Vincent’s angina, also known as acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, is a rare and serious gum disease, which is characterized by the excessive development of bacteria inside the mouth, causing infection and inflammation, leading to the formation of ulcers and death of gingival tissue.
Treatment is generally carried out with antibiotics, but it is also very important to maintain adequate oral hygiene, brushing your teeth after eating and always using mouthwash. Furthermore, when the problem causes very severe pain, the doctor may also prescribe the use of analgesic or anti-inflammatory medications, such as Paracetamol, Naproxen or Ibuprofen, for example, which can help alleviate symptoms.
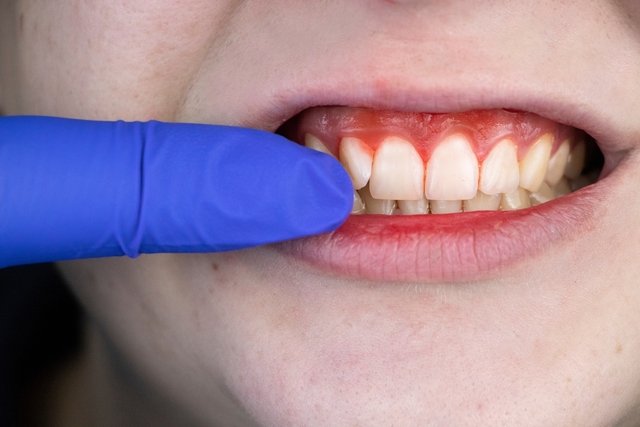
Main symptoms
Due to the overgrowth of bacteria in the mouth, early signs include pain, swelling and redness of the gums or throat. However, after a few hours other symptoms may appear, such as:
- Canker sores on the gums and/or throat;
- Severe pain when swallowing, especially on one side of the throat;
- Bleeding gums;
- Metallic taste in the mouth and bad breath;
- Swelling of the neck areas.
Furthermore, in some cases, the bacteria that develop in the mouth can also produce a thin gray film that makes the gums darker. In these cases, when the film does not disappear with proper oral hygiene, it may be necessary to go to the dentist for a professional cleaning with local anesthesia.
Causes of Vincent’s angina
Vincent’s angina is an infection caused by the excessive development of bacteria in the mouth and, therefore, is more common in situations with a weakened immune system, such as HIV or lupus infections. However, the disease can also appear in cases of poor nutrition, degenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, or in populations in underdeveloped regions, due to lack of hygiene.
How the treatment is carried out
Generally, treatment consists of the administration of antibiotics, such as amoxicillin, erythromycin or tetracycline, to prevent the infection from spreading, debridement with a manual or ultrasonic scraping device, frequent washing with chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide solutions, analgesics and anti-inflammatories. , to reduce pain, such as paracetamol, ibuprofen or naproxen, cleaning carried out by a professional and correct oral hygiene.
To prevent the onset of this disease, it is recommended to practice correct oral hygiene, eat a balanced diet with fruits and vegetables and avoid excess stress, which weakens the immune system. See what to do to strengthen your immune system.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13