Trichuriasis is an infection caused by the parasite Trichuris trichiura whose transmission occurs through the consumption of water or food contaminated by feces containing eggs of this parasite. Trichuriasis causes intestinal symptoms, such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea and weight loss, for example.
It is important that trichuriasis is identified and treated quickly to prevent the disease from progressing and complications arising, such as rectal prolapse, for example. The diagnosis is made through a fecal examination and treatment may be indicated depending on the number of parasites in the intestine and the severity of the symptoms, with the doctor normally recommending the use of Albendazole or Mebendazole.
See a quick summary of trichuriasis and other parasite infections:
Main symptoms
Most cases of trichuriasis are asymptomatic, however, when the number of parasites is very high, some symptoms may appear, such as:
- Diarrhea;
- Pain or discomfort when defecating;
- Frequent urge to defecate;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Weight loss for no apparent reason, due to malabsorption caused by the presence of the parasite in the intestinal wall;
- Iron deficiency anemia;
- Constant headache.
Furthermore, in more serious cases there may be rectal prolapse, in which part of the intestine passes outside the anus, this serious complication being more common in children. Learn more about rectal prolapse.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of trichuriasis is made by identifying the eggs of Trichuris trichiura in feces, also taking into account the symptoms presented by the person.
If the presence of several eggs is verified in the parasitological examination of feces, the doctor may recommend that an endoscopy be carried out so that the intestine can be evaluated and, thus, it is possible to verify the presence of adult worms attached to the intestinal wall.
life cycle of Trichuris trichiura
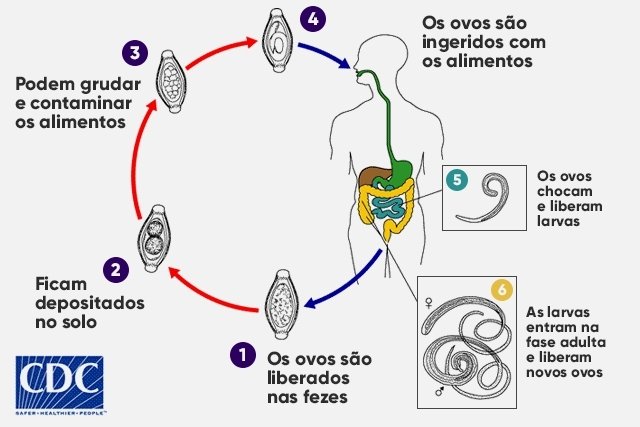
The cycle of Trichuris trichiura It begins when the eggs of this parasite are released into the environment in feces. In the soil, the eggs undergo a maturation process, until they become infective. These mature eggs can be ingested by people through the consumption of contaminated water and food and hatch in the intestine, where they undergo the process of maturation and differentiation between male and female, which reproduce and give rise to new eggs.
Adult worms are cylindrical and measure around 4 cm, with the female being larger than the male. In adulthood, this parasite remains attached to the intestinal mucosa and is not eliminated in the feces. Furthermore, each adult female is capable of producing around 70 eggs per day, which are eliminated in feces. Therefore, it is important that infection by Trichuris trichiura be identified quickly and treatment started immediately to prevent more adult worms from appearing and worsening symptoms.
How to protect yourself from infection
Preventing trichuriasis can be done through basic hygiene measures such as washing your hands before preparing meals, before eating, and always before and after going to the bathroom, in addition to being recommended to avoid getting wet in water that may be contaminated. . Check out some measures to prevent worms.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for trichuriasis is indicated when the person presents symptoms, with the doctor recommending the use of antiparasitic medicines, such as Albendazole or Mebendazole, which should be used according to the doctor’s instructions.
Natural remedies
Watch the following video for some home remedy options for worms and how to protect yourself from them:

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!