Hepatic steatosis is the accumulation of fat in the liver, a very common problem that can cause pain on the right side of the abdomen, a swollen belly, nausea, vomiting and general malaise.
The accumulation of fat in the liver appears to occur mainly due to a high-fat diet, but it can also occur in people who drink alcohol excessively.
In the presence of symptoms indicative of hepatic steatosis, a hepatologist should be consulted to carry out tests that assess the functioning of the liver and initiate appropriate treatment, which tends to include changes in diet and physical exercise. Check out some of the tests that assess liver health.
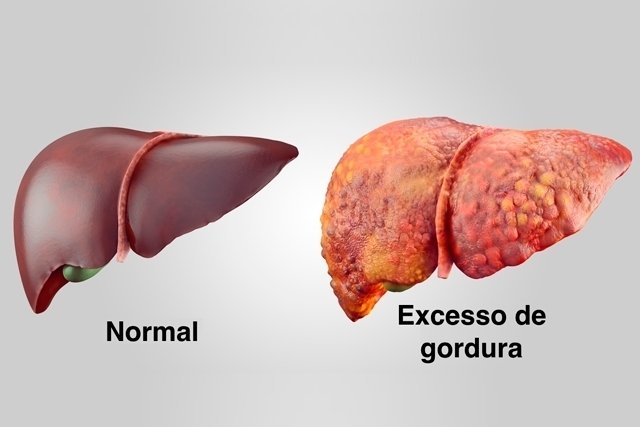
Degrees of hepatic steatosis
Hepatic steatosis can be classified into a few degrees:
- Grade 1 (mild): there is a slight accumulation of fat in the liver, which, in general, corresponds to the involvement of around 30% of liver cells;
- Grau 2 (moderate): there is moderate accumulation of fat, so that up to 60% of liver cells are affected;
- Grau 3 (grave): there is a large accumulation of fat in the liver.
The degrees of hepatic steatosis can initially be identified by performing an abdominal ultrasound, but other tests are necessary to assess whether there is inflammation in the liver and the presence of lesions, for example.
Main symptoms
The most common symptoms of hepatic steatosis are:
- Pain in the upper right side of the abdomen;
- Unexplained weight loss;
- Fatigue and general malaise;
- Nausea and vomiting.
It is also normal that during the first stages of the disease there are no symptoms of any kind and, therefore, hepatic steatosis is often discovered accidentally through tests to diagnose other diseases.
In cases of cirrhosis, other symptoms may also appear, such as yellowing of the skin and eyes, itching of the body and swelling of the belly, legs and ankles. Check out a more complete list of the symptoms of fatty liver disease.
Liver steatosis online test
If you think you may have fatty liver disease, indicate what you are feeling:
How to confirm the diagnosis
Changes in the liver can initially be detected through a blood test that evaluates the substances produced by this organ. And, if there are altered values, which indicate that the liver is not working well, the doctor may order additional tests such as ultrasound, tomography, liver elastography, magnetic resonance imaging or a biopsy.
However, it is important to highlight that liver fat does not always cause changes in blood tests, which can delay the diagnosis of the disease until the patient undergoes an ultrasound to investigate other problems.
When to make an appointment
It is important to consult a hepatologist, gastroenterologist or general practitioner when there is suspicion of fatty liver, especially when symptoms such as pain in the abdomen on the right side, frequent nausea, vomiting and general malaise appear.
Possible causes
The causes of fat in the liver are not yet well understood, however the mechanism that leads to the onset of the disease is the subject of several studies. It is believed that the accumulation of fat in the liver is related to the imbalance between the consumption and synthesis of fat by the body and its use and elimination. This imbalance, in turn, could be related to genetic, nutritional and environmental factors.
Although the causes are not yet known, the risk of developing fatty liver is much higher in people who drink alcohol, and can be increased when there are other risk factors, such as:
- Obesity;
- Type 2 diabetes;
- High pressure;
- High cholesterol;
- Age over 50 years;
- Being a smoker;
- Have hypothyroidism.
Additionally, bariatric surgery and other weight loss procedures increase the risk of developing fatty liver due to changes in metabolism caused by rapid weight loss. However, this problem can also arise in people who do not have any risk factors, and can even affect children and pregnant women. Learn more about the causes of fatty liver.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for fatty liver is mainly done with changes in diet, regular exercise and the elimination of alcohol consumption. In addition, it is also necessary to lose weight and control diseases that worsen the problem, such as diabetes, hypertension and high cholesterol, for example. See an example of what a fatty liver diet should look like.
There are no specific medications to treat fatty liver disease, but your doctor may recommend hepatitis B vaccines to prevent further liver disease from developing. Some home remedies can also be used to aid treatment, such as milk thistle tea or artichoke tea, and it is important to first consult a doctor before using them.
The following video brings tips from our nutritionist to control and reduce liver fat:
Bibliography
- BRAZILIAN SOCIETY OF HEPATOLOGY. Hepatic steatosis. Available at: <https://sbhepatologia.org.br/imprensa/esteatose-hepatica/>. Accessed on June 21, 2022
- V., Juan Pablo A.; C., Kurt AS; J., Marco A. Histological classification for nonalcoholic fatty liver: NAFLD activity score (NAS). Gastroenterol. latinoam. Vol 25. 4 ed; 308-313, 2014
- DONGIOVANNI, Paola; VALENTI, Luca. A Nutrigenomic Approach to Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. International Journal of Molecular Science. Vol 18. 2017
- COBBINA, Enoch; AKHLAGHI, Fatemeh. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) – Pathogenesis, Classification, and Effect on Drug Metabolizing Enzymes and Transporters. Drug Metab Rev. Vol 49. 2 ed; 197-211, 217