Corn hair, also known as corn beard or corn stigmas, is a medicinal plant widely used to treat kidney and urinary system problems, such as cystitis, nephritis, prostatitis and urethritis, due to its diuretic and anti-inflammatory properties. .
This plant has the scientific name of Stigma maydis e Its composition contains substances such as vitamins, proteins and carbohydrates that are important for keeping the body healthy. Corn hair also contains flavonoids, which are compounds also found in fruits and vegetables and which have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, for example.
Generally, corn hair is used in its dry extract form to make tea, and can be purchased in health food stores and some compounding pharmacies.
What is it for
Corn hair is the part that is inside the corn cob and is the yellowish strands that develop during the development of the grains of this food. This part of corn is used in various regions of the world as a medicinal plant to treat various diseases and health problems, such as:
- Cystitis;
- Nephritis;
- Prostatitis;
- Kidney stone;
- Drop;
- Urinary incontinence;
- Swelling.
Corn hair is a natural product with a diuretic effect, this means that it helps to increase urinary frequency and consequently helps to reduce blood pressure. Some studies show that this medicinal plant can also lower blood sugar levels and can help restore the balance of intestinal flora, improving bowel regulation. Understand what intestinal flora is and what it is for.
Main properties
Corn hair contains substances such as proteins, vitamins, carbohydrates, calcium, potassium, magnesium, sodium and compounds such as flavonoids, which are important for delaying aging and have anti-inflammatory effects in the body. Because of this, this plant also has hypoglycemic, purifying and anti-fatigue properties.
The diuretic property of corn hair is well known and occurs because this plant relaxes the lining of the bladder and kidney tubules, reducing irritation and increasing urine elimination. Furthermore, corn hair is considered a mild hypotensive agent, as it helps to lower high blood pressure levels by reducing sodium reabsorption.
How to Use Corn Hair
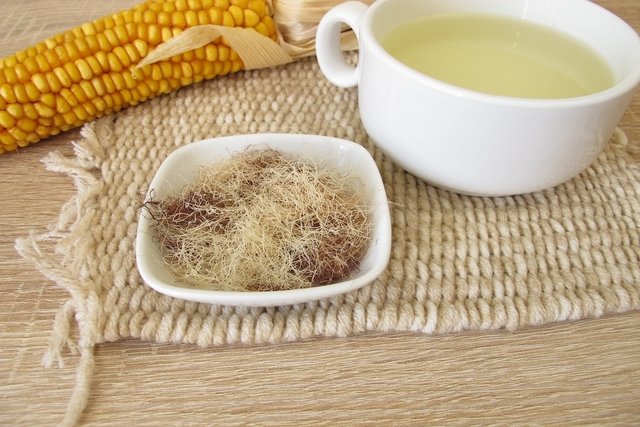

Corn hair is most often used in the form of tea, from the dry extract purchased in health food stores.
Ingredients
- 1 tablespoon dry extract of corn hair;
- 250 mL of water;
Preparation mode
Boil water with dry corn hair extract, cover and let rest for 10 minutes. Then, wait for it to cool a little and strain it, and you can drink this tea up to three times a day.
In addition to tea, corn hair can be found as a food supplement, and the recommended dose in studies is 400 to 450 mg to be taken 2 to 3 times a day, however, before ingesting this type of product it is It is important to consult a herbalist to find out the correct dose to use and you should not abandon conventional treatment advised by your doctor.
Who shouldn’t use
Studies show that corn hair is a safe medicinal plant with few associated side effects, however, it should be used with caution in people with prostate inflammation, as it increases urinary frequency and can cause discomfort when urinating. .
It should not be used by pregnant or breastfeeding women, as it alters levels of the hormone oxytocin, which is responsible for uterine contractions, for example. Furthermore, people who already use medicines to lower blood pressure, anticoagulants, diuretics and diabetes should ask their doctor before starting to use corn hair.
Bibliography
- HASANUDIN, Khairunnisa; HASHIM, Puziah, MUSTAFA, Shuhaimi. Corn Silk (Stigma Maydis) in Healthcare: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review. Molecules. Vol.17, n.8. 9697-9715, 2012
- WANG, Chunyang et al. Effects of Maydis stigma polysaccharide on the intestinal microflora in type-2 diabetes. Pharm Biol. Vol.54, n.12. 3086-3092, 2016
- PINHEIRO, ACS et al. Effect of aqueous extract of corn hair (Zea mays L.) on renal excretion of water and electrolytes and blood pressure in anesthetized Wistar rats. Fox. Brass. Pl. With. Vol.13, n.4. 375-381, 2011
- FLORIEN. corn hair. Available at: <http://florien.com.br/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/CABELO-DE-MILHO-1.pdf>. Accessed on 06 Feb 2020
- BOORHEM, R.L.; LAGE, E.B. Drugs and Plant Extracts Used in Phytotherapy. 37Revista Fitos Vol.4 Nº01 March 2009. Vol.4, n.1. 37-55, 2009

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13



