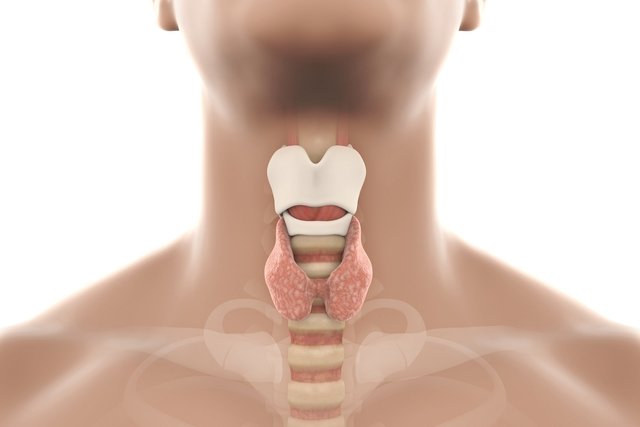
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland, located in the front of the neck, responsible for producing the hormones T3 and T4, whose function is to regulate body metabolism, in addition to temperature and fertility.
Thyroid symptoms, such as weight gain or loss, dry skin or difficulty concentrating, can arise when this gland produces too much or too little hormone, with the most common thyroid problems being hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
If you suspect thyroid problems, it is recommended to consult an endocrinologist, who can recommend thyroid tests in order to identify the type of problem and, thus, initiate the most appropriate treatment.
What is it for
The thyroid gland serves to regulate many body functions, such as:
- Body metabolism rate;
- Heart beats;
- Body temperature;
- Digestion;
- Breathing;
- Fertility;
- Maintenance of bones and skin.
Furthermore, the thyroid also serves to control brain development and mental activity.
Where is the thyroid
The thyroid gland is located at the front of the neck, having two lobes, the right and the left, in addition to the central portion called the isthmus, which gives it the shape of a butterfly.
These lobes surround the trachea, which is a tube that connects the larynx to the lungs.
Because it is in front of the neck, during the physical examination the doctor can feel the thyroid gland.
Thyroid symptoms
The main symptoms of thyroid changes are:
- Weight gain or loss for no apparent reason;
- Fast or slower heartbeat;
- Intolerance to cold or heat;
- Anxiety or depression;
- Dry skin and hair loss;
- Difficulty concentrating:
- Irregular menstruation in women.
Furthermore, in some cases, symptoms such as a feeling of tightness in the throat, swelling in the front of the neck or hoarseness may also occur. Know how to identify all the symptoms of thyroid problems.
It is important to consult an endocrinologist if symptoms of an abnormal thyroid appear, so that tests can be carried out to identify the problem and, thus, provide the most appropriate treatment.
Don’t ignore the signs your body is giving you!
The main thyroid hormones are T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine), produced by this gland and released into the bloodstream.
These hormones are produced through a process that involves the transformation of iodine found in foods, such as iodized salt, boiled eggs, parmesan cheese or salmon, for example. See the complete list of foods rich in iodine.
The production of thyroid hormones is stimulated by the hormone TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) produced by the pituitary gland or pituitary gland in the brain.
In addition to T3 and T4, the thyroid also produces calcitonin, which is a hormone that helps regulate the amount of calcium in the blood.
Most common problems
The most common thyroid problems are
- Hypothyroidism;
- Hyperthyroidism;
- Graves’ disease;
- Tireoidite de Hashimoto,
- Thyroid nodule or cyst;
- Goiter;
- Thyroid cancer.
Some of these thyroid problems occur when the gland is not functioning well and produces more or less hormones than normal. Check out the main thyroid problems and what to do.
What causes thyroid
Thyroid problems can be caused by autoimmune changes, low or excessive iodine intake, or even the use of medications such as amiodarone, potassium iodide or antiarrhythmic drugs.
The diagnosis of the cause of the thyroid problem is made by the endocrinologist through the evaluation of symptoms, health history and medication use, lifestyle habits and thyroid tests.
Thyroid exams
The main tests that evaluate the thyroid are blood tests that measure the levels of thyroid hormones, such as:
In some cases, the endocrinologist may also request imaging tests such as ultrasound or scintigraphy, or even FNAC, which is a thyroid puncture. See the complete list of tests that evaluate the thyroid.
Thyroid medicine
Thyroid medications vary according to the condition being treated, and the doctor may recommend levothyroxine in cases of hypothyroidism, as it helps replace thyroid hormones, relieving symptoms.
Furthermore, depending on the type of thyroid problem, the doctor may recommend medications such as propylthiouracil or methimazole, radioiodine therapy or even chemotherapy or radiotherapy in cases of cancer. Check out the main thyroid medications and how to use them.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13