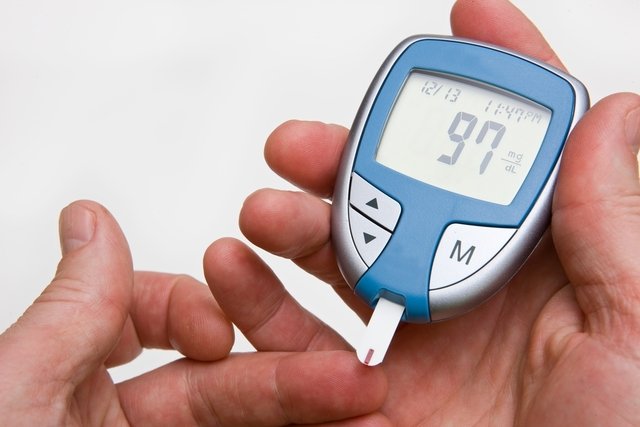
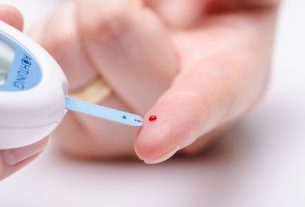
The capillary blood glucose test is carried out with the aim of checking blood sugar levels at a certain time of the day and for this purpose a blood glucose device must be used to analyze a small drop of blood that is taken from the tip of the finger.
Measuring capillary blood glucose is more suitable for people who have hypoglycemia, pre-diabetes and diabetes, in which case it is recommended that the dosage be done before and after meals so that glucose levels can be controlled and, thus, they can Diet adjustments or changes in medication dosage may be made if necessary.
Although the dosage is best recommended before and after meals, the endocrinologist may recommend the dosage at other times of the day, such as before bed and as soon as you wake up, for example, as this way it is possible to check the body’s behavior during periods of fasting, being important in the treatment of diabetic patients.
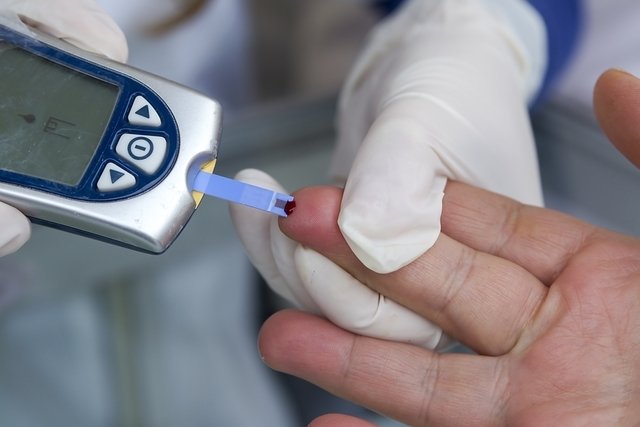
How to measure capillary blood glucose
To measure capillary blood glucose, you must:
- Wash your hands and dry them properly;
- Insert a test strip into the blood glucose meter;
- Prick your finger with the device’s needle;
- Touch the test strip to the drop of blood until the test strip deposit is filled;
- Wait a few seconds until the blood glucose value appears on the device monitor.
To avoid always pricking the same place, you must change fingers with each new capillary blood glucose measurement. The most recent blood glucose devices can also measure blood sugar taken from the arm or thigh, for example. Some blood glucose devices may work differently, so it is important to read the manufacturer’s instructions for use before using the device.
To avoid incorrect readings, it is important that the equipment is cleaned regularly and in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations, that the strips are within their expiration date, that the glucometer is calibrated and that the amount of blood is sufficient to the analysis.
Blood glucose can also be measured using a small sensor that is attached to the arm and takes measurements constantly during the day and night. This sensor indicates real-time blood glucose in the previous 8 hours and the trend of the glycemic curve for the next few moments, making this sensor very effective in terms of controlling diabetes and preventing hypo and hyperglycemia.
Blood glucose reference values
After measuring capillary blood glucose, it is important to compare the result with reference values:
In the case of newborns, it is difficult for the test to be carried out while fasting, so it is recommended that the newborn’s blood glucose levels be between 50 and 80 mg/dL.
If the person does not have diabetes, but the blood glucose value is in the altered blood glucose or diabetes column, it is recommended that they repeat the measurement the following day, and if the result persists, consult the endocrinologist so that a conclusive diagnosis can be made. .
In cases where blood glucose is below 70 mg/dl, you should drink a glass of juice or a glass of water with sugar, for example. Learn about the treatment for low glucose.
Normal values in people with diabetes
In the case of people diagnosed with diabetes, normal values should be:
- Fasting blood glucose: entre 80 e 130 mg/ dL;
- 1 to 2 hours after the meal: less than 180 mg/ dL.
If capillary blood glucose is above normal values, it is recommended that a doctor be consulted to adapt the treatment or take medication according to the dose indicated by the doctor.
To better understand the result of your glucose test, select the test performed in the calculator below and indicate your result:
How to lower glucose levels
Glucose levels can be controlled with simple changes in everyday life, such as practicing regular physical activity and eating a balanced diet low in foods that contain a lot of sugar.
However, if glucose levels do not return to normal, the doctor may recommend the use of some medications, which should be taken as directed. See how to lower blood sugar levels.
Bibliography
- EBSERH. Standard Operating Procedure – Measuring capillary blood glucose (adult). Available at: <http://www2.ebserh.gov.br/documents/1132789/1132848/POP+1.1_AFERI%C3%87%C3%83O+DA+GLICEMIA+CAPILAR+-ADULTO.pdf/b7b5e860-c6c4-46da -8140-bf86541c5850>. Accessed on November 28, 2019
- STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE – MEASUREMENT OF CAPILLARY GLUCOSE (ADULT). EBSERH. Available at: <http://www2.ebserh.gov.br/documents/1132789/1132848/POP+1.1_AFERI%C3%87%C3%83O+DA+GLICEMIA+CAPILAR+-ADULTO.pdf/b7b5e860-c6c4-46da -8140-bf86541c5850>. Accessed on November 28, 2019
- BRAZILIAN DIABETES SOCIETY. Methods for assessing glycemic control. 2015. Available at: <https://www.diabetes.org.br/profissionais/images/pdf/diabetes-tipo-2/010-Diretrizes-SBD-Metodos-para-Avaliacao-pg110.pdf>. Accessed on November 28, 2019
- REGIONAL COUNCIL OF PHARMACY OF ALAGOAS. Capillary blood glucose testing is important for the treatment of diabetic patients. Available at: <http://www.crf-al.org.br/2015/10/teste_da_glicemia_capilar_e_importante_para_o_tratamento_de_pacientes_diabeticos_saiba_mais/>. Accessed on November 28, 2019