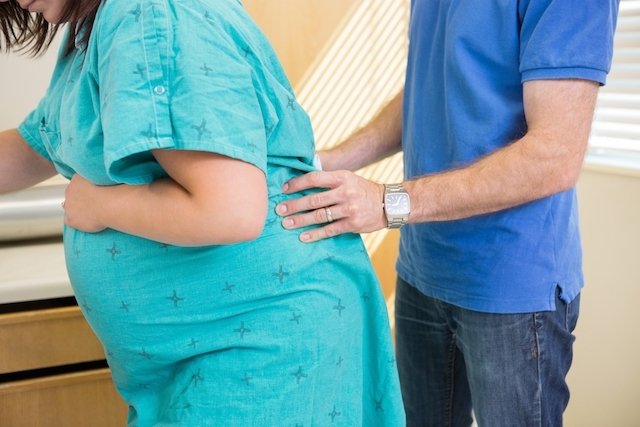
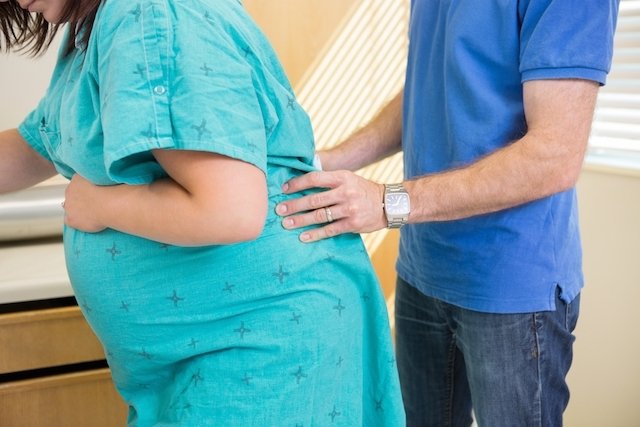
Anesthesia during normal birth can be performed with techniques such as epidural anesthesia, combined spinal-epidural block and pudendal block, which can be used according to the woman’s needs at the time of birth and the doctor’s recommendation.
Although anesthesia can relieve labor pain, side effects such as decreased blood pressure, changes in breathing, nausea and urinary retention can also occur.
If you have any doubts about anesthesia during natural birth, it is important to talk to the obstetrician during prenatal care or consult the anesthesiologist for guidance on anesthesia options and their risks during childbirth.

Types of anesthesia not normal childbirth
The main types of anesthesia indicated for normal birth are:
- Epidural: anesthesia in which an anesthetic medicine is injected into the spine, blocking pain from the waist down;
- spinal anesthesia: anesthesia similar to epidural, but with an effect that lasts for a shorter time;
- Combined spinal-epidural block: anesthesia technique that combines epidural anesthesia and spinal anesthesia;
- Pudendal block: anesthesia in which an anesthetic is injected through the vagina close to the pudendal nerve, preventing the transmission of pain through this nerve.
The choice of the type of anesthesia depends especially on the stage of labor, availability of materials in the hospital and the doctor’s experience. However, at any time the pregnant woman can ask for interventions to alleviate the pain. See more details on the main types of anesthesia.
Effects of anesthesia
The effects of anesthesia in natural birth usually begin quickly. However, this time may vary according to the anesthesia used, taking up to around 15 minutes to begin, in the case of epidural anesthesia.
In this type of anesthesia, when the effect begins, it is possible to notice a progressive loss of sensitivity, heat, a feeling of heaviness in the legs and tingling. However, the pregnant woman usually remains awake and is able to push to help push the baby.
The duration of the effects of anesthesia depends on the type of anesthesia indicated, ranging from 1 to 2 hours, if spinal anesthesia is used, up to a few hours after the birth of the baby, in the case of epidural anesthesia.
Possible side effects
The main side effects of anesthesia in natural birth are:
- Decrease in blood pressure;
- Changes in breathing;
- Difficulty moving;
- Backache;
- Headache, which may appear a few hours after birth;
- Nausea;
- Vomiting;
- Itch;
- Urinary retention.
Furthermore, anesthesia during natural birth can also have side effects on the baby, such as changes in heart rate, drowsiness, breathing problems and difficulty breastfeeding, although the risk is low.
Who shouldn’t do
Anesthesia during natural birth is generally not indicated in case of a history of allergy to the anesthetics used, infection in the skin where the anesthesia is performed and, especially for spinal and epidural anesthesia, changes in coagulation, use of anticoagulants and low platelets, for example.
Natural options to alleviate labor pain
Although they are less effective than anesthesia, some measures that help control pain during labor include:
- Massages performed by the partner, at the time of birth, in the interval between contractions;
- Breathe deeply at the moment of greatest pain and push for the baby to be born;
- Use techniques such as acupuncture or acupressure to relieve pain;
- Have the freedom to move during contractions.
Furthermore, it is very important that pregnant women clarify all their doubts with the obstetrician during the prenatal period so that at the time of birth they feel confident in the medical team and know what is going to happen, facilitating relaxation. Discover other options to alleviate the pain of labor.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13