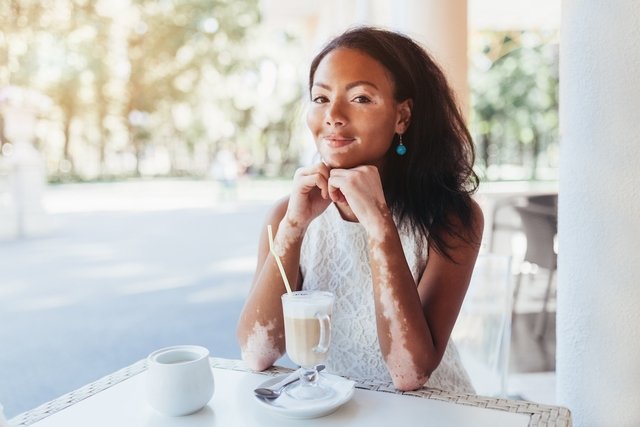
Vitiligo is a skin pigmentation disorder that leads to the appearance of symptoms such as white spots on the body, mainly on the arms, hands, feet or around the eyes or mouth.
These spots can appear due to the absence of melanin in the skin, due to the destruction or death of melanocytes, which are the cells that produce the pigment that gives the skin its color. The exact cause of vitiligo is not yet known, but it appears to be associated with genetic and autoimmune factors.
Vitiligo is not contagious and treatment is carried out by a dermatologist who may recommend the use of corticosteroid or immunosuppressant ointments or tablets, phototherapy, skin depigmentation, surgery or melanocyte transplantation.

Vitiligo symptoms
The main symptoms of vitiligo are:
- Depigmented spots on the skin;
- White spots, with well-defined edges;
- Round, oval or linear shaped spots;
- White spots that may have some normal pigmentation inside;
- White hair or hair in the area of the skin blemish;
- Depigmented patches inside the mouth or nostrils.
Vitiligo spots are most common on the face, especially around the eyes and mouth, back of the hands, neck, scalp, torso or genital region, such as the vulva or penis.
Furthermore, spots can also occur in areas of the body that can suffer trauma more easily, such as elbows or knees. In some cases, vitiligo can affect the eyes or ears.
Depending on the cause of vitiligo, other symptoms may appear, such as goiter, weight loss, gray hair, alopecia areata, anemia or weakness, for example.
Does Vitiligo itch?
Vitiligo does not itch or cause pain, only causing discoloration of the skin and the appearance of white patches. See other causes of white spots on the skin.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of vitiligo is generally clinical, being made by the dermatologist by evaluating the spots on the skin with the naked eye, and a Wood’s lamp can be used to allow a better observation of the spots on the skin.
Make an appointment with a dermatologist in the nearest region:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Furthermore, if necessary, the doctor can perform a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other health conditions, such as depigmentosus nevus or pityriasis alba, for example. Find out how a skin biopsy is performed.
Your doctor may also order blood tests to identify the cause of vitiligo.
Is Vitiligo contagious?
Vitiligo is not contagious, that is, it does not pass from one person to another, as it is not caused by infections by fungi, bacteria or viruses, for example.
Furthermore, vitiligo does not cause harm to health, but it can cause psychological discomfort in the person.
Possible causes
The exact cause of vitiligo is not completely known, but it is believed to be related to genetic, autoimmune factors or oxidative stress, for example.
These factors can lead to the destruction of melanocytes, which are the cells that produce the pigment that gives skin color, melanin, resulting in white spots on the skin.
What age does vitiligo appear?
Vitiligo can appear at any age, however, it is more common to appear before the age of 20, and can appear in babies or even in childhood.
Types of vitiligo
The main types of vitiligo are:
1. Generalized vitiligo
Generalized vitiligo is the most common type, characterized by the appearance of white spots in various regions of the body.
2. Localized vitiligo
Localized vitiligo is characterized by the appearance of white spots located in one or a few regions of the body.
3. Generalized vitiligo
Generalized vitiligo is rarer and occurs in almost all regions of the body, with most of the skin being depigmented, and some regions with normal skin pigmentation.
4. Segmental Vitiligo
Segmental vitiligo, also called unilateral vitiligo, affects only one side of the body, such as only one side of the face or one hand, for example.
This type of vitiligo is not very common, and mainly affects younger people, and the spots normally evolve over 1 to 2 years and then become stable, that is, they do not increase in size or no new spots appear on the skin.
5. Non-segmental vitiligo
Non-segmental vitiligo is characterized by the appearance of white spots on the skin symmetrically on both sides of the body, such as on both hands or both sides of the face, for example.
This type of vitiligo, also known as bilateral vitiligo, is the most common type of vitiligo, presenting rapid evolution, followed by periods in which the spots stagnate.
How the treatment is carried out
Vitiligo treatment must be carried out under the guidance of a dermatologist and varies according to the type of vitiligo, size of the spot on the skin and its location, and aims to stabilize the growth of the spot or promote skin repigmentation.
Thus, the main treatments that may be recommended by the doctor are:
- Topical ointments or creamssuch as corticosteroids, tacrolimus, pimecrolimus or calcipotriene;
- Pills corticosteroids or immunosuppressants;
- Phototherapy with UVB or UVA lightwhich can also be done with the use of psoralen (PUVA);
- Lasertherapyfor stable and limited stains;
- Skin grafts healthy in areas with stable white patches, in the case of segmental or localized vitiligo;
- Melanocyte transplantcarried out on spots that are stable for 1 year and do not improve with other treatments.
In addition, treatment of skin depigmentation, with creams or ointments, may also be indicated in the case of generalized vitiligo. See all treatment options for vitiligo.
Is vitiligo curable?
There is no cure for vitiligo, as the melanocytes, which are the cells that produce melanin, the pigment that gives the skin its color, are destroyed and cannot be regenerated.
However, it is possible to prevent skin depigmentation from progressing by following the treatment recommended by the dermatologist to repigment the white spots.
Possible complications
The main complications of vitiligo are aesthetic discomfort that can result in mental stress or even depression.
Furthermore, when it affects the eyes, vitiligo can cause iritis or uveitis, and if it affects the ears, it can result in hearing loss.
Other complications related to vitiligo are an increased risk of skin cancer or sunburn, as melanin is a natural protective factor in the skin.
Treatment with topical corticosteroids can also cause complications, such as skin atrophy.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13