Most cases of hepatic steatosis are asymptomatic, however some people may experience excessive tiredness, abdominal discomfort, belly swelling, unexplained weight loss, lighter stools and itchy skin.
Symptoms of hepatic steatosis normally appear when the fat in the liver exceeds 10%, with more accumulated fat and inflammation of the liver cells, resulting in the development of symptoms.
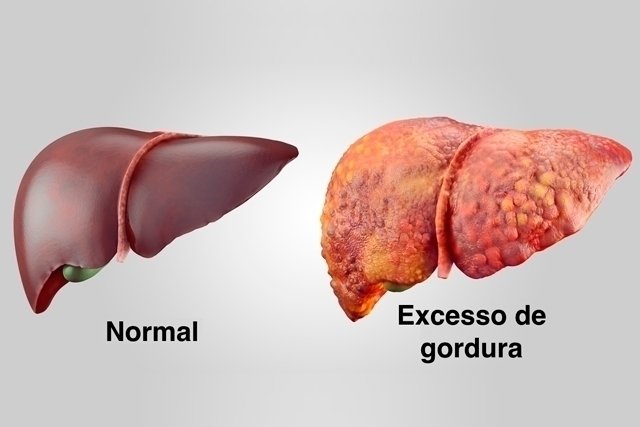
Hepatic steatosis, also known as fatty liver, is a situation in which there is an accumulation of fat in the liver due to genetic factors, obesity, type 2 diabetes or high cholesterol, for example, and it is important that the hepatologist or gastroenterologist is consulted so that it can be the diagnosis is made and the most appropriate treatment is initiated.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of hepatic steatosis are:
- Excessive tiredness;
- Abdominal discomfort on the right side;
- General malaise;
- Swelling in the belly;
- Weight loss without apparent cause;
- Lighter stools;
- Itchy skin;
- Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
Signs and symptoms indicative of the disease are not always identified, as most people are asymptomatic, because the appearance of symptoms depends on the amount of accumulated fat, cause and degree of steatosis. See what the degrees of hepatic steatosis are and the main causes.
Online symptom test
To find out your risk of having fatty liver disease, put the symptoms presented in the following test:
The symptom test is only a guidance tool and does not serve as a diagnosis or replace consultation with a hepatologist, gastroenterologist or general practitioner.
What to do in case of suspicion
In the presence of signs and symptoms of hepatic steatosis, it is important to consult a hepatologist, a gastroenterologist or a general practitioner, so that laboratory and imaging tests can be carried out to help confirm the diagnosis.
The doctor can indicate the dosage of fasting glucose, total cholesterol and fractions and tests that assess liver function such as TGO, TGP and gamma-GT, for example. In addition, palpation of the abdomen and ultrasound or tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen can be performed, which allows changes in the organ to be identified and, thus, the progression of the disease can be assessed.
Make an appointment with your nearest doctor to assess your risk of fatty liver disease:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for hepatic steatosis should be guided by a hepatologist or general practitioner according to the symptoms presented and the cause of fatty liver. Therefore, the doctor may recommend that the person stop drinking alcoholic beverages, practice physical activity regularly, keep cholesterol levels under control and have a healthy and balanced diet, under the guidance of a nutritionist. See what the diet for fat in the liver should be like.
Furthermore, it is important to remember that during pregnancy, the appearance of fat in the liver is a very serious complication, which can cause death for the mother and baby, and it is important to identify and treat it according to the doctor’s advice.
When the treatment of hepatic steatosis is not carried out properly and the person maintains the cause of the disease, excess fat in the liver can increase and cause serious damage to liver cells, resulting in cirrhosis.
Check out some tips in the following video on what to eat to avoid and treat fatty liver disease:
Bibliography
- UPTODATE. Epidemiology, clinical features, and diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adults. 2019. Disponível em: <https://www.uptodate.com/contents/epidemiology-clinical-features-and-diagnosis-of-nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease-in-adults?search=esteatose%20hep%C3%A1tica&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1#H2>. Acesso em 30 abr 2021

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13




