A fecal examination may be requested by the doctor to assess digestive functions, the amount of fat in the feces or parasite eggs, which is useful for knowing the person’s health.
It may be recommended that two to three collections be made on different days, with each sample being stored in a specific container and stored in the refrigerator.
It is important that the person receives guidance from the doctor regarding the collection, whether it should be a single sample or several, and whether after collection it should be taken immediately to the laboratory for analysis or left in the refrigerator to be delivered the next day. In the case of parasitological examination and occult blood testing, feces can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 24 hours.
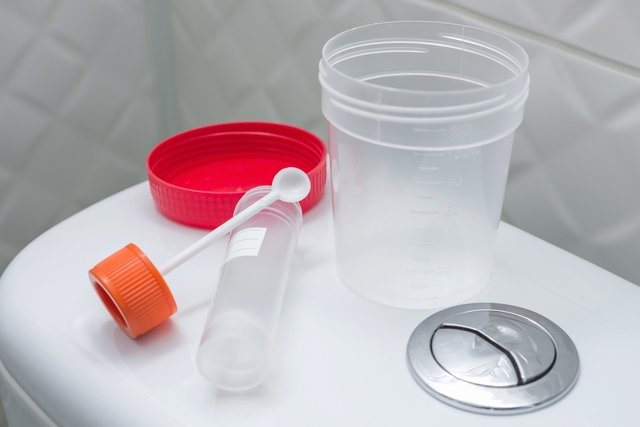
How to make
Stool collection must be done carefully to avoid contamination with urine or toilet water. To collect it you need:
- Evacuate in the chamber pot or on a sheet of white paper placed on the bathroom floor;
- Collect a little feces with a small stick (which comes with the jar) and place it inside the jar;
- Write the full name on the bottle and store it in the refrigerator for 24 hours until taken to the laboratory.
The minimum amount of feces depends on the laboratory recommendation and the test to be performed. Normally, large quantities of feces are not necessary, just a quantity that can be collected with the help of the paddle that is provided with the feces container.
The procedure is simple and should be the same for adults, babies and children, however, if the person uses diapers, the collection should be done immediately after evacuation.
Another way to collect feces more easily is to buy a type of sterilized plastic bag that lines the toilet and evacuate using the toilet normally. This bag does not allow contamination with the water present in the toilet and facilitates the collection of feces, being especially useful for people with reduced mobility and who cannot squat to evacuate in a chamber pot or on a sheet of newspaper, for example.
Check out these tips in the following video about collecting feces for the exam:
What is it for
The stool test can be requested as a routine test or indicated with the aim of investigating the causes of intestinal changes, being mainly requested by the doctor when the person presents signs and symptoms of worms, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, presence of blood in the stools or constipation. Check out other symptoms of worms.
In addition, a stool test may also be requested to investigate the cause of possible bleeding in the digestive system and diarrhea in children, which is normally associated with virus infection.
Therefore, fecal analysis may be recommended to check whether there are parasitic structures, such as eggs or cysts, or bacteria and, in this way, it is possible to confirm the diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatment.
Make an appointment with the nearest gastroenterologist so that the most appropriate stool test can be recommended:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Types of stool examination
The main stool tests that can be requested are:
1. Macroscopic examination of feces
This examination consists of observing the feces macroscopically, that is, with the naked eye, so that the color and consistency of the feces is assessed, which is directly related to the amount of water ingested during the day and possible infection. Therefore, according to the consistency of the stool, the best complementary stool test to perform can be suggested.
2. Parasitological examination of feces
Through parasitological examination it is possible to search for cysts or parasite eggs, which is useful for identifying intestinal worms. In this case, you cannot use laxatives or suppositories before collecting the feces, and the container must be kept in the refrigerator. See how fecal parasitology is done.
3. Coprocultura
The stool culture test is requested to identify the bacteria present in the feces, making it possible to check the health of the intestine from the moment the presence of bacteria that are not part of the normal microbiota is identified.
The feces must be placed in a suitable container and sent to the laboratory within 24 hours, the patient must not use laxatives and the container with the feces must be kept in the refrigerator. Understand how the stool culture exam is carried out.
4. Occult blood test
Fecal occult blood testing is indicated for screening for colon cancer, bowel cancer and investigation of possible hemorrhages in the digestive system, as it serves to evaluate small amounts of blood in feces that cannot be seen with the naked eye. See how the fecal occult blood test is performed.
To carry out this test, the feces must be sent to the laboratory no later than the next day and kept in the refrigerator. It is recommended to avoid collecting feces in case of anal or nasal bleeding or gum bleeding while brushing teeth, as blood may be swallowed, which may interfere with the test results.
5. Rotavirus research
This test’s main objective is to investigate the presence of rotavirus in feces, which is a virus responsible for causing intestinal infections mainly in children and which leads to the development of liquid feces, diarrhea and vomiting.
Feces, preferably when liquid, must be collected at any time of the day and taken to the laboratory within a maximum of 1 hour, with the aim of identifying the rotavirus and, thus, being able to start treatment immediately, avoiding complications.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13