Baby gulping is characterized by the release of a small amount of milk from the mouth after breastfeeding or taking a bottle, without having to make any effort. This condition is very common in newborn babies and lasts until about 6 or 7 months, but it can be uncomfortable for the baby and the parents because the baby may cry afterwards.
Some very important tips for reducing baby gulping include:
- Prevent the baby from swallowing too much air during feeding;
- Always burp the baby during and after feedings;
- Dress the baby in loosely fitting clothes and diapers;
- Avoid moving the baby suddenly after feeding;
- Just put the baby to bed 30 minutes after feeding;
- Babies who are not breastfed can take a specific formula against reflux, such as Aptamil AR, Nan AR or Enfamil AR Premium.
To reduce the amount of air swallowed by the baby, the mother must adopt a correct breastfeeding technique, or, if the baby is bottle-fed, keep the nipple always full of milk. See some positions for breastfeeding.
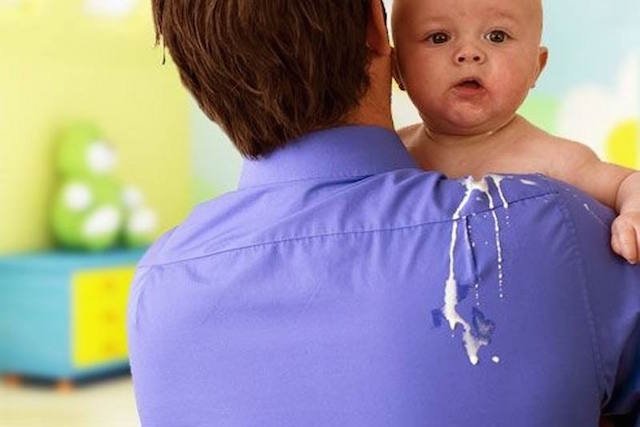

Furthermore, if it is necessary to lay the baby down after burping, a pillow should be placed under the mattress, and not under the baby’s head, to elevate the baby’s head and place him/her lying on his/her side. Another possibility is to place a wedge 5 to 10 cm high at the head of the crib, forming a 30-degree angle, to keep the head always higher than the feet.
In cases where gulf episodes are very frequent and following these measures is not enough, the pediatrician may recommend taking medications such as domperidone or cisapride, for example.
Why Babies Golf
Gastroesophageal reflux, popularly known as baby gurgling, is a normal condition that affects all newborn babies. Swallowing is normal until 6 to 7 months of age, when the introduction of other softer foods begins, such as breast milk and bottles, and also with the child’s more upright position.
When swallowing continues from this stage, the baby must be evaluated by the pediatrician because there may be situations such as congenital stenosis of the esophagus, tracheoesophageal fistula, esophageal atresia, swallowing disorders, hypertrophic stenosis of the pylorus, gastric or duodenal ulcer, annular pancreas, pseudo -intestinal obstruction, food allergy (cow’s milk protein), urinary infection, intestinal parasites, genetic-metabolic diseases, asthma, cystic fibrosis or changes in the central nervous system, for example. Here’s how to know when golfing is normal.
How to burp your baby


To burp your baby, you can use one of the following techniques:
- Place the baby standing against the mother’s shoulder and gently pat the back;
- Place the baby sitting on your lap and hold the baby’s head with one hand and gently pat the baby’s back with the other.
These techniques must be done during breastfeeding and after breastfeeding to eliminate excess air and prevent the appearance of gulfs.
How to differentiate gulf from vomit
To differentiate the gulf from an episode of vomiting, one must observe other signs present, such as: effort that the baby makes with his body, as in the case of vomiting it is necessary to make some effort, while in the gulf no effort is necessary, because the liquid comes out naturally through the mouth. In the case of vomiting, the baby may also show signs that he is not feeling well, whining or crying, while in the gulf, he may be apparently normal.
However, when the baby has frequent episodes of gulf the liquid can be acidic and cause irritation in the esophagus and larynx, and therefore, during an episode of gulf the baby may present excessive crying, irritability, sleep disturbances, agitation and refuse. breastfeed or take a bottle.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13