Ovarian cyst symptoms can appear when the cyst grows, ruptures or twists, resulting in intense pain, nausea and vomiting, as well as pain during the ovulatory period, changes in menstruation, difficulty getting pregnant and back pain, for example.
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac that can form in or around the ovary and can result in pain, delayed menstruation or difficulty getting pregnant, for example. Learn more about ovarian cysts.
In the presence of symptoms of an ovarian cyst, it is important that a gynecologist is consulted so that tests can be carried out and indicated to help identify the presence of the cyst and its type, and the best treatment can be recommended.
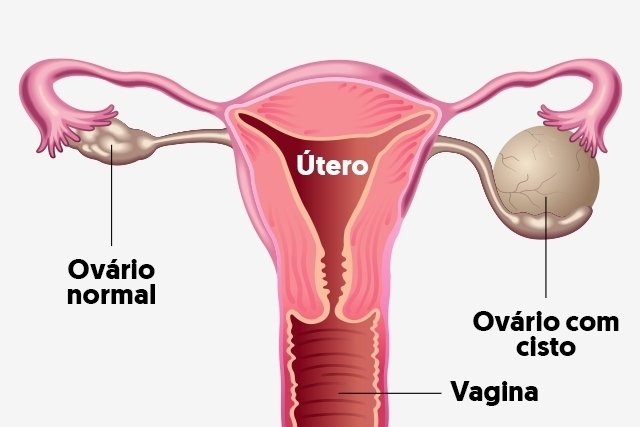
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of ovarian cyst are:
- Pain during the ovulatory period;
- Constant pain in the abdominal region;
- Intense cramps before or during the menstrual period;
- Feeling of a swollen belly;
- Delay in menstruation or irregular menstruation;
- Heavy menstruation;
- Back pain;
- Pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- Increased breast sensitivity;
- Bleeding outside the menstrual period;
- Difficulty getting pregnant;
- Weight gain;
- Frequent feeling of a full stomach;
- Painful bowel movements;
- Increased urinary frequency.
Symptoms can also vary according to the type of cyst, therefore it is necessary to go to the gynecologist to have tests carried out to diagnose the presence, size and severity of the cyst.
Online symptom test
To assess the chance of having an ovarian cyst, select the symptoms you present in the following test:
The symptom test is only a guidance tool and does not serve as a diagnosis or replace a consultation with a gynecologist.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of ovarian cyst is made by the gynecologist initially based on the evaluation of symptoms, physical examination through palpation of the abdomen and imaging tests, such as transvaginal ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, which allow confirming the presence of the cyst and indicating what is the size and its characteristics.
If you think you may have an ovarian cyst, use our tool to find a doctor near you:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
The doctor may order other tests, such as a complete blood count to check for the presence of anemia due to bleeding, a urine test to rule out urinary tract infection or kidney stones, or a microbiological analysis of vaginal secretions, in order to rule out pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). ), which can have symptoms similar to ovarian cysts.
In some cases, the doctor may also request a pregnancy test, beta-HCG, to exclude the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy, which presents the same symptoms, and an examination of the CA-125 tumor marker, which also helps to identify the type of ovarian cyst.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for ovarian cysts is not always necessary and must be recommended by the gynecologist according to the size, characteristics of the cyst, symptoms and age of the woman so that the best form of treatment can be indicated.
When the cyst does not present malignant characteristics and does not cause symptoms, treatment is normally not indicated, and the woman must be monitored periodically to verify the reduction of the cyst.
On the other hand, when symptoms are identified, the doctor may recommend the use of a contraceptive pill with estrogen and progesterone to regulate hormonal levels or the removal of the cyst through surgery. In more serious cases, when there is torsion or suspicion of malignancy, complete removal of the ovary may be indicated. Find out more details about the treatment for ovarian cysts.
Understand the difference between cysts and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and how diet can help with treatment by watching the following video:
Bibliography
- BOTTOMLEY, C.; BOURNE, T. Diagnosis and management of ovarian cyst accidents. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 23. 5; 711-24, 2009
- LIMAIEM, F.; LEKKALA, MR; MLIKA, M. IN: STATPEARLS (INTERNET). TREASURE ISLAND (FL): STATPEARLS PUBLISHING. Ovarian Cystadenoma. 2022. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536950/>. Accessed on September 22, 2022
- ZAHIDY, Z. A. Causes and Management of Ovarian Cysts. The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine . 70. 70; 1818-1822, 2018
- HOLT, VL; et al. Risk of functional ovarian cyst: effects of smoking and marijuana use according to body mass index. Am J Epidemiol. 161. 6; 520-5, 2005
- FARGHALY, S. A. Current diagnosis and management of ovarian cysts. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 41. 6; 609-12, 2014
- CHIKAZAWA, K.; et al. A cystectomic technique with low risk of rupture for women with benign ovarian cyst. J Obstet Gynaecol. 41. 3; 459-461, 2021
- ABBAS, A.; et al. Hemorrhagic ovarian cysts: Clinical and sonographic correlation with the management options. Middle East Fertility Society Journal. 21. 1; 41-45, 2016
- MOBEEN, S.; APOSTOL, R. IN: STATPEARLS (INTERNET). TREASURE ISLAND (FL): STATPEARLS PUBLISHING. Ovarian Cyst. 2022. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560541/>. Accessed on September 22, 2022

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13