Potassium is an essential mineral for the proper functioning of cells, muscles and nerves, as it participates in the formation of muscle tissue and the body’s energy metabolism.
Furthermore, adequate amounts of potassium in the body also promote pH balance in the blood, preventing kidney stones and osteoporosis, and controlling blood pressure.
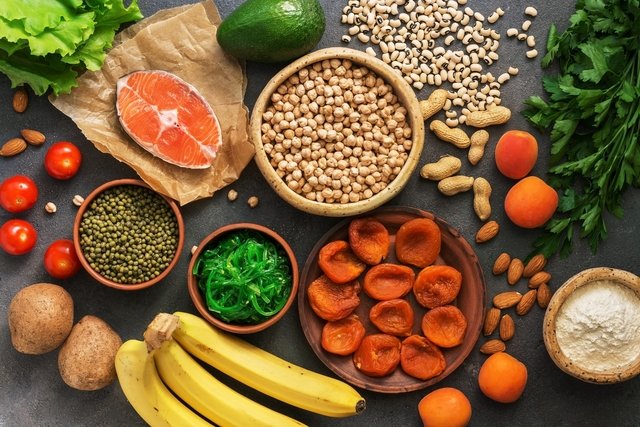
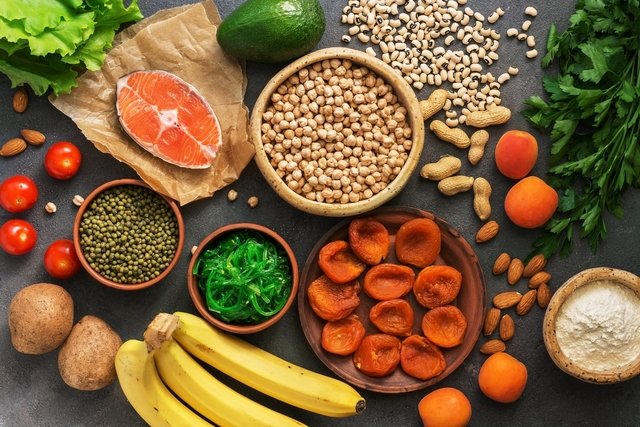
Potassium can be found in optimal amounts in foods such as tubers, fruits, vegetables, whole grains and dairy products. Furthermore, in some cases, potassium may also be recommended in supplement form by a doctor or nutritionist.

What is it for
Potassium helps maintain the proper functioning of the body, as it helps in the formation of muscles, balances the functions of the nervous system and the body’s pH, being essential for:
1. Control and prevent high blood pressure
Potassium is a mineral that promotes the relaxation of arteries, facilitating blood circulation, which prevents high blood pressure. Furthermore, potassium is capable of promoting the elimination of excess sodium circulating in the blood.
2. Prevent osteoporosis
Potassium neutralizes excess acid in the body, which can occur in diets with high amounts of animal protein and cereals, for example. By neutralizing acids, potassium increases the body’s pH, reducing the elimination of calcium in the urine and preventing osteoporosis.
3. Help with weight loss
Potassium favors the elimination of excess body fluid, helping to reduce swelling.
In addition, potassium also helps maintain the proper functions of the hormone insulin, controlling hunger and reducing the desire to eat.
4. Decrease the risk of stroke
Potassium contributes to the relaxation of the arteries, facilitating blood circulation and preventing stroke, as well as helping to balance the contraction of the heart muscles, favoring the maintenance of the heartbeat.
5. Prevent diabetes
Adequate levels of potassium in the body help prevent diabetes, as the mineral improves insulin sensitivity, which is the hormone responsible for balancing blood glucose levels.
6. Prevent kidney stones
By balancing the acids that can be produced in the body, potassium helps to increase the pH level in the body and reduce excess calcium in the urine, thus preventing the formation of kidney stones.
7. Promote muscle recovery
Potassium is necessary for the proper functioning of the muscle and for muscle contraction, and is important for improving muscle performance and recovery immediately after physical exercise, avoiding cramps.
Furthermore, potassium also interferes with protein synthesis, favoring the growth of muscle mass.
Where to find potassium
Potassium can be found in good quantities in foods of plant and animal origin, such as:
- Fresh fruit, such as banana, avocado, kiwi, apricot, persimmon, pomegranate or melon;
- Vegetables, such as spinach, beetroot, kale, broccoli, cauliflower or Brussels sprouts;
- Dairy, such as cheese, milk and yogurt;
- Nuts, such as almonds, hazelnuts, peanuts, cashews and Brazil nuts;
- Whole grains, such as brown rice, whole grain pasta, oats;
- Tubers, such as potatoes, sweet potatoes, yams or baroa potatoes.
Additionally, aromatic herbs such as parsley, coriander, chives and basil are also rich in potassium. See other foods rich in potassium and the recommended amount.
Reference values
The reference value for blood potassium in adults is between 3.6 mEq/L and 5.2 mEq/L. In urine, the reference value for potassium in adults is generally between 20 mEq / L, when only one collection is carried out, and between 25 and 125 mEq per day, when a 24-hour collection is carried out.
When this mineral is far above or below the reference value, it can cause some complications to appear, such as weakness, vomiting, cramps and numbness, for example. Learn the symptoms and how to treat low or high potassium.
How is the test to measure potassium
To measure the level of potassium in the blood, the doctor normally requests a blood collection, and it is not necessary to follow a specific diet or fast to perform this test.
To measure the level of potassium in urine, the doctor orders the test, which can be done with a single collection, or by collecting all urine eliminated during a 24-hour period.
When to use potassium supplement
Potassium supplementation is only recommended in cases of mineral deficiency, caused by low intake, vomiting, diarrhea or use of some diuretic medications. Another indication for using a potassium supplement is to control high blood pressure.
Potassium supplements can be found as potassium chloride or potassium bicarbonate, in capsules or tablets, and are sold in pharmacies or food supplement stores.
The recommended potassium intake is normally between 600 mg and 5 g per day, varying according to the state of health, the levels of the mineral in the body and the person’s age. Therefore, before using a potassium supplement, it is important to consult a doctor or nutritionist.
Possible adverse effects and contraindications
The most common adverse effects that may occur with potassium supplementation are diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, gas, and numbness or tingling in the hands, lips and feet.
In more serious cases, shortness of breath, changes in heartbeat and the presence of blood in the stool may also occur.
People with kidney problems, diabetes, heart disease, gastritis or ulcers should consult a doctor before starting to use potassium supplements.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13