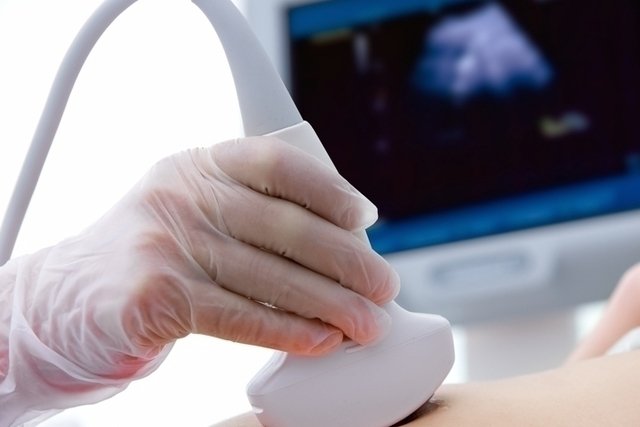
Ultrasonography, also known as echography and ultrasound, is a diagnostic imaging test that serves to visualize any organ or tissue in the body in real time. When the examination is performed with Doppler, the doctor can observe the blood flow in this region.
Ultrasonography is a simple, quick procedure with no restrictions, and can be done whenever the doctor deems it necessary, there is no need to wait between one ultrasound and another.
However, it is important to check whether there are any recommendations for carrying out the exam, such as filling the bladder or taking medication to eliminate excess gas, as this can make it difficult to visualize the organs.
What is it for
Ultrasonography is an imaging test that may be recommended by a doctor with the aim of identifying changes in organs. Therefore, this exam can be recommended for:
- Investigate abdominal, flank or back pain;
- Diagnose pregnancy or evaluate fetal development;
- Diagnose diseases of the uterus, tubes, ovaries;
- Visualize the structures of muscles, joints, tendons;
- To visualize any other structure of the human body.
Ultrasonography must be performed in a laboratory, clinic or hospital, always under medical advice, to assist in the diagnosis or treatment of various situations. Furthermore, before carrying out the exam, you need to find out about preparing for the exams, as in some types of ultrasound it may be necessary to drink plenty of water, fast or take medication to eliminate gas, for example.
How it is made
The ultrasound must be performed with the patient lying on a stretcher and then a thin layer of gel must be placed on the skin and the transducer placed on top of this gel, sliding the device over the skin. This device will generate images that can be viewed on a computer and must be analyzed by the doctor.
After finishing the exam, the doctor removes the gel with a paper towel and the person can go home. The exam does not cause pain or discomfort, is easy to access and is generally not an expensive exam, being covered by several health plans, although it can also be carried out by the SUS.
Main types of ultrasound
The main types of ultrasound that can be performed are:
1. Obstetric ultrasound
Obstetric ultrasound is indicated to check whether the embryo or fetus is developing correctly throughout pregnancy, allowing the doctor to assess its heart rate, growth, position in which it is located or whether it has any congenital disease.
In addition, this type of ultrasound also helps to estimate the length of pregnancy, if it is a multiple pregnancy, monitor the health of the woman’s uterus and ovaries, check the characteristics of the placenta and cervix, evaluate the quality of the amniotic fluid , and if a Doppler is performed, the flow of blood from the umbilical cord to the placenta can also be observed.
This type of ultrasound is performed until the 12th week of pregnancy, transvaginally, and after this week of pregnancy, the ultrasound is performed at the level of the lower abdomen, as the fetus is already larger and is easier to visualize.
In general, obstetric ultrasound is recommended to be performed once in each semester of pregnancy, however, it can be performed as many times as the obstetrician deems necessary.
2. Morphological ultrasound
This is a special type of ultrasound that must be performed during pregnancy, between 20 and 24 weeks of gestation, to check whether the baby is developing correctly or whether it has any malformation, such as Down Syndrome, myelomeningocele, anencephaly, hydrocephalus or congenital heart disease.
The exam duration varies between 20 and 40 minutes and this exam is recommended for all pregnant women.
How it is made: the doctor will place a gel on the pregnant woman’s belly and pass a device throughout the uterine region. The equipment will generate images that can be viewed on the computer. Check out more details about morphological ultrasound.
3. Ultrasound 3D and 4D
This is a type of exam that allows a better visualization of the structure being studied, giving it a more real appearance. 4D ultrasound, in addition to allowing great observation of the baby while still inside the mother’s belly, can capture its movements in real time.
They are particularly indicated for viewing the fetus and can be performed from the 3rd month of pregnancy, but better images are obtained from the 6th month of pregnancy.
4. Breast ultrasound
During a breast ultrasound, the doctor can observe the appearance of a lump that can be felt when palpating the breast. This helps to identify whether it may be a benign, suspicious lump or breast cancer, and is also useful for evaluating the breast ducts and investigating the causes of breast pain, for example.
How is done: The woman must lie down without clothes and bra while the doctor applies the equipment to the entire suspicious area. It is normal to take longer when there are cysts or nodules that need to be investigated. This exam does not replace a mammogram, but may be requested by the doctor if the woman has large, firm breasts, which makes it difficult to undergo a mammogram. Find out more details about breast ultrasound.
5. Thyroid ultrasound
During a thyroid ultrasound, the doctor observes the size of this gland, its shape and whether it has any nodules. This exam can also be carried out to guide a biopsy so that a small sample of tissue can be removed, in case of suspected cancer, for example.
How is done: The person must lie face up, and then a gel is placed on the neck. The doctor will slide the device and see on the computer screen how the person’s thyroid is doing. It is normal during the exam for the doctor to ask if this is the first time he has done the exam or if there have been any changes in previous exams, so that he can compare the results. Check out the symptoms that may indicate thyroid cancer.
6. Pelvic ultrasound
Pelvic ultrasound is indicated to visualize structures such as the uterus, ovaries and blood vessels in this region, and may be necessary to diagnose endometriosis, for example.
This type of ultrasound can be done suprapubically, applying a gel under the skin and placing the transducer in the lower part of the belly to examine the pelvic region. Learn more about pelvic ultrasound.
In addition, pelvic ultrasound can also be done using a device that is inserted into the vagina to capture images on the computer, this type is known as transvaginal ultrasound.
In men, pelvic ultrasound is performed suprapubically or, in some cases, rectally, and is indicated to evaluate the prostate, seminal vesicles and bladder.
Read too: Transvaginal ultrasound: what it is, what it is for and how to prepare it
7. Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is used to investigate pain in the abdomen, whether there is fluid in this region, or evaluate organs such as the liver, kidneys, presence of masses and, in the case of trauma or blow, in the belly region. In addition to being useful in the case of evaluating the kidneys and urinary tract, for example.
How it is done: the doctor will indicate whether it is necessary to do some type of preparation beforehand, but in the case of evaluating the kidneys, urinary tract and the bladder itself, before the exam it is recommended to fast for 6 hours, and the exam needs to be carried out with a full bladder . Therefore, children aged 3 to 10 should drink 2 to 4 glasses of water, teenagers and adults should drink 5 to 10 glasses of water up to 1 hour before the exam, without being able to pee before the exam.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13