Many foods naturally contain sodium in their composition, with meat, fish, eggs and algae being the main natural source of this mineral, which is important for maintaining the proper functioning of the heart and muscles.
However, processed foods, such as snacks, sausages, ready-made sauces or preserved foods, have the highest amount of added salt, which can cause health problems, such as high blood pressure or heart problems.
Although, if you use the words sodium and salt as synonyms, they are not the same thing. Salt is made up of the minerals sodium and chloride, and you should only consume up to 5 g of salt per day, which contains around 2g of sodium, corresponding to 1 teaspoon. Learn more about sodium.
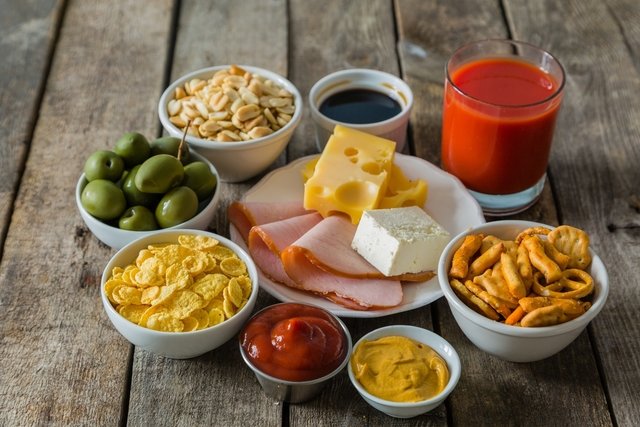

List of foods rich in sodium
The main foods rich in sodium are processed foods:
- Processed meatssuch as ham, mortadella, bacon, sausage and sausage;
- preserved fish, such as sardines and tuna;
- Cheeses such as parmesan, roquefort, gorgonzola and cheddar;
- Ready seasonings such as ketchup, mustard, mayonnaise and salad dressings;
- Ready meals, such as soups and pasta;
- Pickled vegetables such as hearts of palm, peas, corn, pickles, mushrooms and olives;
- Biscuits and biscuits, including salt water crackers, stuffed biscuits and snacks;
- Fast-food, such as pizza, burgers, nuggets or fries;
- Snack bar snacks such as kibbeh, pie, pastry, rissole and coxinha;
- Butter and margarine.
To follow the recommendation of consuming up to 5 g of salt per day, it is important to avoid buying these foods, opting for fresh foods whenever possible.
Amount of sodium in food
The following table shows the amount of sodium for every 100 g of some natural foods:
The main natural foods rich in sodium are those of animal origin, such as meat, fish, eggs and milk, which can be consumed daily, as they promote health.
It is important to avoid adding salt when preparing natural foods that already contain sodium in their composition. This is because excess salt is harmful to your health. Know the health risks of excess sodium.
Bibliography
- NATIONAL LIBRARY OF MEDICINE: MEDLINEPLUS. Sodium in diet. Available at: <https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002415.htm>. Accessed on Nov 18, 2022
- WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION. Salt intake. Disponível em: <https://www.who.int/data/gho/indicator-metadata-registry/imr-details/3082#:~:text=A%20salt%20intake%20of%20less,much%20more%20salt%20than%20recommended.>. Acesso em 18 nov 2022
- CAMPINAS STATE UNIVERSITY. Brazilian Food Composition Table – TACO. 2011. Available at: <http://www.nepa.unicamp.br/taco/contar/taco_4_edicao_ampliada_e_revisada.pdf?arquivo=taco_4_versao_ampliada_e_revisada.pdf>. Accessed on Nov 18, 2022
- UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH SERVICE . USDA Food Composition Database. Available at: <https://fdc.nal.usda.gov>. Accessed on Nov 18, 2022

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13