Vasectomy is a surgery that prevents a man from having children, as it consists of cutting, blocking or sealing the vas deferens, which is the channel that carries sperm from the testicles to the penis, interrupting their flow during ejaculation, thus preventing , pregnancy.
It is important that a condom is used after surgery, as in addition to not providing protection against sexually transmitted infections, around 25 ejaculations and a spermogram are required afterwards, to ensure that there are no more sperm in the canal.
Vasectomy surgery is performed by a urologist and can be offered free of charge by the SUS, as a form of family planning, or performed in private hospitals.
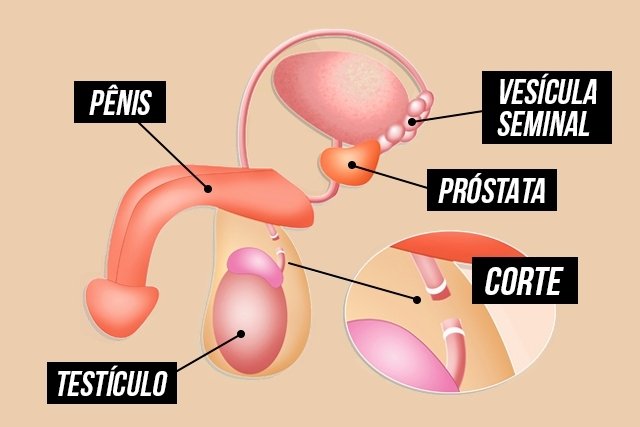
When is it indicated
Vasectomy is recommended for men who do not wish to have any more children. However, it is important that the surgery is discussed by the couple together with the doctor so that all doubts can be clarified.
How is a vasectomy performed?
Vasectomy surgery is a simple procedure, performed by a urologist, lasting around 15 to 30 minutes.
To perform a vasectomy, the doctor must follow some steps, such as:
- Cleanse the skin of the scrotum with a topical antimicrobial solution;
- Apply local anesthesia to avoid pain and discomfort from the procedure;
- Palpate the region to identify the vas deferens;
- Make a small cut in the upper part of the scrotum;
- Locate the vas deferens;
- Pull out the vas deferens through the cut made in the scrotum;
- Cut, burn and tie the vas deferens;
- Place the ends of the vas deferens inside the scrotum;
- Close the cut made in the scrotum, using stitches or surgical glue.
After the procedure, the man can now return home, and it is recommended to apply ice packs and rest for around 7 days.
How a vasectomy works
A vasectomy works by preventing pregnancy, since the surgery prevents sperm from entering the semen, which is the ejaculate liquid, and in this way, sperm do not reach the penis during ejaculation.
Thus, semen that does not contain sperm is not capable of fertilizing the egg, and the woman cannot become pregnant.
This surgery is usually a definitive method for male sterilization.
How to prepare for surgery
Before undergoing a vasectomy, some precautions are important, such as:
- Clarify all doubts about the surgery with the urologistrecovery and complications;
- Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of vasectomy with your doctoras well as the method to be carried out;
- Tell your doctor if you are allergic to anesthetics or any other medicine;
- Inform your doctor about the use of anticoagulant medicationssuch as warfarin, heparin, rivaroxaban, acetylsalicylic acid or clopidogrel, as the doctor may advise you to stop these medications a few days before surgery.
Before performing a vasectomy, the doctor must also perform a physical examination of the scrotum, with the aim of evaluating the mobility of the vas deferens, and the presence of hernias, scrotal varices, masses or testicular tenderness.
In addition, the doctor must evaluate the entire health history, sexual and social, genitourinary problems, trauma or genital surgery, scrotal pain or testicular cancer.
Care after vasectomy
After vasectomy surgery, it is normal for men to feel pain and discomfort in the region. Therefore, it is recommended that you rest and apply a cold compress to the area in accordance with medical advice. Furthermore, it is recommended that you wear comfortable clothing and avoid sexual intercourse for around 14 days or until medical approval.
It is important that a condom is used during sexual intercourse after vasectomy, as it is possible that there are sperm in the vas deferens, so that they can still be released during ejaculation.
Therefore, to ensure that there are no more sperm, it is recommended that the urologist be consulted regularly to perform a semen analysis, also known as a spermogram, which should demonstrate the absence of sperm, or azoospermia, or rare immobile sperm.
Advantages and disadvantage of vasectomy
The main advantage of a man having a vasectomy is greater control over a woman’s pregnancy, because after about 3 months of this procedure, the woman will not need to use contraceptive methods, such as the pill or injections, for example. This time may vary from one person to another, because it takes around 25 ejaculations to completely reduce sperm in the ducts. Therefore, it is advisable to ask your doctor what waiting time is appropriate for your case.
However, one of the disadvantages is that a vasectomy does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases and therefore, to prevent diseases such as HIV, syphilis, HPV and gonorrhea, you will still need to use a condom during every sexual encounter, especially if you have more than one. sexual partner.
Is a vasectomy reversible?
In some cases, vasectomy can be reversed by ligating the vas deferens, but the chances of success vary according to the time that has passed since the surgery. This is because, over time, the body stops producing sperm and begins to produce antibodies that eliminate the sperm produced.
Therefore, after several years, even if the body produces sperm again, they may not be fertile, making pregnancy difficult.
For this reason, vasectomy should only be a procedure used when the couple is sure they do not intend to have any more children, as it may not be reversible. See how to get pregnant after vasectomy.
Possible complications
Vasectomy is a procedure considered safe, however, in rare cases complications may arise, such as:
- Hematoma in the scrotum;
- Bleeding or formation of clots inside the scrotum;
- Blood in the sperm, which usually improves without the need for medical intervention;
- Infection at the surgical site;
- Epididimite;
- Spermatocele;
- Chronic scrotal pain;
- Hydrocele;
- sperm granuloma;
- Vasectomy failure, requiring repeat surgery.
Furthermore, after having a vasectomy, it is important to immediately inform your urologist or seek the nearest emergency room if symptoms of infection such as fever, redness, worsening of pain or swelling appear, so that the use of antibiotics can be assessed and started. , if necessary.
Common questions about vasectomy
Below we clarify the most common questions about vasectomy:
1. Can it be done through the SUS?
Vasectomy, like tubal ligation, is one of the surgical procedures that can be done free of charge through the SUS, however, you must meet two minimum requirements, which include being over 25 years old or at least having two children.
2. Is recovery painful?
Vasectomy surgery is quite simple, however, the cut made in the vas deferens can cause inflammation, leaving the scrotum more sensitive, which can cause a painful sensation when walking or sitting in the first few days.
The pain decreases over time, and it is possible to return to driving and doing almost all daily activities approximately 7 days after surgery. Intimate contact should only be initiated after 4 weeks to allow adequate healing.
3. How long does it take to take effect?
It is advisable to use other contraceptive methods, such as condoms, for up to 3 months after surgery, as, although the effects of vasectomy are immediate, preventing sperm from reaching the penis, some sperm may still remain inside the ducts, making pregnancy possible.
On average, up to 25 ejaculations are needed to eliminate all the sperm remaining in the canals and to perform a spermogram afterwards to ensure the success of the surgery. Only after this test indicates the absence of sperm, sexual intercourse is allowed without a method of contraception, just a condom to prevent sexually transmitted infections.
4. Does the man stop producing ejaculatory fluid?
Ejaculatory fluid is made up of sperm and other fluids, produced in the prostate and seminal vesicle, which help sperm to move.
Thus, since the prostate and seminal vesicle continue to function and release their fluids normally, the man continues to produce ejaculatory fluid, but it does not contain sperm, which prevents pregnancy.
5. Is there a risk of impotence?
The risk of impotence is zero, as the surgery is performed on the vas deferens that are inside the scrotum, not affecting the penis. However, some men may suffer from anxiety, which makes it difficult to get an erection, especially during the first few weeks, while the genital area is still sore, for example.
6. Can it reduce pleasure?
Vasectomy does not cause any change in a man’s sexual pleasure, as it does not cause sensory changes in the penis. In addition, men also continue to produce testosterone normally, the hormone responsible for increasing libido.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13