Diet for thalassemia helps control iron levels, reducing fatigue from anemia and relieving muscle pain, in addition to strengthening bones and teeth and osteoporosis.
The diet plan depends on the type of thalassemia presented, because no special diet is necessary for the minor forms of the disease, which are less serious and normally do not cause symptoms. Understand better what changes in each type of thalassemia here.
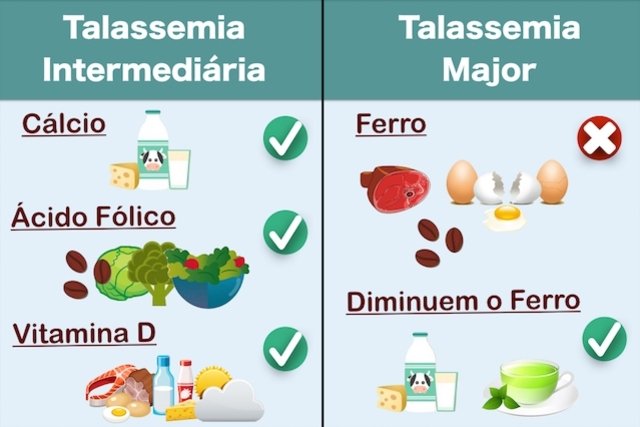
Diet for Thalassemia Intermediate
In thalassemia intermedia, in which the patient has moderate anemia and may not need to receive a blood transfusion, it is necessary to increase the levels of calcium, vitamin D and folic acid to improve quality of life.
Calcium
Calcium is important for strengthening bones, which may be weakened in thalassemia due to increased blood production, to reduce the anemia that the disease causes.
Therefore, you should increase your intake of foods rich in calcium, such as milk and dairy products, green vegetables such as spinach, kale and broccoli, tofu, almonds and chestnuts. See all foods rich in calcium.
Folic acid
Folic acid is important for stimulating the body to increase blood production, helping to reduce anemia caused by the disease.
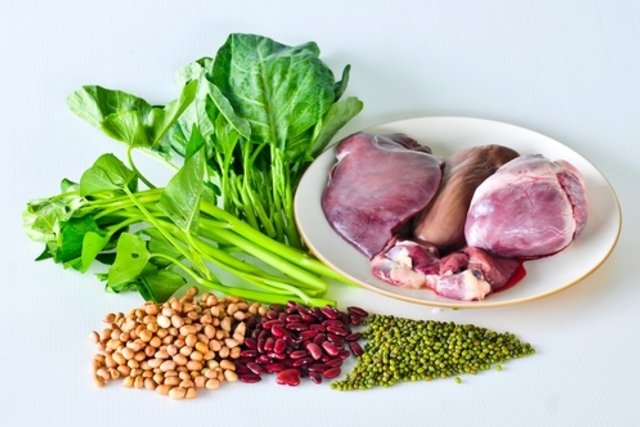
Foods rich in folic acid are mainly lentils, beans and dark green vegetables, such as kale, spinach, broccoli and parsley. See other foods here.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is important for increasing the fixation of calcium in bones, also helping to prevent osteoporosis. It is present in foods such as fish, eggs and milk and derivatives.
However, most of the vitamin D in the body is produced from skin exposure to sunlight. Therefore, it is important to sunbathe at least 3 times a week for around 20 minutes. See more tips at: How to sunbathe effectively to produce Vitamin D.
Diet for Thalassemia Major
Thalassemia major is the most serious form of the disease, in which the patient needs to receive frequent blood transfusions. Due to transfusions, there is an accumulation of iron in the body, which can be harmful to organs such as the heart and liver.
Therefore, you should avoid excess foods rich in iron, such as liver, red meat, seafood, egg yolks and beans. See the list of other foods here.
In addition, you should also increase your intake of foods that hinder the absorption of iron in the intestine, such as milk and dairy products and black tea. During a lunch or dinner where the main dish is red meat, for example, dessert can be yogurt, which is rich in calcium and helps to hinder the absorption of iron present in meat.
See how treatment with medications and blood transfusions is carried out for each type of thalassemia.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13