Folliculitis is a skin infection that affects the hair follicles, the structures responsible for the formation and growth of hair, causing symptoms such as redness, pimple-like bumps and itching, being more common in the groin, buttocks, scalp or beard, but it can happen anywhere on the body that has hair.
Folliculitis can be caused by ingrown hairs, but it can also arise due to an infection caused by bacteria or fungi. However, people who use antibiotics or have illnesses such as diabetes and HIV are also at risk of developing folliculitis.
Read too: Ingrown hair: symptoms, causes, treatment (and how to remove it)
The treatment of folliculitis should be guided by a general practitioner or dermatologist, who may indicate improved hygiene, the use of antibiotics or antifungals in the form of creams, ointments or tablets.
Sensitive content
This image may contain content that is uncomfortable for some people.
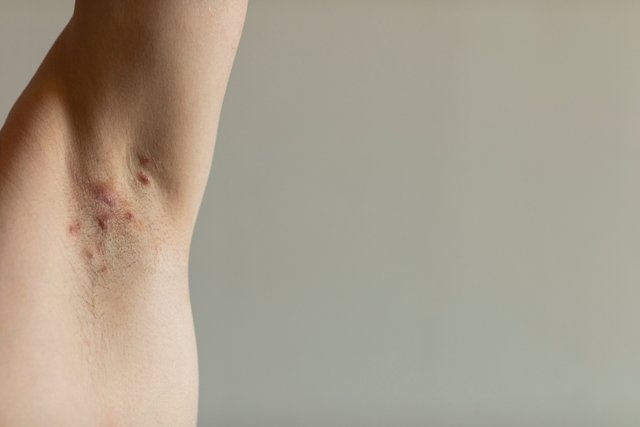
Folliculitis symptoms
The main symptoms of folliculitis are:
- Red dots that look like acne;
- Small blisters with pus on the hair roots;
- Itching in the area;
- Pain and sensitivity in the skin;
- Redness and swelling in the region.
The small red dots usually appear close to each other and can affect areas containing hair, such as the face, arms, armpits, legs, buttocks or groin. Discover other causes of bumps on the skin.
Typically, folliculitis symptoms improve within a few days even without treatment. However, in some cases this condition can worsen, causing a boil, an infection that causes the formation of a lump with pus, redness, increased local temperature or pain.
How to confirm the diagnosis
Folliculitis can be identified by observing changes in the skin. However, it is important that the diagnosis is confirmed by the dermatologist through a physical examination, to confirm the diagnosis and initiate the most appropriate treatment.
If you want to check for the presence of folliculitis, make an appointment with the dermatologist in the region closest to you:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Types of folliculitis
According to location, folliculitis can be classified into the following types:
- Groin folliculitis: Shaving with razors or wax can ingrown hairs, favoring the emergence of this type of folliculitis. Furthermore, wearing tight clothing can increase friction, heat and humidity in the region, favoring bacterial infection and folliculitis;
- Scalp folliculitis: it can be caused by fungi or bacteria and can appear in people who frequently wear wigs, caps, hats or helmets, for example. This type of folliculitis is characterized by small balls filled with pus, which are itchy and painful;
- Folliculitis on the buttocks: it is quite common in men and women and is caused by bacteria, leading to the appearance of small red, pus-filled and painful balls;
- Genital folliculitis: it can be caused by shaving in this region, because, in some cases, the hair cannot come out and grows under the skin, causing inflammation;
- Folliculitis in the legs: It can arise due to hair removal with razors, or wax, or due to infections caused by bacteria, fungi or viruses. Find out more about folliculitis in the legs;
- Underarm folliculitis: it can appear in men and women, and is usually caused by waxing or shaving, causing itching, painful red balls filled with pus;
- Folliculitis on the face: This type of folliculitis can be caused by the use of razors or depilatory wax, affecting the entire face and beard area.
Furthermore, folliculitis can also appear in regions such as the back, shoulders, arms and neck, and may be caused by fungi or sun exposure.
Possible causes
Folliculitis is generally caused by the multiplication of fungi, viruses, mites or bacteria on the skin, around the hair or body hair, causing inflammation.
Some factors that can also favor the appearance of folliculitis are:
- Shaving or waxing frequently;
- Wear tight clothes;
- Frequent use of helmets, hats, wigs or long boots;
- Have dermatitis or acne;
- Maintain poor skin or hair hygiene;
- Frequently use bandages or adhesive tapes on the hair;
- Using bathtubs or saunas that are not adequately sanitized;
- Using medicines such as antibiotics, lithium or cyclosporine for long periods.
Additionally, people with illnesses such as diabetes, obesity or HIV also have a higher risk of developing folliculitis.
How the treatment is carried out
Folliculitis treatment must be indicated by a dermatologist and varies depending on the cause of the condition and the affected region, and may include adequate hygiene, ointments, medicines, soaps or surgeries.
1. Proper hygiene
In the simplest cases of folliculitis, adequate skin and scalp hygiene, using soap, shampoos and warm water can resolve this condition within 7 to 10 days.
2. Ointments
Some ointments, such as nebacetin, mupirocin and clindamycin, may be recommended to combat bacteria and alleviate the symptoms of folliculitis, such as itching and pain in the area.
For the treatment of folliculitis caused by fungi, the doctor may prescribe the use of ointments such as itraconazole and fluconazole.
3. Oral antibiotics
When ointments are unable to treat folliculitis, antibiotics such as cephalexin, ampicillin, ciprofloxacin or dicloxacillin may be recommended by the doctor to help fight the bacteria.
4. Shampoos
Frequently washing your hair with anti-dandruff shampoos containing ketoconazole or ciclopirox olamine, for example, may be indicated mainly for the treatment of scalp folliculitis.
5. Soaps
Performing local hygiene, with antiseptic soaps and warm water, may be recommended for treating folliculitis on the face, beard, legs, genitals and groin, for example.
6. Surgeries
In cases of deeper folliculitis or boils, the doctor may perform a small surgery to remove excess pus, thus relieving symptoms and helping with healing.
Other care to treat folliculitis
Some precautions that also help in the treatment and prevention of folliculitis include:
- Place a warm compress on the affected area to reduce itching;
- Take a shower with neutral soap immediately after using the pool, bathtub or sauna;
- Do not scratch or pick at the balls;
- Perform laser or pulsed light hair removal;
- Avoid using creams, perfumes or other irritating products on the lesions;
- Use an electric shaver instead of razors. See other tips for taking care of beard folliculitis;
- Avoid frequently wearing hats, helmets, wigs or caps;
- Wear looser clothing.
If folliculitis symptoms do not improve after 2 weeks, it is recommended to consult your dermatologist again so that other treatments can be indicated.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13



