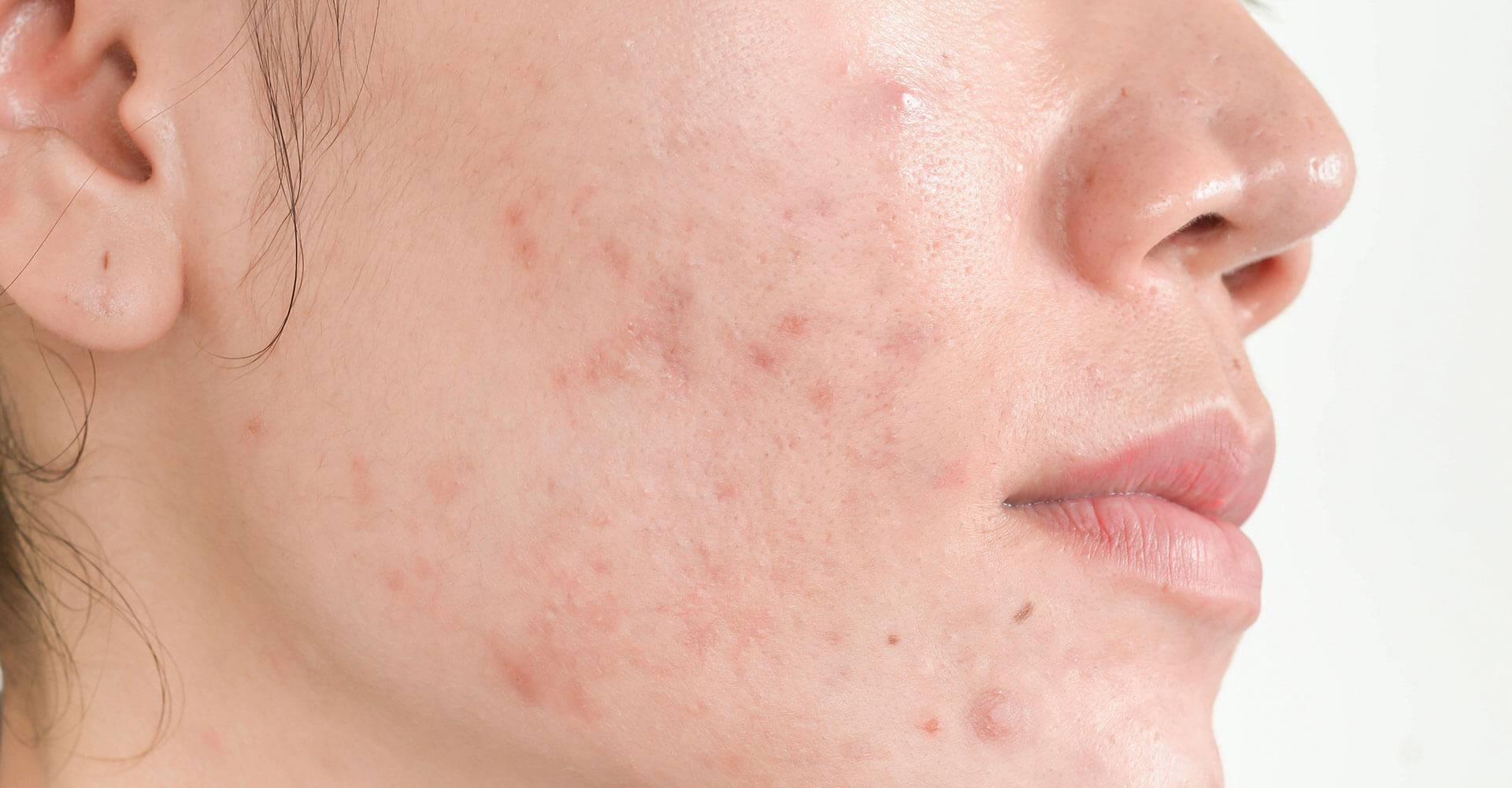
Fungal acne, as the name suggests, is caused by a fungus, and despite being similar to common acne, it requires specific care.
A fungal acne It is a type of acne very similar to the common acne that everyone knows. The one that is generally caused by excess sebum on the skin and hormonal problems. However, fungal acne, despite presenting similar symptoms, has a different cause, in this case a fungus, as the name suggests.
Therefore, despite being commonly confused with acne vulgaris, it is a little more complex and requires special care. Furthermore, to be diagnostic it is necessary for a specialist to analyze the case, and if fungal acne is confirmed, specific treatment will be necessary to treat the condition.
Next, Let’s better understand what fungal acne is, the causes, symptoms and how to care for it.
What is fungal acne?
Fungal acne is caused by a fungus, as dermatologist Betina Stefanello explained to the website Buscapé. “It is a type of acne similar to common acne, but instead of being associated with bacteria infecting the hair follicles, it is caused by a fungus which, in most cases, is Malassezia”.
Acne occurs when pores are clogged by dead cells, which leads to a buildup of sebum, which is an oily substance produced in the sebaceous glands. In the case of fungal acne, the buildup of sebum on the skin is caused by that specific fungus.
What are the causes of fungal acne?
So, fungal acne is caused by the Malassezia fungus. This fungus is present in the dermis of approximately 90% of the population. However, it is only a source of problem when excess sebum accumulated on the skin increases the proliferation of the fungus, and this is the main cause of fungal acne.
However, other factors can also influence the appearance of this specific type of acne, the main ones being a genetic predisposition and also the use of specific products. “In some conditions, such as after sun exposure or treatments with antibiotics or immunosuppressants, this fungus can become pathogenic, generating this type of lesion”highlights dermatologist Ísis Fiorello Mesquita, for Biossance.
Furthermore, another factor that can cause this type of acne is oily hair. So, when hair is in constant contact with the skin, it can trigger the condition, which is most common on the face, shoulders, back and chest.
How to identify?
Because it is very similar to common acne, and they can be easily confused just by looking, it is difficult to determine whether or not it is fungal acne. Therefore, if there is any suspicion of fungal acne, the ideal is to see a dermatologist. So, he can carry out the necessary tests and exams for diagnosis.
“It is often difficult to make a diagnosis, so we can use an antifungal test or therapeutic test when we have acne that we believe to be common/vulgar, but that does not improve with treatment”explains Dr. Betina, to Buscapé.
How to avoid and treat this type of acne?
As previously stated, although similar to common acne, fungal acne is more complex and requires specific treatment. Therefore, the dermatologist, after making the diagnosis, will indicate the best treatment for your case, which usually includes the use of antifungals and skin care routine.
However, we have already said that fungal acne has no cure. But it has several types of treatments, which, if followed correctly, can alleviate pimples and blemishes on the skin. And in addition to the treatment recommended by the dermatologist, some basic care can help a lot.
Firstly, always keep your skin clean, using products suitable for acne-prone skin and not wearing makeup. Furthermore, take care to keep your skin dry and hydrated. Avoid using antiseptic soaps and tight, stuffy clothing when the acne is on parts other than the face. In other words, basically adhering to a skincare routine appropriate to the condition.
Finally, always keep your hair clean and free of dandruff, and invest in a balanced diet.
Differences between common acne and fungal acne
Although visually similar, the two types are different. Starting with common acne, it is characterized by lesions of varying aspects, such as comedones or blackheads, papules, pustules or pimples (papules with pus). As well as nodules and cysts, which are even larger and more inflamed lesions than common pimples.
In the case of fungal acne, it also has pustules, those little red balls that look like blackheads. But in most cases there are no comedones. However, in this type of acne it is common for there to be itching or itching in the region, in addition to lesions of the same pattern.
READ MORE:
Bibliography:
- Américo Figueiredo, António Massa, António Picoto, Assessment and treatment of patients with acne – Part II, Portuguese Journal of General and Family Medicine: Vol. 27 No. 1 (2011): Revista Portuguesa de Clínica Geral. Available at: https://www.rpmgf.pt/ojs/index.php/rpmgf/article/view/10822. Accessed October 29, 2022.
- Brazilian, Eilzo Ferreira, Fungal dermatoses in primary health care. Available at: https://www.revistas.mpmcomunicacao.com.br/index.php/saudecoletiva/article/view/1138
- Vaz, Ana Lúcia. ACNE vulgaris: Bases for its treatment. Available at: https://www.rpmgf.pt/ojs/index.php/rpmgf/article/view/9989. Accessed October 29, 2022.
Sources: Biossance Buscapé Sallve

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13