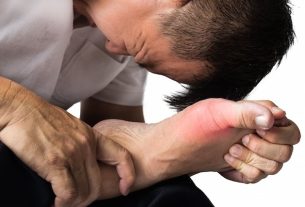
Symptoms of high uric acid, such as joint pain, redness of the skin, formation of small hard lumps in the joints or kidney cramps, generally appear when uric acid accumulates in the joints or kidneys to form crystals.
In most cases, an increase in the amount of uric acid in the blood, called hyperuricemia, does not cause symptoms and is only discovered during a blood test, in which a concentration of uric acid above 6.8 mg/dL is verified, or an examination of urine, in which uric acid crystals can be microscopically visualized.
When symptoms appear, it is indicative that a disease has developed, such as gout or kidney stones, due to the accumulation of uric acid in excess in the blood, caused by the increased production of uric acid and/or the decrease in its elimination in the urine via the kidneys, and it is important to consult a general practitioner, orthopedist or rheumatologist.

The main symptoms of high uric acid are:
1. Joint pain and swelling
Pain and swelling in the joints is a common symptom of gout, and can appear when excess uric acid from the blood is deposited in the joints in the form of crystals, causing inflammation, and is common to occur in the big toe or toes. hands, resulting in intense pain in the joint that lasts a few days and worsens with movement.
2. Small, hard lumps on joints
Uric acid crystals deposited in the joints of the fingers, elbows, knees and feet can lead to the formation of small, hard lumps that are painful to the touch.
In the case of gout, the pain is most common in the big toe, but it can also affect other joints such as ankles, knees, wrists and fingers, with the most affected people tending to be men, people with a family history of arthritis and people who consume a lot of alcohol.
3. Difficulty moving the affected joint
Due to the presence of lumps and swelling in the joints, it may be difficult to move the joint affected by the uric acid crystals.
4. Redness of the skin
The inflammation caused by the deposition of uric acid crystals in the joints can also cause redness of the skin and peeling of the affected skin in the area of the lump, as well as a feeling of “sand” when touching the area where the crystals were deposited. See other symptoms of gout.
5. Severe lower back pain
Severe pain in the lower back can arise when uric acid crystals accumulate in the kidney, causing renal colic, and affecting the lower back, or side of the body.
Generally, this pain appears when the crystals are very large and become stuck in the kidneys or when they leave the kidney and begin to descend towards the ureter or bladder.
This pain is often described as being similar to labor pain, and can also cause difficulty moving the body.
6. Spikes in intense kidney colic
Kidney colic can occur in peaks of intense pain that come and go, which can last around 20 to 60 minutes, and generally appear when the stone formed by excess uric acid becomes trapped or blocks some part of the urinary tract, such as the kidneys. , ureter or bladder.
7. Nausea and vomiting
Kidney stones formed by excess uric acid can cause nausea and vomiting, which is a very common symptom, and occurs due to stimulation of the splanchnic nerve, which is an innervation shared by the lining capsule of the kidneys and the stomach.
8. Pain or burning when urinating
Pain or burning when urinating can be a sign of a urinary tract infection, which can be caused by the movement of the uric acid stone in the urethra to be eliminated through urine or by blocking the passage of urine.
In addition, there may be a need to urinate frequently, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, for example. See other symptoms of urinary tract infection.
9. Presence of blood in the urine
When uric acid stones in the kidneys move, they can cause damage to the cells lining the urinary tract, which can lead to the appearance of small amounts of blood in the urine. However, this symptom is generally more related to the stone passing through the urethra to be eliminated through urine, or a urinary infection.
10. Fever or chills
Fever or chills may also appear as a sign of a kidney infection caused by the presence of uric acid stones in the kidney or a urinary tract infection. Whenever these symptoms occur, seek emergency services as soon as possible. Know how to identify other symptoms of kidney stones.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of high uric acid is made by a general practitioner, orthopedist or rheumatologist through evaluation of symptoms, health history and lifestyle habits.
In addition, the doctor must request a test for the level of uric acid in the blood and urine, as well as a complete blood count, lipid profile, calcium and phosphate levels in the blood, which allow the doctor to assess whether there are other health conditions that may be present. causing an increase in uric acid in the blood.
Other tests that the doctor may order are X-rays of the joints, to assess swelling and confirm the diagnosis of gout, or even a kidney ultrasound, to check for the presence of uric acid stones.
How the treatment is carried out
The treatment of high uric acid must be carried out under the guidance of a general practitioner, orthopedist or rheumatologist who may recommend the use of anti-inflammatory medicines or corticosteroids to relieve pain or swelling in the joints, or medicines to reduce uric acid levels. in the blood, such as allopurinol or probenecid, for example. Check out other treatments for gout.
In the case of kidney stone formation, the doctor may also prescribe antispasmodics and analgesics, such as dipyrone and scopolamine. However, if the pain is severe, you should go to the emergency room to take medication via vein. See how kidney stones are treated.
Furthermore, to lower uric acid levels, it is important to make changes to your diet, guided by a nutritionist who should recommend increasing your intake of foods such as apples, beets, carrots or cucumbers, as well as avoiding alcoholic beverages and red meat. , seafood and fish, for example. Find out what the diet for high uric acid should be like.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13