Diverticulitis can cause symptoms such as pain in the lower left part of the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, belly swelling, diarrhea or constipation, and fever.
Diverticulitis is the inflammation of diverticula, which are sac-shaped changes in the intestinal wall, being more common in people with constipation, sedentary and who have a diet rich in fat and low in fiber. Understand better what diverticulitis is.
If diverticulitis is suspected, it is recommended to seek hospital emergency care for evaluation and confirmation of the diagnosis. Treatment is usually done with antibiotics and, in the most serious cases, may need to be done in the hospital, sometimes surgery may be indicated.
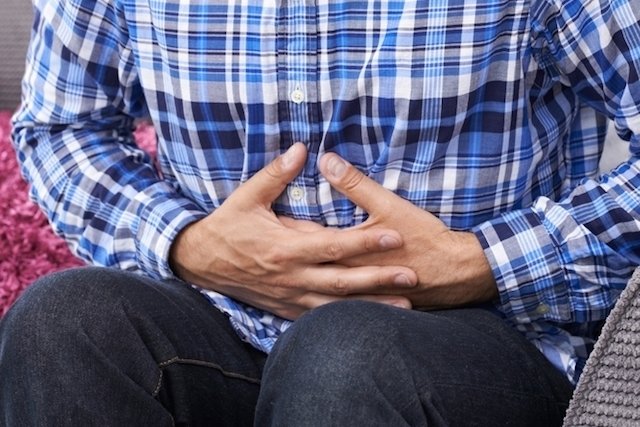

Main symptoms
The main symptoms of diverticulitis are:
1. Pain in the lower left part of the abdomen
Diverticulitis typically causes pain in the abdomen that tends to be constant and especially affects the lower left side of the belly.
2. More sensitive abdomen
Due to the inflammation caused by diverticulitis, it is common for the abdomen to become more sensitive and the pain to worsen, especially when pressing the belly with your hand.
3. Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting can arise due to the inflammation caused by diverticulitis, which can affect the functioning of the intestine, impairing the passage of feces and, sometimes, causing intestinal obstruction.
4. Fever
Diverticulitis can cause fever, especially when the inflammation leads to the accumulation of pus in the abdomen, forming an abscess, or when the inflamed diverticulum perforates.
5. Loss of appetite
Loss of appetite can happen due to nausea and changes in bowel function caused by inflammation.
6. Swollen belly
Diverticulitis can cause belly swelling in some cases, especially when constipation appears.
7. Changing the frequency of evacuation
Changes in the frequency of bowel movements are common in diverticulitis due to inflammation of the intestine, leading to diarrhea and, especially in the case of intestinal obstruction, constipation.
Symptom Test
To find out your risk of having diverticulitis, select the symptoms presented in the following test:
The symptom test is only a guidance tool and does not serve as a diagnosis or replace consultation with a gastroenterologist or general practitioner.
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of diverticulitis is made by a gastroenterologist or general practitioner taking into account the symptoms and test results, such as abdominal ultrasound and computed tomography, which help to confirm the inflammation of the diverticula.
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Furthermore, after treating diverticulitis, the doctor may sometimes recommend a colonoscopy to identify changes in the intestine that may indicate diseases such as tumors or inflammatory bowel disease. Find out how a colonoscopy is performed.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for diverticulitis must be guided by a gastroenterologist or general practitioner and, sometimes, can be done at home with the use of medications such as antibiotics, for around 10 days, and analgesics to relieve pain.
During treatment for diverticulitis, rest is recommended and, initially, for 3 days, a liquid diet, slowly adding solid foods. After treating diverticulitis, it is important to eat a diet rich in fiber, guided by a nutritionist, to prevent the diverticula from becoming inflamed again.
In more serious cases, in which complications such as perforation of the diverticulum or generalized infection arise, treatment may need to be carried out in the hospital and, sometimes, surgery. See more details on the treatment for diverticulitis.
Bibliography
- ELLISON, Deborah L. Acute Diverticulitis Management. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. Vol.30, n.1. 67-74, 2018
- STATPEARLS. Acute Diverticulitis. 2022. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459316/>. Accessed on March 22, 2023
- STRATE, Lisa L; MORRIS, Arden M. Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Treatment of Diverticulitis. Gastroenterology. Vol.156, n.5. 1282–1298, 2019
- WILKINGS, Thad; EMBRY, Katherine; GEORGE, Ruth. Diagnosis and management of acute diverticulitis. Am Fam Physician. Vol.87, n.9. 612-20, 2013
- CAMPOS, Fábio G. Acute diverticulitis. Available at: <https://cbcsp.org.br/wp-content/uploads/2016/aulas/Diverticulite.pdf>.
- REGERT, REBECA; BERGMANN, GABRIELA A.; FILLMANN, LUCIO S. Diagnosis and management of acute diverticulitis. Available at: <https://docs.bvsalud.org/biblioref/2018/02/879424/diagnostico-e-manejo-da-diverticulite-aguda.pdf>. Accessed on January 20, 2021
- BRAZILIAN SOCIETY OF COLOPROCTOLOGY. Diverticulitis: Diagnosis and Treatment. Available at: <https://diretrizes.amb.org.br/_BibliotecaAntiga/diverticulite-diagnostico-e-tratamento.pdf>. Accessed on January 20, 2021

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13