Appendicitis is a dangerous situation in pregnancy because its symptoms are slightly different and delay in diagnosis can rupture the inflamed appendix, spreading feces and microorganisms into the abdominal cavity, leading to a serious infection that can endanger the life of the pregnant woman and the baby. baby at risk.
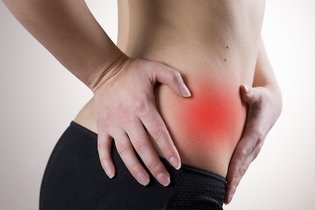
The symptoms of appendicitis in pregnancy manifest themselves as persistent abdominal pain on the right side of the abdomen, around the navel and which can move to the lower part of the belly. At the end of pregnancy, during the 3rd trimester of pregnancy, the pain of appendicitis can spread to the bottom of the belly and ribs and can be confused with common contractions at the end of pregnancy, making diagnosis difficult.
Location of appendicitis pain in pregnancy

Symptoms of appendicitis in pregnancy
Symptoms of appendicitis in pregnancy can be:
- Abdominal pain on the right side of the abdomen, close to the iliac crest, but may be slightly above this region and the pain may be similar to colic or uterine contraction.
- Low fever, around 38º C;
- Loss of appetite;
- There may be nausea and vomiting;
- Change in intestinal habit.
Other less common symptoms may also appear, such as diarrhea, heartburn or excess intestinal gas.
The diagnosis of appendicitis is more difficult at the end of pregnancy because due to uterine growth, the appendix can change position, creating a greater risk of complications.
What to do in case of appendicitis during pregnancy
What should be done when a pregnant woman has abdominal pain that does not go away and a fever is to consult the obstetrician to carry out diagnostic tests, such as an abdominal ultrasound, and confirm the diagnosis, as symptoms can also occur due to changes during pregnancy, without be a sign of appendicitis.
Treatment for appendicitis in pregnancy
The treatment of appendicitis in pregnancy is surgical. There are two types of surgery to remove the appendix, open or conventional appendectomy and laparoscopic appendectomy. The preference is for the appendix to be removed from the abdomen via laparoscopy, reducing postoperative time and associated morbidity.
Generally, laparoscopy is indicated for the 1st and 2nd trimesters of pregnancy, while open appendectomy is restricted to the end of pregnancy, but this decision is up to the doctor because there may be a risk of premature birth, although in most cases the pregnancy continues without problems. for mother and baby.
The pregnant woman must be admitted to the hospital for the surgery and after the procedure, be under observation. The pregnant woman must go to the doctor’s office every week to assess the healing of the wound and, thus, avoid possible maternal-fetal infections, ensuring a good recovery.
Find out more about surgery and post-operative care at:

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13