Tuberculosis is spread through the air, when the infected person releases the bacteria from Koch in the environment, through coughing, sneezing or speaking, remaining suspended in the air and being able to be inhaled by other people, which can result in illness.
The bacillus Koch it can remain in the air for many hours, especially if it is a cramped and poorly ventilated environment, such as a closed room. Thus, the main people who can become infected are those who live in the same environment as the person with tuberculosis, such as sharing the same room, living in the same house or sharing the same work environment, for example.
Only pulmonary tuberculosis is transmissible, because particles containing the bacteria must remain suspended in the air. Therefore, other types of extrapulmonary tuberculosis, such as miliary, bone, intestinal or lymph node tuberculosis, are not transmitted from one person to another. Find out more about tuberculosis.
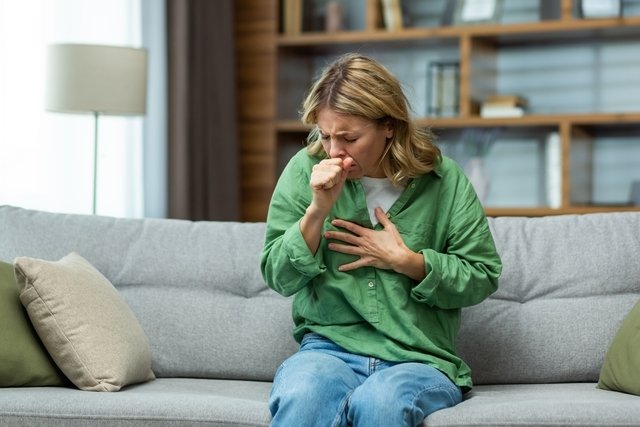

How transmission happens
The transmission of tuberculosis occurs through the inhalation of droplets containing the bacteria that are released into the environment when a person with tuberculosis speaks, coughs or sneezes, for example.
What does not transmit tuberculosis
Although pulmonary tuberculosis is an easily transmitted infection, it is not transmitted through shaking hands, sharing food and drinks, or wearing the clothes of a person with tuberculosis.
Furthermore, tuberculosis is also not transmissible through kisses, because the presence of pulmonary secretions is necessary to transport the tuberculosis bacillus. Kochwhich does not happen in kissing.
It is important to remember that a person diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis stops transmitting the disease 15 days after starting treatment with the antibiotics recommended by the doctor, but this only happens if the treatment is strictly followed.
How to avoid the disease
The most important and effective way to prevent tuberculosis infection is through the BCG vaccine, carried out in the first month of life. Although this vaccine does not prevent contamination by the Koch, is capable of preventing serious forms of the disease, such as miliary or meningeal tuberculosis, for example. Check out when to take and how the BCG vaccine against tuberculosis works.
Furthermore, it is recommended to avoid living in the same environment as people with pulmonary tuberculosis, especially if you have not yet started treatment. If it is not possible to avoid it, especially people who work in health centers or caregivers, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment, such as an N95 mask.
Furthermore, for those people who have lived with people infected with tuberculosis, the doctor may recommend preventive treatment, with the antibiotic Isoniazid, if a high risk of developing the disease is identified.
Bibliography
- CDC. Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis. Available at: <https://www.cdc.gov/tb/education/corecurr/pdf/chapter2.pdf>. Accessed on April 16, 2019
- CDC. How TB Spreads. Available at: <https://www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/basics/howtbspreads.htm>. Accessed on April 16, 2019

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13