Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is a type of skin cancer that causes symptoms such as wounds that do not heal, bleed easily and rough patches on the skin, with irregular edges and a reddish or brown color.
This type of skin cancer, also called squamous cell carcinoma, appears mainly in the mouth, tongue and esophagus, in most cases it is caused by excessive exposure to UV rays from the sun, and is more common in people with thicker skin and eyes. clear.
Read too: Skin cancer: what it is, symptoms, types and treatment
The treatment of squamous cell carcinoma is carried out by a dermatologist or oncologist, with surgery to remove the tumor and/or chemotherapy or immunotherapy, for example, which varies depending on the size and stage of the cancer.
Sensitive content
This image may contain content that is uncomfortable for some people.
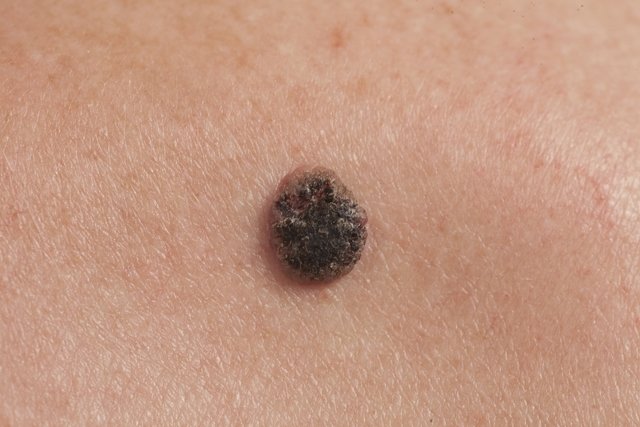
Squamous cell carcinoma symptoms
The main symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma are:
- Flat, scaly, rough or crusty lesion;
- Nodule firm on front;
- Wound that does not heal and bleeds easily;
- Pink, red, brown or black spot on the skin;
- Injuries to old scars;
- Pain or increased sensitivity at the site;
- Lesions with irregular edges.
The symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma appear mainly on the lips or inside the mouth, however, it can appear on any part of the body that has been heavily exposed to the sun, such as the face, bald scalp, forearms, hands or shins, for example.
Furthermore, this type of skin cancer can appear in the esophagus, lungs or anal or genital region, for example.
Squamous cell carcinoma often arises from skin lesions called actinic keratosis. Understand what actinic keratosis is.
In the presence of symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma, you should consult a dermatologist to confirm the diagnosis and initiate the most appropriate treatment.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma is made by the dermatologist through the evaluation of symptoms and physical examination observing the characteristics of the skin lesions.
Make an appointment with the dermatologist in the region closest to you:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor must perform a skin biopsy, taking a small sample of the lesion to analyze in the laboratory, which also allows the grade of the tumor to be identified, as well as its stage. Find out how a skin biopsy is performed.
Stages of squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma can be classified into different stages according to the characteristics of the tumor, the depth of the lesion and the invasion of cancer cells into other parts of the body.
The main stages of squamous cell carcinoma are:
- Stage 0: the tumor develops in the most superficial layer of the skin, called the epidermis;
- Stage 1: the tumor affects deeper layers of the skin, but does not reach the lymph nodes;
- Stage 2: the tumor affects deeper layers of the skin, causing metastases in the lower layers of the skin;
- Stage 3: the tumor spreads to nearby lymph nodes;
- Stage 4: the tumor spreads to other areas of the skin or internal organs, such as the lungs or brain.
Squamous cell carcinoma generally grows slowly and rarely metastasizes. See more about how metastasis happens.
However, it is important to consult a dermatologist as soon as symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma are noticed, to begin the most appropriate treatment, reducing the chances of the tumor spreading to other areas of the body.
Is squamous cell carcinoma curable?
Squamous cell carcinoma can be cured when detected in the early stages and the treatment recommended by the doctor is carried out.
The more advanced the disease, that is, when it spreads to other parts of the body, the more complex the treatment and the lower the chances of a cure.
Possible causes
The main causes of squamous cell carcinoma are:
- Excessive exposure to UV rays from the sun or tanning beds;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Prolonged exposure to chemicals, such as cigarette tar, toxic vapors and acids;
- Severe burn scar;
- Ulcers or chronic wounds;
- HPV infection, mainly in the genital region.
Additionally, other factors that may increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma are having fair skin, light eyes, or naturally red or blonde hair.
How the treatment is carried out
The treatment of squamous cell carcinoma must be carried out under the guidance of a dermatologist and/or oncologist, according to the size, depth, location and stage of the tumor.
The main treatments for squamous cell carcinoma are:
1. Surgery
Surgery for squamous cell carcinoma is performed by the doctor to remove the tumor, and different techniques can be used according to the characteristics of the lesion.
Thus, curettage, cryotherapy, electrocoagulation, laser therapy or Mohs surgery can be performed, for example.
2. Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy uses beams of radiation directly to the tumor to eliminate cancer cells, and can be done after surgery, or when the person does not want or cannot have surgery.
Generally, this type of treatment for squamous cell carcinoma is done when the tumor is large or has reached the innermost layers of the skin.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma is recommended by the oncologist using chemotherapy drugs, which prevent the division and multiplication of cancer cells, eliminating them from the body. Understand what chemotherapy is and how it is done.
Therefore, the use of topical chemotherapy with the application of 5-fluorouracil or imiquimod to the skin may be indicated when the tumor is more superficial, having not reached deeper layers of the skin or spread to other regions of the body.
Furthermore, when squamous cell carcinoma has caused metastases in internal organs, oral or intravenous chemotherapy may be indicated.
5. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is done using medications that help the body’s immune system eliminate squamous cell carcinoma cells.
Thus, some immunotherapeutics that may be recommended by the doctor are imiquimod in the form of an ointment to be applied to the lesion or pembrolizumab applied directly to the vein. Learn more about immunotherapy.
Read too: 5 treatments for skin cancer (melanoma and non-melanoma)

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13