Syphilis in the mouth is the oral manifestation of syphilis, causing symptoms such as a single wound or ulcer on the lip or tongue, swelling in the neck, fever or sore throat, for example.
Syphilis in the mouth, or oral syphilis, is transmitted through unprotected oral sex with a person infected with the bacteria Treponema pale that enters the mucosa of the mouth or lips through small cuts, lesions or openings.
The treatment of syphilis in the mouth is carried out by an infectious disease specialist, stomatologist or general practitioner and involves the use of antibiotics, such as benzathine penicillin G, to eliminate the bacteria and avoid serious complications in other organs such as the brain and heart.
Sensitive content
This image may contain content that is uncomfortable for some people.
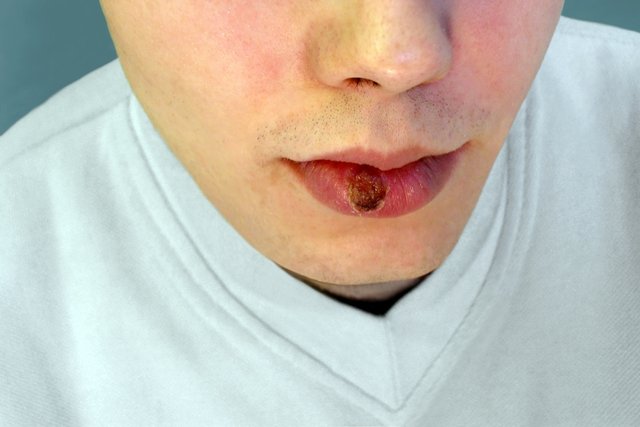
Symptoms of syphilis in the mouth
The main symptoms of syphilis in the mouth are:
- Single wound or ulcer on the lip or tongue;
- Red, purple or brown spot and a raised border;
- Grayish or whitish, irregular plaques that do not cause pain;
- Hard lump with an irregular surface anywhere in the mouth;
- Sore throat or headache;
- Soreness in the neck;
- Fever.
These symptoms are more common in the primary and secondary stages of syphilis, whereas in the case of latent syphilis the person usually has no symptoms. Check out the main symptoms of syphilis by stage.
The symptoms of oral syphilis can often be confused with thrush, herpes simplex, erosive lichen planus or cancer, for example.
Therefore, it is important to consult an infectious disease specialist, stomatologist or general practitioner as soon as possible whenever symptoms of syphilis appear in the mouth, so that a diagnosis can be made and treatment can be started.
Don’t ignore the signs your body is giving you!
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of oral syphilis can be suspected by the doctor through evaluation of symptoms, physical examination of lesions on the lips, tongue or oral cavity, and history of unprotected intimate contact.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor must request a blood test, the VDRL, which detects the presence of circulating antibodies and their concentration. See how the VDRL exam is performed and understand the results.
Another test that the doctor may order is a biopsy of the tissue or fluid from the lesion in the mouth, to detect the presence of the bacteria Treponema pallidum.
How transmission happens
Oral syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum that can penetrate the lining of the mouth or lips through a small opening, cut or lesion.
This bacteria is transmitted through unprotected oral sex with an infected person, and oral syphilis lesions in the mouth usually appear where the bacteria have penetrated. Understand better how syphilis is transmitted.
How the treatment is carried out
The treatment of oral syphilis must be carried out under the guidance of an infectious disease specialist, stomatologist or general practitioner, with the use of antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria.
The antibiotic normally indicated is benzathine penicillin G, applied to the muscle in the hospital or health center, and the number of injections varies depending on the stage of syphilis. Find out how syphilis is treated at each stage of the infection.
For people allergic to penicillins, the doctor may recommend the use of other antibiotics, such as tetracycline or doxycycline, for example.
It is important to follow the treatment for the time indicated by the doctor, even if the syphilis wounds or lesions disappear, and blood tests should also be carried out regularly.
Care during treatment
During the treatment of syphilis in the mouth, intimate contact should be avoided.
In addition, the partner must also consult a doctor for tests and treatment for syphilis.
Possible complications
Syphilis in the mouth, when not treated properly, can cause complications as the bacteria spread to other organs such as the brain or heart, and put life at risk.
In this way, complications such as neurosyphilis can occur, with symptoms such as progressive general paralysis or dementia, or cardiovascular syphilis, which can cause damage to the valves and arteries of the heart, heart failure or even stroke.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13