Tirzepatide is a medicine indicated for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults, as it helps to increase the production of insulin by the pancreas and reduce the amount of glucose produced by the liver, which allows blood sugar levels to be lowered.
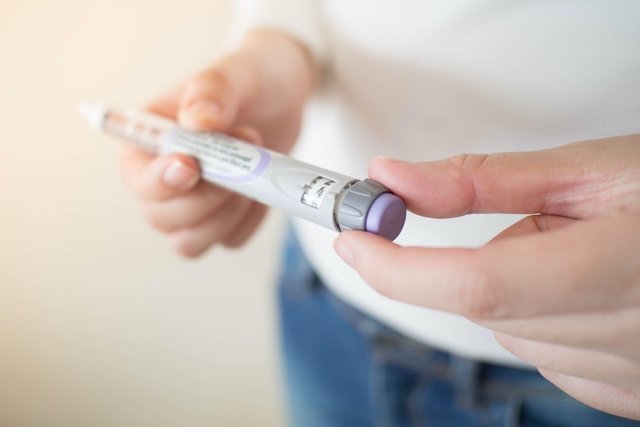
This remedy is found in the form of an injection for weekly application, under the trade name Mounjaro, and can be used alone or in conjunction with other antidiabetic medications, and associated with a balanced diet and physical exercise.
Tirzepatide should be used with the recommendation of an endocrinologist and regular medical monitoring, to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and the emergence of side effects.
What is it for
Tirzepatide is indicated for the treatment of uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus, and should be part of a balanced diet and physical exercise to control blood sugar levels.
This medicine can be used alone when the person has intolerance or contraindications to treatment with metformin or be used in conjunction with other antidiabetic medicines, according to the endocrinologist’s guidance. Check out the main diabetes remedies.
How it works
Tirzepatide has a dual action, as it acts on GPL-1 receptors (glucagon-like peptide-1) and GIP receptors (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) present in the pancreas, brain, intestines, heart, kidneys, adipose tissue, leukocytes and blood vessels.
GPL-1 and GIP are hormones, called incretins, produced naturally by the intestine, and whose function is to stimulate the release of insulin by pancreas cells, reduce the amount of glucose produced by the liver, reduce gastric emptying and promote satiety.
In this way, this medicine helps to regulate blood sugar levels, reduce glucagon levels, improve insulin sensitivity, reduce the feeling of hunger during food intake, and modulate fat metabolism.
Is Tirzepatide useful for losing weight?
Tirzepatide has been shown to reduce weight in people with type 2 diabetes, as it sends satiety signals to the brain and reduces gastric emptying, reducing hunger, resulting in a reduction in the amount of calories ingested daily and, therefore, , this medicine can also lead to weight loss.
Some studies (1,2) have shown that tirzepatide has a greater effect on weight reduction than semaglutide in people with obesity or overweight, as in addition to activating GPL-1 receptors, it also stimulates GIP receptors.
However, this remedy does not have an official indication approved by ANVISA for weight loss, in cases of obesity or overweight, and does not replace regular physical activity and a balanced diet for weight loss. Find out how to follow a balanced diet to lose weight.
How to use
Tirzepatide should be used through injections applied to the subcutaneous layer of the skin (under the skin) of the belly, thigh or upper arm, and can be applied before or after a meal, at any time of the day. See how to inject under the skin correctly.
The normally recommended doses of tirzepatide for adults are:
- Initial dose: 1 application of 2.5 mg of tirzepatide, once a week. After 4 weeks, the dose can be increased by the doctor to 5 mg, once a week;
- Maintenance dose: 5 mg, 10 mg or 15 mg of tirzepatide, once a week, as per medical advice.
Increasing doses of tirzepatide should be done with the guidance of the endocrinologist, with increments of 2.5 mg, after at least 4 weeks with the same dose, according to the response to treatment, tolerance to this medicine and the emergence of effects collaterals.
The maximum dose of tirzepatide should not exceed 15 mg per week.
Tirzepatide is available in the form of a prefilled injectable pen, with doses of 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg, 12.5 mg and 15 mg, and it is recommended to vary the application site each week.
What to do if you forget
If you forget to apply the weekly dose on the correct day and time, you can apply it immediately up to a maximum of 4 days of forgetting.
After 4 days of forgetting, you should skip the missed dose and continue the weekly schedule as scheduled.
Do not apply 2 doses, with an interval of 3 days between one dose and another.
Possible side effects
The most common side effects of tirzepatide are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal or stomach pain, excess intestinal gas, frequent burping, gastroesophageal reflux, constipation, swollen belly or fatigue.
Additionally, tirzepatide can reduce blood sugar too much and cause hypoglycemia, especially when used with other diabetes medications. Know how to identify the symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Tirzepatide can also cause side effects at the injection site, such as pain, itching, irritation, lesions and bruises near the injection site.
Although it is rare, tirzepatide can cause serious allergic reactions, and you should stop using it and seek emergency help immediately if symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, feeling of a closed throat, swelling in the mouth, tongue or face appear, or hives.
You should seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms of pancreatitis, such as pain in the upper part of the abdomen that can radiate to the back or yellow or white stools with signs of fat, for example. See all the symptoms of pancreatitis.
Who shouldn’t use
Tirzepatide should not be used by children and adolescents or by people who have type 1 diabetes, pancreatitis or allergies to this medicine or any other component of the formula.
Furthermore, this remedy should be used with caution in people with serious gastrointestinal diseases, such as gastroparesis, or those with diabetic retinopathy, or elderly people over 85 years of age.
During pregnancy or breastfeeding, tirzepatide should only be used if recommended by the doctor, after evaluating the benefits of the treatment for the woman and potential risks for the baby.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13