Cerebral hemorrhage is a type of cerebrovascular accident (CVA) in which bleeding occurs around or within the brain, due to the rupture of a blood vessel, usually an artery.
It is a serious event, usually caused by a blow to the head, which can lead the person to a state of deep unconsciousness, as well as feelings of nausea, vomiting, decreased heart rate and loss of balance.
Whenever there is a suspicion of a cerebral hemorrhage, it is very important to call for medical help, to confirm the diagnosis and start treatment as quickly as possible, in order to avoid consequences, such as difficulty walking, speaking or eating, for example.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage are:
- Severe and sudden headache that can last for days;
- Numbness or tingling in any part of the body;
- Vomiting;
- Loss of balance;
- Tremor in the hands;
- Decrease in heart rate;
- Generalized weakness;
- Changes in vision, such as seeing everything very dark, having a reduced field of vision or blindness;
In more serious conditions, there may also be sudden epileptic seizures or profound and prolonged loss of consciousness in which the person is unable to respond to stimuli.
Don’t ignore your symptoms!
How to confirm the diagnosis
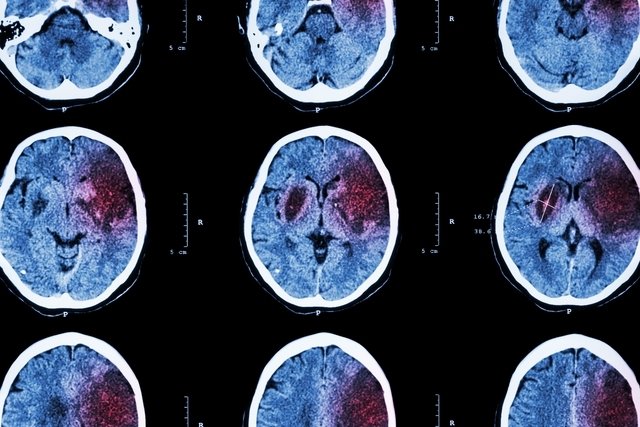
The diagnosis of cerebral hemorrhage is made through imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography and angiography, with or without contrast, which allow the presence of bleeding or lesions in the brain to be assessed.
The doctor may also request a lumbar puncture, in which a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is taken and evaluated in the laboratory to identify the presence of blood.
The best doctor to confirm the diagnosis of cerebral hemorrhage and recommend the most appropriate treatment is a neurologist. However, as this is a medical emergency, whenever there is a suspicion of cerebral hemorrhage, it is important to go quickly to the emergency room.
Types of brain hemorrhage
Cerebral hemorrhage can be classified according to the location in which it occurs:
1. Intraparenchymal or intracerebral hemorrhage
Intraparenchymal hemorrhage is more likely to occur in the elderly and appears when the bleeding occurs inside the brain. It is the most serious type, but also the most common. It usually occurs due to tumors, coagulation disorders and malformed vessels.
2. Hemorragia intraventricular
Intraventricular hemorrhage occurs in the cerebral ventricles, which are cavities in the brain where cerebrospinal fluid is produced. This type of hemorrhage normally occurs in premature newborns, within the first 48 hours after birth, or who had some complication immediately after birth, such as respiratory distress syndrome.
3. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
This hemorrhage usually occurs due to the rupture of an aneurysm, but it can also be the result of a blow, and is characterized by bleeding in the space between two layers of the meninges, the arachnoid and the pia mater.
The dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater are the constituent layers of the meninges, which are membranes that cover and protect the central nervous system. Subarachnoid hemorrhage usually happens in people between the ages of 20 and 40.
4. Subdural hemorrhage
Subdural hemorrhage occurs in the space between the dura mater and arachnoid layers of the meninges and is the most common result of trauma.
5. Hemorragia epidural
This bleeding occurs between the dura mater and the skull and is more common in children and adolescents as a result of a skull fracture.
What causes brain hemorrhage
The main cause of cerebral hemorrhage is head trauma, caused by a strong blow to the head. However, there are other less common conditions that can promote bleeding, such as:
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure;
- Excessive and chronic alcohol consumption;
- Use of drugs, such as cocaine or amphetamines;
- Amyloid angiopathy, which is the inflammation of small vessels in the brain;
- Blood diseases, such as thrombocythemia and hemophilia, which hinder the clotting process;
- Use of anticoagulants, as they make clotting difficult, which can promote bleeding;
- Brain tumors.
Another common cause of cerebral hemorrhage is a cerebral aneurysm, which is a dilation in a blood vessel in the brain. This dilation causes the walls of the vessel to become thin and fragile and can rupture at any time, causing hemorrhage. Know the symptoms that help identify a brain aneurysm.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for cerebral hemorrhage must be carried out as quickly as possible in the hospital and is normally done with surgery to remove the blood that is accumulating inside the skull, in order to reduce pressure and avoid permanent damage to the brain.
In addition to surgery, the doctor may also recommend treatment with medication to control blood pressure, seizures and possible infections. In more serious cases, blood transfusions may also be indicated.
To improve quality of life after bleeding and avoid injuries, it is important to see a physiotherapist or occupational therapist. See what recovery is like after a stroke.
Consequences of cerebral hemorrhage
After bleeding, some people may have sequelae, such as difficulty speaking, swallowing, walking, carrying out daily activities or may become paralyzed.
As soon as the first symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage appear, you should go to the doctor immediately so that treatment can begin, as the severity of the consequences depends on the degree of bleeding.
The best way to prevent the occurrence of cerebral hemorrhage and, consequently, its consequences, is by performing physical activities and having a healthy, balanced diet, low in fat and salt.
Bibliography
- MAGID-BERNSTEIN, Jessica; GIRARD, Romuald; POLSTER, Sean et al. Cerebral Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Future Directions. Circulation Research. Vol 130. Vol 8; 1204 – 1229, 2022
- ROCHA, Eva; ROUANET, Carolina; REGES, Danyelle et al. Intracerebral hemorrhage: update and future directions. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. Vol 78. 10 ed; 651 – 659, 2020
- TAVARES, João; CARNEIRO, Patrícia; PARREIRA, Mário; PEDROSO, Ermelinda. Assessment and Management of Patients with Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Review Article. Journal of the Portuguese Society of Internal Medicine. Vol 28. 3 ed; 288 – 298, 2021

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13