Hypoglycemia, or low glucose, happens when blood sugar levels are lower than normal. The normal fasting glucose value is, in general, up to 99 mg/dL, and hypoglycemia is considered when blood glucose levels are between 55 and 69 mg/dL.
When glucose becomes too low it can cause symptoms such as dizziness, tremors, tiredness, chills, mental confusion, palpitations and even fainting. Know how to recognize all the symptoms of hypoglycemia.
When identifying hypoglycemia, it is recommended to eat 15 g of simple sugar, such as 1/2 cup of fruit juice or 1 tablespoon of sugar or honey, for example, and assess blood glucose 15 minutes later. When the sugar level is below 55 mg/dL, you should take a glucagon injection and then seek the nearest emergency care.

Main symptoms
The main symptoms of hypoglycemia are:
- Tremors;
- Dizziness;
- Tiredness;
- Chills;
- Headache;
- Irritability and mental confusion;
- Fainting;
- Rapid heartbeat.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia generally appear quickly and when blood glucose levels are below 70 mg/dl. However, some people can tolerate lower blood sugar levels, while other people may have symptoms even at higher blood sugar levels.
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of hypoglycemia must be made by an endocrinologist or general practitioner, through evaluation of the symptoms presented and the person’s health and family history.
If you want to assess your risk of hypoglycemia, make an appointment with the endocrinologist closest to you:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Furthermore, to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor also orders a blood test to assess glucose, insulin, proinsulin and C-peptide levels.
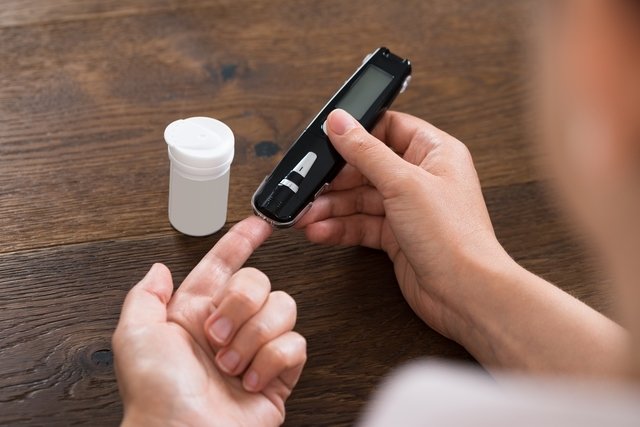
People who have diabetes need to check their blood sugar level daily, using the capillary blood glucose test, which is done using a rapid glucose measuring machine, which can be found in pharmacies and provides the result instantly. See how to measure capillary blood glucose.
Possible causes
Hypoglycemia can occur due to the use of insulin or oral medications to treat diabetes, which can lead to an excessive decrease in blood glucose levels.
Furthermore, hypoglycemia can also arise due to low carbohydrate intake, high consumption of alcoholic beverages, after surgery, prolonged fasting, hormonal deficiencies, excessive physical activity, or due to liver, kidney or heart disease. for example.
What is the treatment like?
The treatment of hypoglycemia varies depending on the severity of the condition. If the person is conscious, it is important to consume foods or drinks rich in simple sugar to balance sugar levels more quickly.
The main recommendations in cases of hypoglycemia are:
- Take 15g simple sugar, such as 1/2 cup (tea) of fruit juice, such as apple, orange or grape; 1/2 can of regular soda; or 1 tablespoon of sugar, honey or corn syrup;
- Measure glucose approximately 15 minutes after the intake of simple sugar and, if blood glucose is still below 70 mg/dL, it is recommended to eat 15g of simple sugar again until the glucose value is normalized;
- Have a carbohydrate-rich snack when glucose values are already within normal values. Some snack options include bread, toast or crackers;
- Avoid eating carbohydrates rich in fiber, such as beans, chickpeas or lentils, or carbohydrates with a lot of fat, such as chocolate, as fiber and fat slow the absorption of sugar;
In cases of severe hypoglycemia, when blood sugar is below 55 mg/dL, glucagon injection should be administered, if available at home. After applying glucagon, you must wait about 20 minutes and assess blood glucose levels. If it still remains low, it is important to call the nearest emergency service. See other tips on what to do in a hypoglycemia crisis.
As children generally need less than 15 grams of simple sugar to treat hypoglycemia, it is recommended to consult your pediatrician to advise on the recommended amount of sugar depending on the child’s age.
How to prevent hypoglycemia
Some tips to avoid new episodes of hypoglycemia, especially for diabetics, are:
- Take the correct doses of medications.
- Follow a diet guided by a nutritionist, with ideal amounts of carbohydrates;
- Do not skip meals;
- Avoid the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- Do physical exercise regularly and moderately;
- Check blood glucose before and after physical activities;
- Check blood glucose before and after meals.
If your doctor has approved the consumption of alcoholic beverages, it is important to follow some guidelines to avoid hypoglycemia, such as drinking slowly and always having a meal or snack before or immediately after drinking.
In addition, it is also recommended to always have a quick source of simple sugar in your bag, such as a juice box, sugar or glucose candies, in case your blood sugar levels get too low.
Bibliography
- AMERICAN DIABETES ASSOCIATION. Alcohol and diabetes. Disponível em: <https://diabetes.org/healthy-living/medication-treatments/alcohol-diabetes>. Acesso em 18 out 2023
- CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION. How To Treat Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia). Available at: <https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/low-blood-sugar-treatment.html>. Accessed on October 18, 2023
- MATHEW P; THOPPIL D – STATPEARLS (INTERNET). TREASURE ISLAND (FL): STATPEARLS PUBLISHING. Hypoglycemia. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534841>. Accessed on October 18, 2023
- AMERICAN DIABETES ASSOCIATION. Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Glucose). Disponível em: <https://diabetes.org/living-with-diabetes/treatment-care/hypoglycemia>. Acesso em 18 out 2023
- NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF DIABETES AND DIGESTIVE AND KIDNEY DISEASES. Low Blood Glucose (Hypoglycemia). Disponível em: <https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/preventing-problems/low-blood-glucose-hypoglycemia>. Acesso em 18 out 2023

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13