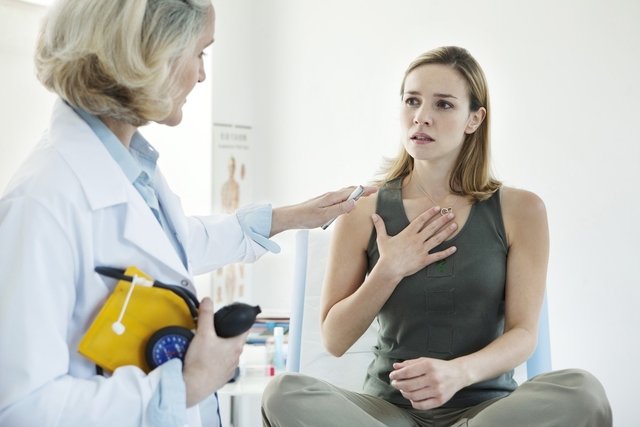
The main symptoms of asthma are shortness of breath, wheezing, tightness in the chest and coughing, especially at night or early in the morning.
These symptoms tend to appear suddenly and intensely, usually when the person has an allergy to dust or pollen, or is a consequence of intense physical exercise, for example. The episode of intense symptoms is usually known as an asthma attack, which should be treated as quickly as possible. See more about asthma.
It is important to consult a pulmonologist or general practitioner, in the case of adults, or a pediatrician or pediatric pulmonologist, in the case of children, if asthma symptoms appear, so that the most appropriate treatment can be diagnosed and indicated.

Main symptoms of asthma
The main symptoms of asthma are:
1. Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath can appear mildly or intensely, being caused by the release of inflammatory substances in the bronchi, such as prostaglandins, histamine, leukotrienes and cytokines, for example, leading to spasms and contractions of the bronchi and consequently the narrowing of these structures, resulting in decreased air flow to the lungs and shortness of breath and difficulty filling the lungs.
Additionally, in some cases, persistent inflammation of the airways can cause edema or swelling of the bronchi and production of mucus, further decreasing airflow to the lungs.
2. Wheezing
Wheezing or noise when breathing arises due to inflammation of the bronchi and their contraction, known as bronchoconstriction or bronchospasm, which makes the airways narrower, making breathing difficult and causing a wheezing sound, as if it were a whistle, or noise when breathing. .
3. Dry cough
Dry cough is another symptom of asthma that also occurs due to inflammation, spasms and contractions of the bronchi, and is more common to appear at night or early in the morning. In some cases, when there is intense production of mucus in the respiratory tract, a cough with phlegm may occur.
4. Feeling of tightness in the chest
The feeling of tightness, pressure or oppression in the chest occurs due to the difficulty of the lungs in eliminating the air from breathing, due to the narrowing of the bronchi, which causes the air to be “trapped” inside the lungs.
This tightness, oppression or pressure in the chest can lead to a feeling of suffocation or cause chest pain.
5. Excessive tiredness
Excessive tiredness can arise due to low oxygenation of the body, due to decreased air flow to the lungs, especially when the person frequently has asthma symptoms, a chronic cough or uncontrolled asthma.
Furthermore, coughing attacks at night can affect and interrupt sleep resulting in excessive or chronic tiredness, drowsiness during the day and a feeling of lack of energy, reducing quality of life.
6. Rapid, shallow breathing
Rapid and shallow breathing, also called tachypnea, occurs due to difficulty breathing and eliminating air from the lungs.
Tachypnea is defined as more than 20 breaths per minute in adults, and may be worse at night, after physical exercise or be a symptom of an asthma attack.
7. Rapid heartbeat
Rapid heartbeats, also called tachycardia, can occur as a response from the body to increase tissue oxygenation, due to a decrease in oxygen and an increase in carbon dioxide in the body, due to inflammation and contractions of the bronchi that make gas exchange through the lungs difficult. .
8. Feelings of anxiety or panic
The feeling of anxiety or panic can arise, especially during an asthma attack, due to difficulty breathing, shortness of breath and a feeling of pressure in the chest.
Asthma Symptom Test
To find out your chances of having asthma, please select the symptoms you are experiencing:
The symptom test is only a guidance tool and does not serve as a diagnosis or replace consultation with a pulmonologist, allergist or general practitioner.
Asthma attack symptoms
During an asthma attack, symptoms are generally more intense and appear suddenly, and may also include:
- Intense and constant cough;
- Intense shortness of breath;
- Very fast breathing;
- Dizziness;
- Mental confusion;
- Chest pain;
- Difficulty speaking;
- Spasms in the neck or chest;
- Pale skin;
- Cold sweat;
- Bluish lips or fingers;
- Anxiety or panic crisis;
- Fainting.
When a person is experiencing an asthma attack, it is recommended that the medication prescribed by the doctor be used as quickly as possible and that the person should sit with the body slightly tilted forward.
When symptoms do not go away, it is recommended that an ambulance be called or go to the nearest hospital. See in more detail what to do in an asthma attack.
Asthma symptoms in baby
In the case of babies, asthma attacks can be identified through symptoms such as:
- Purple or bluish fingers, lips, tongue or area around the eyes;
- Breathing faster than normal;
- Exaggerated movements in the belly or chest when breathing;
- Nostrils more open and moving when breathing;
- Difficulty recognizing or responding to parents;
- Excessive tiredness or drowsiness;
- Slow movements;
- Constant cough;
- Irritation or agitation;
- Difficulty breastfeeding or eating.
When the baby presents these symptoms, the baby must be taken to the hospital immediately. Learn how to recognize asthma symptoms in your baby.
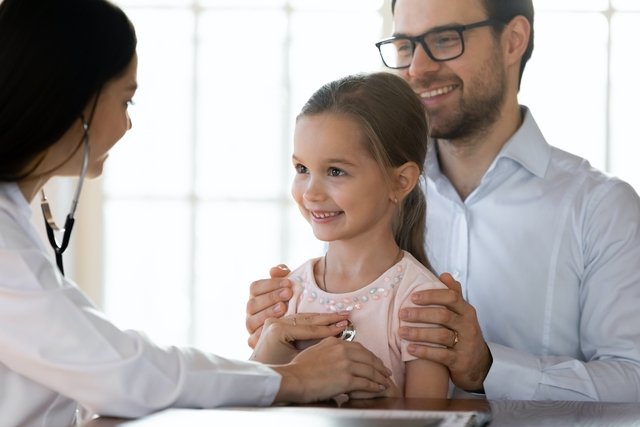
How to confirm if it is asthma
To confirm whether it is asthma, it is recommended to consult a pulmonologist or general practitioner, in the case of adults, or a pediatrician or pediatric pulmonologist, in the case of children, to evaluate symptoms, health and allergy history, and physical examination when requesting the person. to breathe in and out, while listening to the lungs with a stethoscope, to check for noises made during breathing.
Make an appointment with a pulmonologist to confirm whether it is asthma:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
In addition, the doctor must order tests to confirm whether it is asthma and rule out other diseases that have similar symptoms, such as obstruction of the bronchi by a foreign body or tumor, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), for example.
Main exams for asthma
The main asthma tests that may be recommended by your doctor are:
- Oximetry, placing a device on one of the fingers of the hand to measure the amount of oxygen in the blood;
- Arterial blood gas analysis, which measures oxygen and carbon gas levels in arterial blood;
- Spirometry, which measures the volume of air inspired to check whether they are satisfactory or not;
- Chest X-ray;
- Computed tomography.
In addition, the doctor can carry out bronchoprovocation tests, where the doctor tries to trigger an asthma attack and offers asthma medicine, to see if the symptoms disappear after using it. Find out more about tests to diagnose asthma.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13