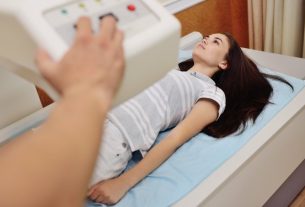
The tilt test, also called tilt test, is an exam used to investigate and evaluate episodes of fainting and falls, which is done by observing heart rate and blood pressure, and symptoms such as weakness and dizziness, during changes in mood. position.
The test is generally considered positive when fainting symptoms occur due to low heart rate and blood pressure during position changes and may indicate conditions such as orthostatic hypotension and vasovagal syncope. However, even if the result is negative, other tests such as an electrocardiogram or echocardiogram may be necessary to complete the evaluation.
The tilt test is a simple exam, which does not require hospitalization to be carried out, but it is important to follow the preparation instructions in accordance with the doctor’s instructions, such as fasting for at least 4 hours, to avoid discomfort and nausea during the test.

What is it for
The tilt test is recommended to investigate situations such as:
- Suspected vasovagal syncope;
- fainting episodes;
- Convulsive crises that do not improve despite appropriate treatment;
- Suspected orthostatic hypotension;
- Recurrent episodes of falling;
- Dysautonomia.
- Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome is suspected.
Vasovagal syncope is usually the main cause of fainting in people without heart problems and can be triggered by changes in body position, which is why the tilt test can be indicated to identify this condition. Understand what vasovagal syncope is and how to treat it.
The tilt test is normally recommended by a cardiologist or general practitioner, and it is common for other tests to be ordered together to rule out other cardiac changes, such as a blood test, electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, 24-hour Holter monitor or ABPM.
How should the preparation be
To carry out the tilt test, it is important that the person is completely fasting, including not drinking water, for at least 4 hours, as position changes will be made during the test, the person may feel nausea and malaise if they have a full stomach. Furthermore, it is also recommended that the person go to the bathroom before the exam, so that there are no interruptions.
Before starting the exam, the doctor may ask what medications the person uses daily and will also ask questions about the onset of symptoms and whether there is any situation that makes the symptoms worse.
How the tilt test is done
The tilt test is usually carried out in an electrophysiology laboratory at a hospital or clinic and must be carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist and a nurse or nursing technician.
Its duration can vary according to the indication of the exam, generally between 5 and 60 minutes, and the person is evaluated on a special stretcher that is capable of tilting at different angles. To do this, the person is normally secured by some belts to the stretcher so that they do not fall during the movement.
Additionally, monitoring devices are connected to the person before the exam begins to measure blood pressure and heart rate during the tests. Generally, the person is observed for about 5 to 20 minutes in a horizontal position and then in an upright position for about 20 to 45 minutes.
Sometimes it may be necessary to perform the tests again using some medications such as nitroglycerin or isoproterenol to increase the chance of identifying changes during the tests. However, this procedure is not always indicated.
At any time during the exam, if the blood pressure becomes too low or the person feels very unwell, the doctor may stop the exam. Therefore, it is important to communicate what you are feeling.
Care after the exam
After the tilt test, the person may feel tired and a little nauseous, so they should lie down for 30 minutes to be observed by the nurse or nursing technician.
After this period, the person is free to resume normal activities, however, it is recommended to avoid driving for at least 2 hours. If the person felt unwell, had very low blood pressure or fainted during the examination, they may need to remain under the care of the doctor and nurse for longer.
Tilt test contraindications
The tilt test is not recommended for pregnant women, people with narrowing or obstruction of the carotid or aortic artery or with orthopedic changes that prevent the person from standing.
How to understand the result
The result of the tilt test is generally positive or negative, depending on the changes identified by the doctor during the examination, who observes measurements, such as heart rate and blood pressure, and the presence of symptoms such as dizziness or nausea.
Tilt test positivo
The result of the tilt test is usually positive when symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, weakness or sweating occur due to low blood pressure and heart rate after changing from a horizontal to a vertical position.
Although a positive result sometimes occurs in healthy people, it may indicate conditions such as orthostatic hypotension and vasovagal syncope.
Tilt test negativo
A negative result generally indicates that no changes in pressure or heart rate were found during the test.
In this case, other tests, such as a 24-hour Holter monitor or echocardiogram, may be indicated to complement the evaluation.
Bibliography
- STATPEARLS. Tilt Table. 2022. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482320/>. Accessed on Jul 19, 2022
- KULKARNI, Nitin; MODY, Purav; LEVINE, Benjamin D. Abolish the Tilt Table Test for the Workup of Syncope!. Circulation. Vol.141, n.5. 335-337, 2020
- WHITE, Laura; JONES, Howell T; DAVIES, Anne. What is a tilt table test and why is it performed during the investigation of syncope?. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). Vol.82, n.10. 1-7, 2021
- CHESHIRE, William P; GOLDSTEIN, David S. Autonomic uprising: the tilt table test in autonomic medicine. Clin Auton Res. Vol.29, n.2. 215-230, 2019
- TEODOROVICH, Nicholas; SWISSA, Moshe. Tilt table test today – state of the art. World J Cardiol. Vol.8, n.3. 277-282, 2016
- DANTE PAZZANESE INSTITUTE OF CARDIOLOGY. Tilt Test: what the clinician should know. Available at: <https://s3-sa-east-1.amazonaws.com/publisher.gn1.com.br/relampa.org.br/pdf/v31n4a01.pdf>. Accessed on 06 Feb 2020
- AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION. Tilt-Table Test. Disponível em: <https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack/diagnosing-a-heart-attack/tilt-table-test>. Acesso em 06 fev 2020
- IDEAL DIAGNOSIS. Tilt Test – episodes of syncope and unknown origin. Available at: <https://www.ecgweb.com.br/tilt-test/>. Accessed on 06 Feb 2020
- MACEDO, Paula G. et al. Tilt test (Tilt-test) – from necessary to essential. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. Vol.96, n.3. 246-254, 2011

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13