The presence of hemoglobin in urine, scientifically called hemoglobinuria, occurs when red blood cells, which are elements of the blood, are destroyed and one of its constituents, hemoglobin, is eliminated in the urine, giving it a reddish and transparent color.
However, the presence of hemoglobin in urine does not always cause symptoms and is only detected through a chemical test with a reagent strip or microscopic examination, and should be treated as soon as possible by a urologist.
Hemoglobin in urine can appear in children, adults and even during pregnancy, due to kidney infections, the presence of kidney stones or serious kidney diseases, such as pyelonephritis or cancer, for example. Sometimes, hematuria occurs simultaneously with hemoglobinuria, which is bloody urine and it is necessary to see a doctor to analyze the cause. Know about bloody urine.
Main symptoms
Hemoglobinuria does not always cause symptoms, however, changes in urine may appear, such as red and transparent urine. In severe cases, due to the loss of a large amount of hemoglobin, which is responsible for transporting oxygen and nutrients, it can cause easy tiredness, fatigue, paleness and even anemia.
Don’t ignore your symptoms!
In a normal urinalysis, hemoglobin should not be found in the urine. However, hemoglobin can appear as a consequence of some situations, such as:
- Kidney problems, such as acute nephritis or pyelonephritis;
- Severe burns;
- Kidney cancer;
- Malaria;
- Transfusion reaction;
- Tuberculosis of the urinary tract;
- Sickle cell anemia;
- Strenuous physical activity;
- Menstrual period;
- Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome.
Furthermore, the presence of hemoglobin in the urine may be due to excessive cold or paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, which is a rare type of hemolytic anemia in which there is a change in the red blood cell membrane, which results in its destruction and the presence of red blood cell components. in urine. Find out more about Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria.
How to identify
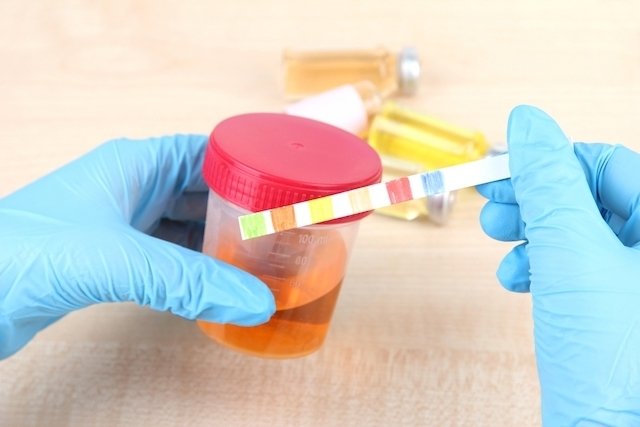
Hemoglobin in urine is positive when, after the chemical test with a reagent strip, signs, dashes or crosses appear on the strip and negative when there are no changes.
Generally, the more dashes or crosses present on the strip, the greater the amount of blood in the urine. However, it is always necessary to read the instructions on the reagent strip packaging, as the analysis of the results depends on the reagent strip laboratory.
In addition to the strip test, a microscopic examination can also be carried out using sedimentoscopy, which detects the amount of blood present. In this case, it is considered normal to have fewer than 3 to 5 red blood cells per field or fewer than 10,000 cells per ml. See how to understand the urine test.
How to treat hemoglobin in urine
Treatment for hemoglobin in urine depends on the cause and should be guided by a urologist. During treatment, it may be necessary to use medications such as antibiotics or antianemics or the application of a bladder catheter.
Bibliography
- MUNDT, Lilian A.; SHANAHAN, Kristy. Graff Urine and Body Fluid Examination. 2nd ed. Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2012. 25-55.
- LIU, Jen-Jane; JONES, Stephen; RAO, Pravin K. Urinalysis in the Evaluation of Hematuria. JAMA. Vol.315(24). 2726-2727, 2016
- STRASINGER, Susan K.; DI LORENZO, Marjorie S. Urianalysis and body fluids. 5th ed. United States: E. A Davis Company, 2008. 66.
- UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA SAN FRANCISCO. Hemoglobinuria. Available at: <https://www.ucsfbenioffchildrens.org/tests/003363.html>. Accessed on 15 Jul 2019

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13