Skin cancer is a disease where skin cells multiply rapidly and form a malignant tumor, which can cause symptoms such as the presence of transparent, red, brown or multicolored spots, spots or raised lesions on the skin, which can itch, crust and bleed .
Skin cancer can be of the melanoma type, which is less common, being the most serious type, or non-melanoma, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and Merkel carcinoma, which are more frequent and have a high chance of cure, when identified in the initial phase. Learn more about the different types of skin cancer.
In the presence of signs and symptoms that may indicate skin cancer, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist, so that the diagnosis can be made in the initial phase and, if necessary, treatment can be recommended that includes surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy and radiotherapy.
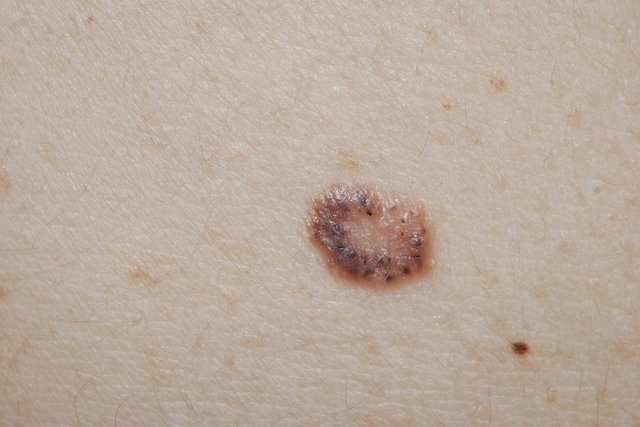
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of skin cancer are:
- Raised spots on the skin of bright, transparent, pink, red, brown, black or various colors;
- Crusted skin lesion that bleeds easily and does not heal;
- Paint on the skin that changes color and texture;
- Moles with irregular contours that increase in size;
- Spot or sore on the skin that itches or burns.
Skin cancer is more common in areas of the skin that are more exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or artificial tanning, such as the face, neck, scalp and ears. However, although it is rarer, skin cancer can also appear in the eyes, nails, mouth, nose, throat, anus, vagina or gastrointestinal tract.
Does skin cancer itch?
In some cases, skin cancer can itch, as this type of tumor can cause inflammation, irritating the nerve endings in the skin and thus causing an itchy sensation.
The main types of skin cancer that can cause itching are basal cell and squamous cell.
Types of skin cancer
The main types of skin cancer are melanoma and non-melanoma, which vary depending on the frequency and severity of this condition.
1. Melanoma skin cancer
Melanoma is a malignant skin cancer that develops in melanocytes, which are the skin cells responsible for producing melanin. Some of the symptoms of this type of cancer are asymmetrical spots, spots or moles on the skin, with irregular edges and different colors, for example.
Furthermore, in the case of metastasis to other organs, as in the case of metastatic melanoma, the person may also experience symptoms such as lumps on the skin, shortness of breath, pain in the stomach and headache, for example. Know all the symptoms of metastatic melanoma.
2. Non-melanoma skin cancer
Non-melanoma skin cancer develops in the basal or squamous cells of the skin, being the most common type and which has the lowest mortality rate when treated appropriately.
The main types of non-melanoma skin cancer are:
- Basal cell carcinoma: is the most common type of skin cancer and causes the appearance of a small red spot that grows slowly over time, a wound that does not heal or a raised white skin on the face, back or neck. Know how to recognize the symptoms of basal cell carcinoma.
- Squamous cell carcinoma, or squamous cell carcinoma: a type of skin cancer that appears mainly in the mouth, tongue and esophagus and causes symptoms such as wounds that do not heal and bleed easily, and rough patches on the skin, with irregular edges and red or brown in color.
In addition, there is also Merkel carcinoma, a rare type of skin cancer that occurs when cells called Merkel cells grow uncontrollably and can cause signs and symptoms such as pink, red or purple lumps on the skin, which do not hurt and can bleeding from the face, neck, arms or legs, for example.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of skin cancer must be made by a dermatologist by evaluating the color, shape and size of the spots or spots and through the person’s health history.
If you want to check your risk of skin cancer, make an appointment with the dermatologist closest to you:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
To confirm the diagnosis, the dermatologist also performs dermatoscopy, an examination in which a device called a dermatoscope is used that allows the image of the skin to be magnified up to 400 times, being useful for evaluating and diagnosing possible changes. Understand better what dermoscopy is for and how it is performed.
In addition, the doctor may also recommend performing a skin biopsy, which is done by removing the lesion to be analyzed in the laboratory to confirm or rule out the diagnosis of skin cancer.
Possible causes
Skin cancer is mainly caused by excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun, which causes oxidative stress and alters the DNA of skin cells, favoring the emergence of cancer.
Furthermore, some risk factors that also favor the emergence of skin cancer are:
- Have light skin and eyes, naturally red or blonde hair, or be albino;
- Personal or family history of skin cancer;
- Work under direct exposure to the sun;
- Prolonged and repeated exposure to the sun;
- Use of artificial tanning cameras;
- Presence of serious or prolonged lesions on the skin.
Furthermore, having HPV, smoking, having a weakened immune system and being exposed to radiation or chemical compounds, such as arsenic and petroleum, can also promote the development of skin cancer.
How the treatment is carried out
Skin cancer treatment varies depending on the type and severity of the disease, including surgery, chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy, immunotherapy and radiotherapy.
1. Surgery
Surgery may be recommended by the doctor mainly to treat non-melanoma skin cancer, which may include:
- Excisional surgery: the tumor is removed with a scalpel, presenting high cure rates and, therefore, it can be done in cases of recurrent tumors;
- Curettage and electrodesiccation: they are used in smaller tumors, by scraping the lesion with a curette and using an electric scalpel to destroy the cancer cells;
- Cryosurgery: carried out without cutting or bleeding, this procedure destroys the tumor by freezing it with liquid nitrogen, and can be a good option in cases of small or recurrent tumors;
- laser surgery: removes cancer cells using a carbon dioxide laser or erbium YAG laser, making it a good option for people with blood disorders.
There is also Mohs Micrographic surgery, a procedure where the tumor and a piece of surrounding skin is removed with a curette and then the material is analyzed under a microscope. This procedure is done several times, until there are no more cancer cells. This surgery is generally indicated in cases of undefined tumors or in delicate areas, such as the face.
2. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment, which involves the use of medicines, in the form of tablets or injections, that eliminate or block the growth of cancer cells. Understand better how chemotherapy is performed.
Chemotherapy sessions can be daily, weekly or every 2 to 3 weeks, for example, and can be indicated for all types of skin cancer, especially in cases of melanoma or other more advanced types of non-melanoma cancer.
3. Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is a treatment that aims to destroy or prevent the growth of cancer cells, through the application of concentrated radiation directly to the tumor. Find out more about what radiotherapy is for.
Radiotherapy can be done alone, along with chemotherapy or after surgery, to reduce the risk of skin cancer returning. This treatment may be recommended in cases of skin cancer that cover a large area, in regions of the body that are difficult to operate on, for people who cannot or want to undergo surgery, or when the cancer has spread to other organs, such as lymph nodes or lungs.
4. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a treatment that strengthens the immune system, giving the body a greater capacity to fight skin cancer. It can be indicated in cases of advanced skin cancer or that has spread to other parts of the body, or for people who have They cannot have surgery.
5. Photodynamic therapy
In photodynamic therapy, your doctor applies a cream that contains a photosensitizing compound, such as 5-aminolevulinic acid, to the skin. After a few hours, the area to be treated is exposed to an intense light source to activate the compound and destroy the tumor cells. This therapy is mainly recommended to treat non-melanoma skin cancer.
Is skin cancer curable?
Both melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers are curable, as long as they are identified and treated in the early stages of this disease.
However, diagnosing skin cancer in more advanced stages increases the chances of the tumor spreading to other organs, which may reduce the chances of a cure.
How to prevent skin cancer
Some important tips to prevent skin cancer are:
- Use sunscreen frequently whenever you leave the house, even on cloudy days;
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours or after swimming or sweating;
- Avoid exposure to the sun between 10:00 and 16:00, which is the time of highest radiation;
- Prefer sunglasses that have UV protection.
In addition, you can also use physical protectors, such as hats, umbrellas, umbrellas and clothing with UV protection.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13