invertase); with addition of acid (cream of tartar, citric or hydrochloric acid); together with cookingthat is, you have to put heat also.
The enzyme breaks the bond between glucose it’s at fructose that form the sucrose molecule. The method that uses acid and cooking has the same function, just through a different mechanism.
When passing a special light (polarized light) by common sugar syrup (sucrose), the light deviates to the right. And by doing the same, moving on to special light by the fur invert sugar (glucose and fructose syrup), the light deviates to the left. In other words, there was a “inversion” in the direction of the light and thus giving rise to the name.
The basic functions of invert sugar: substitute for sugar (it’s slightly sweeter);
food source for fermentos; assists in consistency e textura; control in crystallization do sugar e água; retention of umidade; favors the reaction of Maillard
References
- BELITZ, H.-D.; GROSCH, WERNER; SCHIEBERLE, PETER. Food Chemistry. Springer Science & Business Media, 2009
- FENNEMA, Owen R. . Food chemistry. 3rd ed. New York: Marcel Dekker, 1996. (Portuguese, affiliate link)
- McGEE, Harold. On food and cooking: the science and lore of the kitchen. New York: Scribner, 2004. (Portuguese, affiliate link)
- Khan Academy: Optical activity
Transparency note: the article has links to an affiliate program, if you purchase, PratoFundo may receive a commission on the sale that helps keep the site running. Price variations may occur.




