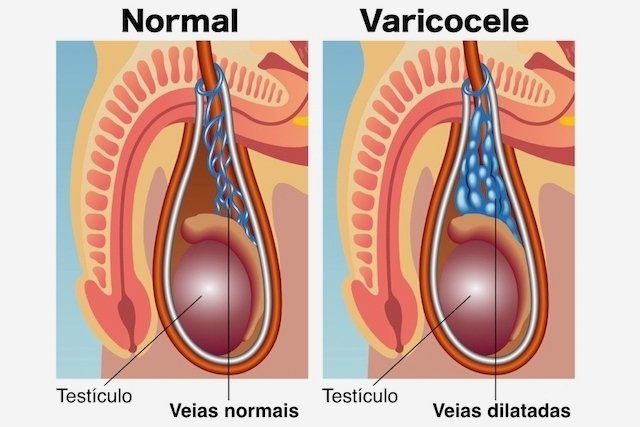
Varicocele is a dilation of the veins in the testicles that causes blood to accumulate, leading to symptoms such as pain, a feeling of heaviness and swelling in the area. Normally, it is more common in the left testicle, but it can appear on either side, and can even affect both testicles at the same time, being known as bilateral varicocele.
Since varicocele can cause infertility, as the accumulation of blood can reduce the production and quality of sperm, whenever this problem is suspected, it is important to consult a urologist to begin appropriate treatment and avoid complications.
Varicocele can be cured through surgery, but not all cases are able to achieve fertility, especially if there is already damage to the structures of the testicles. Learn about other causes that can cause infertility in men.
Varicocele symptoms
Common symptoms of varicocele may include:
- Pain in the testicles, which can range from discomfort to intense pain;
- Pain that improves when lying on your back;
- Swelling or presence of a lump in the testicles;
- Feeling of heaviness in the testicles;
- Infertility;
There are also cases in which varicocele does not present any symptoms and can therefore only be diagnosed during routine consultations with a urologist.
See other problems that can cause pain in the testicles and what to do in each case.
Main causes
The most likely cause of varicocele is a defect in the valves of the veins present in the scrotum, just above the testicles, responsible for regulating the flow of blood to and from the testicles.
Therefore, when blood flow does not occur normally and the blood “returns”, the veins dilate, resulting in varicocele.
How to confirm the diagnosis
Varicocele can be identified by the doctor through a palpation examination of the testicles, which must be done lying down and standing up, as in some cases the varicocele may not be felt in certain positions, and therefore an evaluation must be carried out. in more than one position.
However, it may also be necessary to undergo an ultrasound to identify in greater detail the affected area and the position of the testicular structures.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for varicocele is generally only recommended when a man has symptoms. Therefore, if there is exaggerated pain or swelling, the urologist may recommend taking analgesic medications, such as Dipyrone or Ibuprofen, and the use of testicular suspenders.
However, in cases of infertility, pain that does not improve or problems with testicular function, it may be necessary to undergo surgery, called varicocelectomy, which eliminates the problem once and for all.
Varicocele surgery
This type of surgery can be done in 3 different ways:
- Open surgery: this is the most classic type of surgery in which the doctor makes a cut in the groin area to observe the varicocele and ties a “knot” in the affected vein, allowing blood to circulate only through normal veins;
- Laparoscopy: it is similar to open surgery, but in this case the doctor makes small cuts in the abdomen and inserts thin tubes through which he repairs the varicocele;
- Percutaneous embolization: This is a less common technique in which the doctor inserts a tube through a vein in the groin to the site of the varicocele, and then releases a liquid that closes the dilated varicocele vein.
Depending on the type of surgery used, recovery time may vary, with the longest being open surgery, followed by laparoscopy and finally embolization. Learn more about varicocele surgery.
In any type of surgery, it is possible that there will be slight pain and, therefore, you should wear comfortable underwear and apply ice to the area for the first 24 hours, and you can return to normal activities after about 10 days. or as directed by your doctor.
Possible complications
When the testicle has a varicocele, it is very common for it to decrease in size and become softer over time, losing function. Although the specific cause of why this happens is not known, it is possible that it is related to the change in temperature in the area, the presence of free radicals near the testicles and also an increase in pressure in the area.
Furthermore, if the accumulation of blood in the varicocele causes an increase in temperature around the testicles, it is also possible for the quality of sperm to be affected, even in the testicle that is not affected, which can cause infertility.
Bibliography
- Vanlangenhove Peter, et al. Pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of varicoceles: a review. Minerva urologica e nefrologica = The Italian journal of urology and nephrology . 66. 4; 257-282, 2014

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13