The diet for high cholesterol should prioritize the consumption of fruits, vegetables and whole grains, because they are foods rich in fiber that help reduce the absorption of total cholesterol at the intestinal level. Furthermore, it is important to avoid foods rich in saturated fat, such as pizza and nuggets, for example.
Furthermore, it is also important to increase your intake of antioxidant foods such as tomatoes, grapes, saffron and chestnuts. This is because these foods help to lower “bad” cholesterol, LDL, in the blood, preventing diseases such as heart attack and atherosclerosis. See more foods that help lower cholesterol.
It is also essential to practice physical activities regularly, as they improve the health of the arteries and increase the levels of “good” cholesterol, HDL, in the blood, maintaining heart health. Learn more about HDL cholesterol.
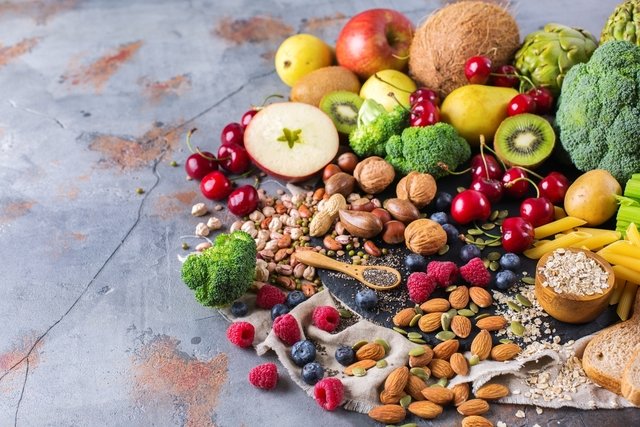

Allowed foods
The foods allowed in the high cholesterol diet are:
- Fiber-rich foods, such as oatmeal, wholemeal bread, brown rice, wholemeal pasta;
- Fruits with pomace and peel (whenever possible), such as orange, apple, lemon, pear, grape, avocado, strawberry, watermelon, papaya and cashew;
- Vegetables and greens, such as lettuce, watercress, garlic, tomatoes, carrots, broccoli, chicory, artichokes and jiló;
- Legumes, such as beans, chickpeas, lentils and soybeans;
- Oilseeds in small quantities, such as walnuts, almonds, Brazil nuts;
- Vegetable oils in moderation, such as olive oil, avocado oil and flaxseed oil;
- Milk and skimmed dairy products, giving preference to low-fat white cheeses, such as ricotta and cottage cheese;
- Seedssuch as pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, flax seeds and sesame seeds;
- lean proteins, such as chicken, eggs, tofu and turkey;
- Fish rich in omega 3, such as sardines, salmon, mackerel, tuna and herring;
- Herbs and spices, such as rosemary, cinnamon, saffron, basil, parsley and coriander;
- Drinks, such as water, coconut water, coffee and unsweetened teas, as well as teas with hypocholesterolemic properties, such as artichoke or dandelion tea.
Food should always be cooked, roasted, grilled or steamed, avoiding fried foods. Additionally, some teas that help lower cholesterol can also be consumed, such as artichoke or dandelion tea. Check out other teas for cholesterol.
It is also essential to practice physical activities 3 to 5 times a week, including aerobic exercises, such as swimming and running, and resistance exercises, such as weight training and pilates. This is because physical exercise improves artery health and increases HDL cholesterol levels in the blood, preventing diseases such as heart attack and stroke.
Foods that should be avoided
Some foods that should be avoided from the high cholesterol diet are:
- Viscera, such as liver, kidneys, gizzard and heart;
- Built-ins, such as sausage, chorizo, bacon, sausage, salami, mortadella and ham;
- Proteins rich in fat, such as pork, beef and lamb;
- High-fat dairy products, such as whole milk and yogurt, butter, yellow cheeses and margarine;
- Ready-made sauces and seasonings, such as ketchup, mayonnaise, barbecue, powdered or diced seasonings;
- Fried food, such as French fries, coxinha, pastries;
- Processed foods, such as ice cream, hamburgers, pizza and fast food-type meals;
- Alcoholic beverages, such as beer, wine, sparkling wine or whiskey.
Furthermore, foods rich in sugar such as cakes, cookies and chocolates should also be avoided, because excess sugar favors the production of cholesterol in the liver.
Diet menu for high cholesterol
The following table shows an example of a 3-day menu to lower cholesterol:
The types and quantities of food on the menu vary depending on the person’s age, physical activity and health status. Therefore, it is advisable to consult a nutritionist so that a complete assessment can be carried out and a nutritional plan tailored to individual needs can be created.
If you want to follow a diet that suits your needs, schedule an appointment with the nutritionist closest to your region:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Do eggs increase cholesterol?
Egg yolk is rich in cholesterol, however the cholesterol found in natural foods has a low risk of causing changes in blood cholesterol levels in most people.
However, people who have a genetic predisposition to high cholesterol, familial hypercholesterolemia, should consume eggs in moderation, as excessive consumption of this food can increase blood cholesterol levels in this situation.
The American Heart Association recommends that a healthy person can consume 1 to 2 units of eggs per day. In the case of people with diabetes or heart disease, the ideal is to consume up to 1 egg unit per day. Therefore, it is possible to include eggs in the diet to lower cholesterol, as long as they are not consumed in excess.
How to know if your cholesterol is good
To know if cholesterol is good and does not pose a health risk, it is important to measure total cholesterol and fractions in the blood, such as LDL, HDL and triglycerides, which must be indicated by your doctor.
If you have had a blood test recently, enter your result into the calculator below and see if your cholesterol is good:
The cholesterol test can be done either fasting for up to 12 hours or without fasting, however it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendation, especially if another test has been indicated.
Bibliography
- WANG, Yating; DANIANG, Xu. Effects of aerobic exercise on lipids and lipoproteins. Lipids in Health and Disease. 16. 1 ed; 1 – 8, 2017
- ISLAM, Ashraful; AMIN, Muhammad N.; SIDDIQUI, Shafayet A. et al. Trans fatty acids and lipid profile: A serious risk factor to cardiovascular disease, cancer and diabetes. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews. 13. 2 ed; 1643 – 1647, 2019
- RONDANELLI, Mariangela; GIACOSA, Attilio; OPIZZI, Annalisa F., et al. Beneficial effects of artichoke leaf extract supplementation on increasing HDL-cholesterol in subjects with primary mild hypercholesterolaemia: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition. 64. 1; 7 – 15, 2013
- PIZZINI, Alex; LUNGER, Lukas; DEMETZ, Egon et al. The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Reverse Cholesterol Transport: A Review. Nutrients. 9. 10; 1 – 12, 2017
- TRAN Gia-Buu; PHA, Tan-Viet; TRINH, Ngoc-Nam. Medicinal Plants – Use in Prevention and Treatment of Diseases. 2020. 1 – 13.
- LIBERALE, Luca; BONAVENTURA, Aldo; MONTECUCCO, Fabrizio et al. Impact of Red Wine Consumption on Cardiovascular Health. Current Medicinal Chemistry. 26. 19 ed; 1-21, 2019
- AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION . Are eggs good for you or not?. Disponível em: <https://www.heart.org/en/news/2018/08/15/are-eggs-good-for-you-or-not>. Acesso em 03 fev 2023
- BRAZILIAN SOCIETY OF CARDIOLOGY. Update of the Brazilian Guideline on Dyslipidemia and Prevention of Atherosclerosis. 2017. Available at: <https://www.scielo.br/j/abc/a/whBsCyzTDzGYJcsBY7YVkWn/?format=pdf&lang=pt>. Accessed on February 3, 2023
- TREASURE ISLAND (FL): STATPEARLS PUBLISHING. Low Cholesterol Diet. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551722/>. Accessed on February 3, 2023
- BRAZILIAN SOCIETY OF CARDIOLOGY. Update of the Brazilian Guideline on Dyslipidemia and Prevention of Atherosclerosis. 2017. Available at: <https://www.scielo.br/pdf/abc/v109n2s1/0066-782X-abc-109-02-s1-0001.pdf>. Accessed on September 15, 2020

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13