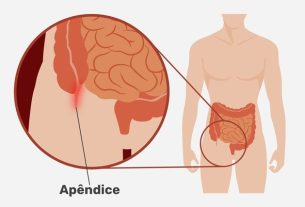
Appendicitis is normally caused by a blockage in the appendix, due to the accumulation of feces, increased mucus production or the presence of intestinal worms, for example, leading to inflammation or infection of the appendix, and the appearance of symptoms such as pain on the right side. and under the abdomen, low fever, vomiting, diarrhea and nausea.
The appendix is an organ of the digestive system that is located between the large and small intestine and has the function of constantly producing mucus that mixes with the feces. But because it is an organ shaped like a glove finger, whenever there is obstruction of the appendix, the organ becomes inflamed, generating appendicitis. Check out all the symptoms of appendicitis.
Appendicitis treatment must be carried out as quickly as possible whenever symptoms appear, in order to avoid complications such as rupture of the appendix and infection of the lining of the abdomen by bacteria, which can cause damage to internal organs and put life at risk.
Main causes
The main causes of appendicitis are:
1. Accumulation of feces inside the appendix
The accumulation of feces inside the appendix can cause an obstruction of the appendix orifice, leading to inflammation and bacterial growth inside the appendix, such as Escherichia coli, Peptostreptococcus, Bacteroides e Pseudomonasfor example, causing infection, which can result in an abscess or even rupture of the appendix.
2. Intestinal worms
Intestinal worms can enter the appendix and prevent the mucus produced by it from escaping, leading to the organ’s enlargement and consequent rupture.
3. Fecalito
Fecalith is a stone formed by hardened feces that can cause blockage of the appendix, causing inflammation and the development of appendicitis.
4. Lymphoid hyperplasia
Lymphoid hyperplasia is a growth of the inner lining of the appendix, usually due to a response by the immune system to fight microorganisms, such as bacteria, resulting in an accumulation of secretions within the appendix, which leads to its obstruction and inflammation, and the development of appendicitis. .
Furthermore, lymphoid hyperplasia can arise due to the presence of intestinal worms in the cecum, which is the initial part of the large intestine, connected directly to the appendix, leading to an increase in antibodies to fight the worms, resulting in accumulation of mucus, obstruction and inflammation of the cecal appendix, known as reactive lymphoid hyperplasia.
5. Abdominal injuries
Appendicitis can also be caused by abdominal trauma, such as strong blows to the stomach and car accidents, which can lead to inflammation, infection or rupture of the appendix.
6. Intestinal infections
Intestinal infections caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites, such as Bacteroides, Peptostreptococcus, Fusobacterium, Campylobacter jejuni or Bilophila, can cause inflammation and infection of the appendix, resulting in appendicitis. Check out the main intestinal infections.
7. Lymph node pressure
Pressure from the lymph nodes exerted on the appendix due to an infection can also cause appendicitis.
8. Accumulation of gases inside the appendix
Gases produced by bacteria that normally live inside the appendix can accumulate, leading to irritation and inflammation of the appendix and resulting in appendicitis.
9. Low fiber diet
A diet low in fiber can lead to a decrease in bowel movements, causing feces to remain in the intestine longer, which can favor the formation of fecaliths and the development of acute appendicitis.
Furthermore, a diet rich in processed, industrialized foods, fast food, Red and high-fat meats, or foods rich in sugar, can also lead to a constant fermentation and digestion process, increasing the risk of appendicitis.
Which doctor to see
In the presence of symptoms that may indicate appendicitis, such as on the right side and under the abdomen, hardening of the belly, nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite, it is recommended to go to the emergency room as soon as possible and consult a general surgeon, to avoid the disruption of the organ and its consequences. Know all the symptoms of appendicitis.
If you would like an evaluation by a general surgeon, schedule an appointment in the nearest region:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of appendicitis is made by observing the characteristics of the individual’s pain and through the analysis of diagnostic tests such as ultrasound or tomography of the abdomen, abdominal X-ray, simple urine and blood tests.
These tests serve to exclude the hypothesis of other diseases and serve to confirm inflammation of the appendix. If the doctor is still in doubt, laparoscopy will be able to confirm the diagnosis of appendicitis.
As soon as the diagnosis is given, the doctor will recommend removing the appendix through surgery. This procedure prevents reinfection of the organ and reduces the risk of death due to complications of appendicitis, such as the entry of harmful bacteria into the abdominal cavity and bloodstream.
Treatments for appendicitis
The main treatments for appendicitis are:
Treatment for acute appendicitis
Treatment for acute appendicitis is surgery to remove the appendix, called appendectomy.
Surgery must be performed as quickly as possible to prevent new inflammation and the appendix from rupturing, as if it ruptures it can cause complications, such as sepsis, which is a serious infection of the body that can lead to death.
Currently, the most used surgical technique to remove the appendix is laparoscopy, in which 3 small holes are made, allowing a faster and less painful recovery. However, traditional surgery can be used by making a cut in the right region of the abdomen to remove the appendix.
Hospitalization lasts around 1 to 2 days, recovery usually occurs around 15 days after surgery, reaching 30 days in the case of traditional appendectomy and returning to physical activities after 3 months.
In the first few days after surgery, the individual should rest, eat foods rich in fiber, avoid lifting heavy objects, drink plenty of fluids and avoid driving. Check out more details about what to eat after appendicitis.
Treatment for chronic appendicitis
Chronic appendicitis is treated with analgesics, antipyretics, antibiotics and anti-inflammatories. However, it is possible that the medications are not enough and the individual may have to undergo surgery to remove the appendix.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13