Testicular cancer is a rare type of tumor that affects the testicle and usually causes symptoms. However, some men may notice the presence of hard, painless nodules in the testicle, pain when palpating the testicle and an increase in size.
Testicular cancer occurs more frequently in men between the ages of 20 and 34, in addition to being more common in men who have already suffered trauma to the region, as in the case of athletes, for example.
If testicular cancer is suspected, it is important that a urologist is consulted so that the diagnosis can be made and the most appropriate treatment can be initiated, which is normally done through surgery.
Main symptoms
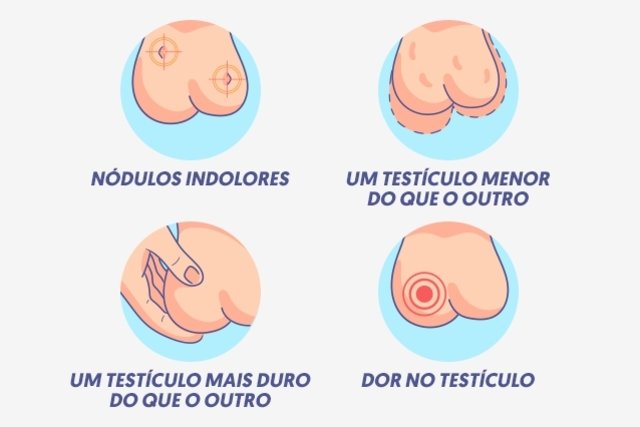
The main symptoms of testicular cancer are:
- Presence of hard nodules and painless about the size of a pea;
- Increase in size and, consequently, the weight of the testicle;
- Breast augmentation or sensitivity in the region;
- A harder testicle than the other;
- Testicular pain when feeling it or pain in the testicle after intimate contact.
Cancer generally develops without showing symptoms and, therefore, can be difficult to identify. Therefore, it is important that self-examination of the testicles is carried out regularly, especially if there is a family history, as this makes it possible to identify changes early that could turn into cancer.
There are also other testicular problems that can cause symptoms very similar to those of cancer, especially the presence of a lump, but which are a sign of less serious situations, such as epididymitis, cysts or varicocele, and it is important that a urologist is consulted. See 7 other causes of lumps in the testicle.
How to confirm the diagnosis
If changes appear during self-examination, it is recommended to consult a urologist to carry out diagnostic tests, such as ultrasound, specific blood tests or tomography, to confirm the diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatment, if necessary.
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
In some cases, the doctor may also recommend performing a biopsy of the tissue from one of the testicles, if changes appear suggestive of cancer.
Symptoms of advanced cancer
When cancer is already at a more advanced stage, it can end up spreading to other parts of the body and generating other symptoms such as:
- Constant pain in the lower back;
- Feeling short of breath or frequent coughing;
- Constant pain in the belly;
- Frequent headache or confusion.
These signs are rarer and usually indicate that the cancer has spread to other locations such as lymph nodes, lung, liver or brain, for example.
At this stage, cancer is more difficult to fight, however, treatment is carried out to try to reduce the size of the lesion and alleviate symptoms.
Possible causes of testicular cancer
The cause of testicular cancer is not yet completely understood, however, there are some factors that appear to increase a man’s risk of developing this type of cancer, the main ones being:
- Having an undescended testicle;
- Have a family history of testicular cancer;
- Have ever had cancer in a testicle;
- HIV infection.
- Be between 20 and 34 years old.
Furthermore, being Caucasian also appears to increase the risk of having this type of cancer by up to 5 times, when compared to being black, for example.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for testicular cancer depends on the evolution of the disease, usually starting with surgery to remove the affected testicle and all the cancer cells, which is sufficient in less developed cases of cancer. In more advanced cases, it may be necessary to undergo radiotherapy or chemotherapy after surgery, to eliminate any remaining tumor cells that may remain.
After treatment, the urologist makes several appointments to perform blood tests and CT scans, in order to assess whether the cancer has been completely eliminated.
Does the treatment cause infertility?
Generally, a man only becomes infertile when it is necessary to remove both testicles, which happens in few cases. However, in these cases it is possible to preserve some sperm in specialized laboratories before surgery, which can then be used to carry out artificial insemination, for example, allowing children to be born.
Is testicular cancer curable?
Testicular cancer is curable in most cases, even when metastases have formed, as long as it is identified and treated as soon as the diagnosis is made.
Testicular cancer stages
There are 4 main stages in the development of testicular cancer:
- Stadium 0: the cancer is only found in the seminiferous tubules inside the testicle and has not spread to other parts, nor to the lymph nodes.
- Stadium I: cancer cells have grown outside the seminiferous tubules and, therefore, may be affecting structures close to the testicle, however, the cancer has not yet reached the lymph nodes;
- Stadium II: The cancer may have grown outside the testicle or the size cannot be assessed correctly. Additionally, it may have spread to one or more lymph nodes;
- Stadium III: The cancer may have grown outside the testicle, but the size cannot be correctly assessed. The cancer may also have reached the lymph nodes and other nearby structures.
Normally, the more advanced the cancer stage, the more difficult the treatment may be, and it may be necessary to remove the testicles to obtain a cure.
We regularly update our content with the latest scientific information, so that it maintains an exceptional level of quality.
Bibliography
- AMERICAN CANCER SOCIETY. Risk Factors for Testicular Cancer. Disponível em: <https://www.cancer.org/cancer/testicular-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/risk-factors.html>. Acesso em 20 jul 2022
- GOLDMAN, Lee; SCHAFER, Andrew I.. Goldman-Cecil Medicina. 25 ed. Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier, 2018. p. 1392-1394.
- Townsend, Courtney M. et al . Sabiston treatise on surgery: the biological basis of modern surgical practice. 20 ed. Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier, 2019. p. 2101-2103.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13