During drowning, respiratory function is impaired due to the entry of water through the nose and mouth. If there is no rescue quickly, water can accumulate in the lungs, which prevents the passage of oxygen, putting life at risk.
Some measures can be taken to save a drowning person, but it is first necessary to ensure your own safety and check that the location does not pose any risks. Then you must:
- Ask someone else nearby for helpso that both can continue with the help;
- Call the fire ambulance immediately on 193if this is not possible, you must call SAMU on 192;
- Provide some floating material to the drowning personsuch as empty plastic bottles, surfboards or Styrofoam or foam materials;
- Try to provide assistance without entering the water. If the person is less than 4 meters away, it is possible to extend a branch or broomstick, however, if the victim is more than 4 meters away, you can throw a buoy with a rope, holding the end opposite. When the victim is close, it is important to always offer your foot instead of your hand, as the victim may be nervous and pull the rescuer into the water;
- Enter the water only if you know how to swim;
- If the person is removed from the water, it is important to check your breathing for 10 seconds, observing the movements of the chest and listening to the air come out through the nose. If you are breathing, it is important to leave the person lying on their side until professionals arrive at the scene;
- If the person is conscious, without symptoms, only with a dry cough or the presence of foam at the mouth, it is recommended to observe breathing, asking the person to lie on their side, keeping them warm, relaxed and calm until the arrival of the firefighters or SAMU;
- If you are unconscious and not breathing, It is recommended to start cardiac massage on the victim.
To confirm that the person is not breathing, you must bring your ear closer to the victim’s nose and mouth and perform the “VOS” method: Ver if there are movements of the chest, To hear if there is breathing noise and To feel whether there is air coming out of the mouth or nose.
What to do if the person is not breathing
If the person is unconscious and not breathing, before the rescue team arrives at the scene, cardiac massage must be started:
- Call the fire department, no 193, ou para o SAMU, no 192;
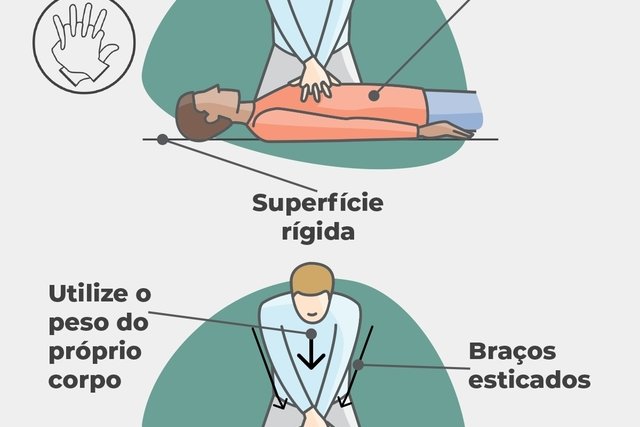
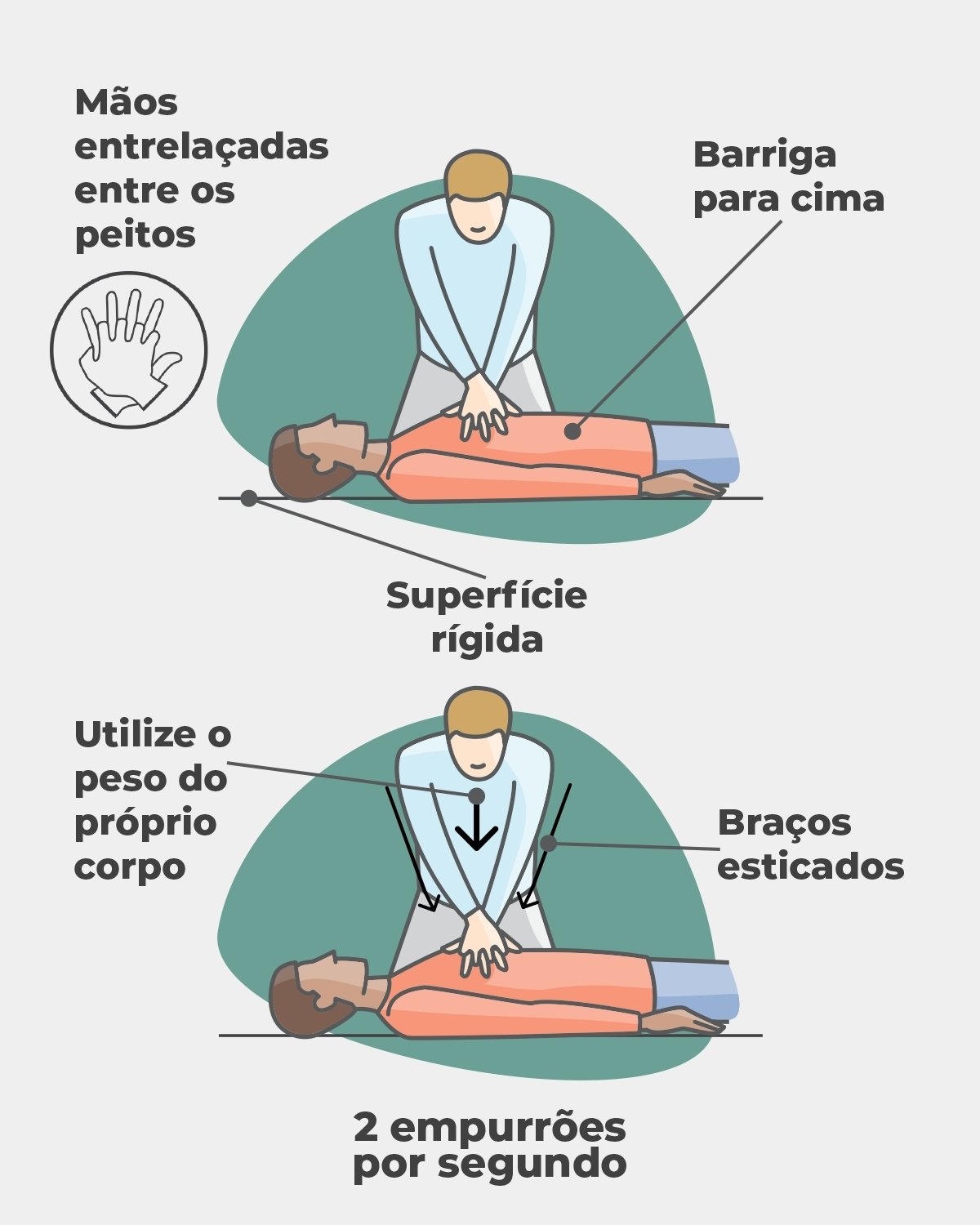
- Lay the person on a firm surfacewith the belly up;
- Place your hands on the victim’s chestinterlacing your fingers and keeping your arms straight, as shown in the figure below;
- Push your hands tightly against your chest, between the nipples, using the weight of one’s own body, and performing 2 compressions per second until the victim recovers or until help arrives. It is important to allow the person’s chest to return to its normal position between each push.
In the case of children, only one hand should be used to perform cardiac massage, placing only the palm of one hand on the child’s chest, with fingers raised, performing 2 compressions per second.
In babies up to 1 year old, it is recommended to place only 2 fingers in the middle of the chest, performing 100 to 120 compressions per minute. See how to give your baby a cardiac massage.
Care when trying to save someone in water
After helping the drowning victim with the support of floating materials, you can try to remove them from the water, however, this should only be done if the rescuer knows how to swim and is confident in the area. Other precautions need to be considered in the case of water rescue, such as:
- Warn other people that a rescue attempt will be made;
- Remove clothes and shoes that could weigh down the water;
- Bring flotation material such as a board or buoy;
- Do not get too close to the victim, as the person could grab it and pull it to the bottom of the water;
- Only remove the person if there is strength and experience;
- Stay calm, always calling for help.
These precautions are important so that the rescuer does not drown and it is always necessary to have someone outside pointing out directions and calling out loud.
What to do if you are drowning
If you are drowning, it is important to remain calm as fighting the current or struggling causes muscle wastage, weakness and cramps. It is also important to try to float, wave for help and only shout when someone can hear you, to avoid getting water in your mouth.
If the drowning occurs at sea, you can let yourself be carried to the high seas, out of reach of the surf and avoid swimming against the current. If drowning happens in rivers or floods, it is important to keep your arms open, try to float and try to reach the bank by swimming with the current.
How to avoid drowning
Some simple measures can prevent drowning, such as swimming or bathing in places that know the depth, that do not have currents and that are monitored by firefighters or lifeguards.
It is also important to avoid swimming right after eating, consuming alcoholic beverages and drugs, or after being exposed to the sun for a long time, especially if your body is hot and the water temperature is very cold, as this can cause cramps, making it difficult to move around in the water. from water.
Furthermore, it is necessary to respect the signs on rivers and seas, just as it is important to wear a life jacket on boat trips or jet skis and avoid being close to swimming pool pumps, as they can suck in your hair or body.
Children and babies are more susceptible to drowning and, therefore, some additional care is needed, such as not leaving them alone near or in bathtubs, buckets full of water, swimming pools, rivers or the sea, as well as avoiding access to bathroom, putting locks on the doors.
Younger children should always have floaties when they are in the pool, river or sea and, when possible, it is recommended to install protective fences around the pool and enroll them in swimming lessons.
Bibliography
- SPANISH ASSOCIATION OF PEDIATRICS. First aid. Available at: <https://www.aeped.es/sites/default/files/documentos/capitulo_5_0.pdf>. Accessed on Aug 2, 2021
- AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS. Updates Recommendations to Prevent Drowning in Children. 2019. Disponível em: <https://www.aap.org/en-us/about-the-aap/aap-press-room/Pages/AAP-Updates-Recommendations-to-Prevent-Drowning-in-Children.aspx>. Acesso em 21 nov 2019
- MILITARY FIRE DEPARTMENT. – GOIÂNIA. Firefighter operational manual: lifeguards. 2017. Available at: <https://www.bombeiros.go.gov.br/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/MANUAL-GUARDA-VIDAS-2017.pdf>. Accessed on November 21, 2019
- SZPILMAN, DAVID. Drowning Resuscitation Guideline. 2017. Available at: <http://www.szpilman.com/new_szpilman/szpilman/ARTIGOS/afogamento_szpilman_diretriz_17.pdf>. Accessed on November 21, 2019
- BRAZILIAN AQUATIC RESCUE SOCIETY. Drownings. 2019. Available at: <http://www.sobrasa.org/new_sobrasa/arquivos/baixar/Manual_de_emergencias_aquaticas.pdf>. Accessed on November 21, 2019
- ESPÍRITO SANTO FIRE DEPARTMENT – GOVERNMENT OF THE STATE OF ESPÍRITO SANTO. Water rescue technical manual. Available at: <https://cb.es.gov.br/Media/CBMES/PDF%27s/Manual%20T%C3%A9cnico%20de%20Salvamento%20Aqu%C3%A1tico%20-%20CBMES.pdf>. Accessed on November 4, 2021

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13