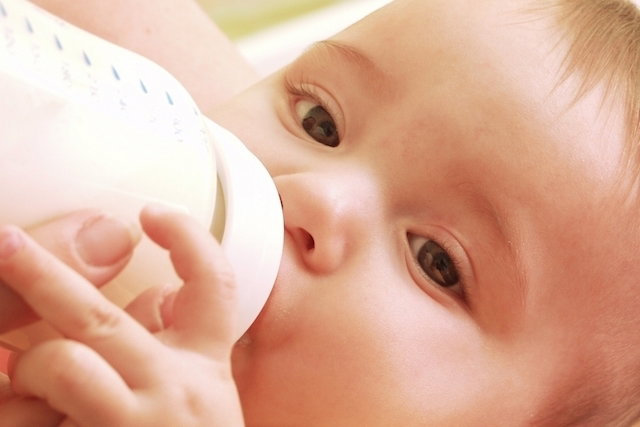
Goat’s milk for the baby is an alternative when the mother cannot breastfeed and in some cases when the baby is allergic to cow’s milk. This is because goat’s milk does not have the Alpha S1 casein protein, which is mainly responsible for the development of allergies to cow’s milk.
Goat’s milk is similar to cow’s milk and has lactose, but is more easily digested and has less fat. However, goat’s milk is low in folic acid, as well as deficient in vitamin C, B12 and B6. Therefore, it may be vitamin supplementation, which should be recommended by the pediatrician.
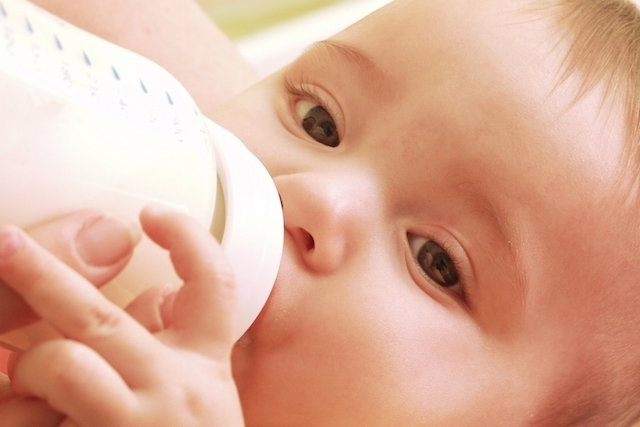

To give goat’s milk you need to take some precautions, such as boiling the milk for at least 5 minutes and mixing the milk with a little mineral water or boiled water. The quantities are:
- 30 ml per day goat milk for newborn baby in the 1st month + 60 ml of water,
- Half a glass of goat milk for baby 2 months + half a glass of water,
- From 3 to 6 months: 2/3 goat’s milk + 1/3 water,
- Over 7 months: you can give pure goat’s milk, but always boiled.
O goat milk for baby with reflux It is not recommended when the baby’s reflux is due to the consumption of cow’s milk proteins, as although goat’s milk has better digestion, they are similar and this milk can also cause reflux.
It is important to remember that goat’s milk is not the ideal substitute for breast milk, and before making any dietary changes to the baby, it is important to seek advice from a pediatrician or nutritionist.
Goat milk nutritional information
The following table compares 100 g of goat’s milk, cow’s milk and breast milk.
Furthermore, goat’s milk contains adequate amounts of calcium, vitamin B6, vitamin A, phosphorus, magnesium, manganese and copper, but is low in iron and folic acid, which increases the risk of developing anemia.
See other alternatives to breast milk and cow’s milk at:

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13