The main signs and symptoms of melanoma on the skin are asymmetrical lesions or spots, with irregular edges, different colors and a diameter greater than 6 millimeters, in addition to increasing in size over time, which can be identified using the ABCDE method.
Knowing how to identify melanoma on the skin early is the best way to ensure successful treatment, as it can prevent skin cancer from developing and creating metastases that are difficult to eliminate, even with treatment.
Therefore, even with daily sun care, applying sunscreen or avoiding the hottest hours, it is very important to evaluate the skin at least once a month, even in the scalp and soles of the feet, to identify whether there are new or different moles that could be a sign of cancer.
Signs and symptoms of melanoma on the skin
One of the best ways to assess whether a mole could be melanoma is by observing its characteristics, using a rule known as ABCDE. If the spot has more than two of these characteristics, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist.
A – asymmetry
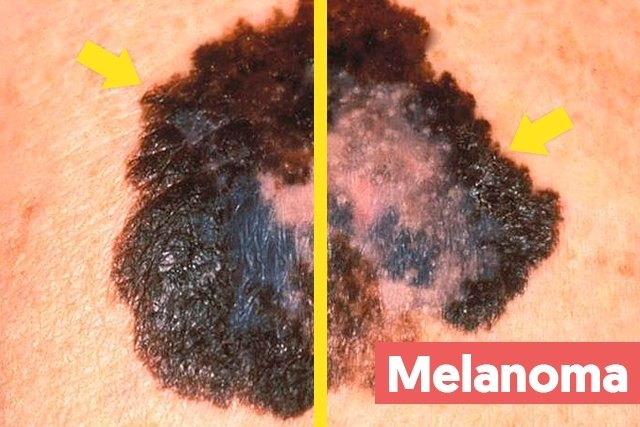
Generally, the moles that are most likely to be malignant are asymmetrical and, therefore, if an imaginary line is drawn in the middle of the mole, the two parts are not similar.
Most moles are symmetrical and, therefore, are not a sign of alarm, but it is important to know that there are also benign and asymmetrical moles, so if the mole is asymmetrical, it should be evaluated by a dermatologist just to ensure that it is not malignant.
B – edges
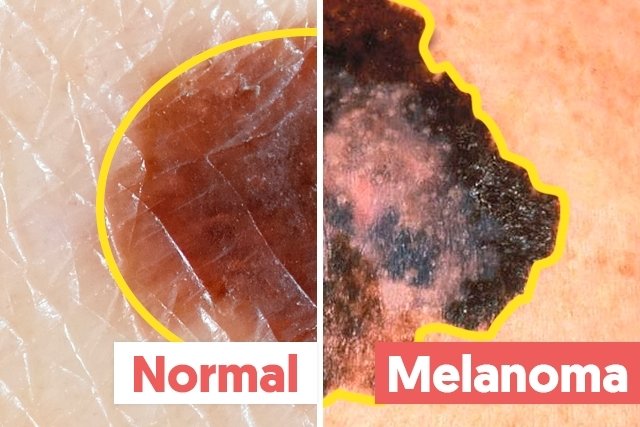
A mole with regular, smooth edges is usually benign and does not present a health hazard. Moles with irregular and poorly marked edges may be a sign of skin cancer.
C – cor
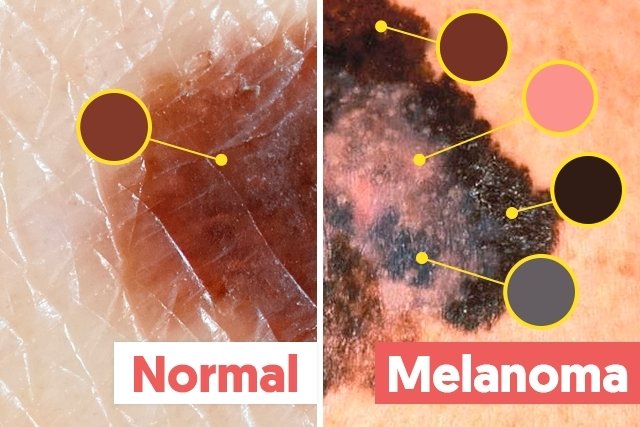
Normal moles without risk of cancer generally have a brown color, without major changes in color. Signs of melanoma usually present darker colors or even a mixture of several colors, such as black, blue, red or white, for example.
D – diameter
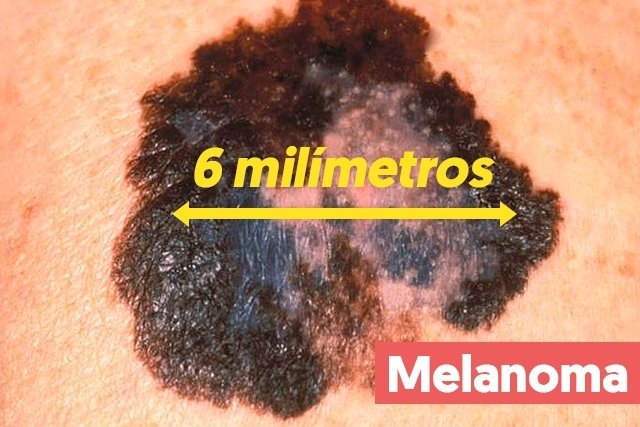
The melanoma spot is usually greater than 6 millimeters in diameter. Therefore, if a mole is larger than normal, it is very important to consult a dermatologist, even if it is normal in color, with regular edges, and even if it is symmetrical.
Furthermore, malignant signs can also grow over time, starting as a small mole, which increases until it becomes a spot measuring more than 6 mm.
E – evolution
The evolution of the spot on the skin is also important to help identify melanoma on the skin.
This evolution corresponds to an increase in the size of the spot, lesion or mole on the skin over time, or changes in its color or shape.
Furthermore, the spot, mole or lesion on the skin can also evolve and present other signs, such as itching or bleeding.
Other symptoms of skin cancer
Although the best way to identify a possible melanoma is to observe the spot on the skin, some people may experience other symptoms, such as:
- Burning sensation;
- Frequent itching;
- Bleeding.
These symptoms appear exactly at the location of the stain, but can also spread to a few centimeters around.
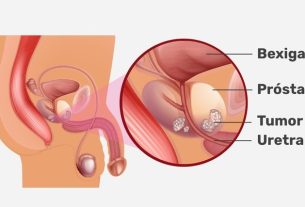
In addition to melanoma visible on the skin, there are other types of melanoma, which can be more difficult to detect, as they are found in more hidden places, such as melanomas under the nail, in the mouth, digestive tract, urinary tract or in the eye. , for example, which also need to be treated as early as possible. See the main symptoms of each type of skin cancer.
How to confirm the diagnosis
To confirm the diagnosis of melanoma or another type of skin cancer, it is very important to consult a dermatologist to evaluate the characteristics of the spot.
If you have signs and symptoms of melanoma, make an appointment in the nearest region:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
If cancer is suspected, the doctor may recommend performing a small local surgery to remove the stain. After that, the removed piece is sent to the laboratory to evaluate whether there are cancer cells.
If cancer cells are detected, the doctor may recommend removing more skin around the area where the spot was, or starting other treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy, for example, depending on the degree of cancer development. Find out more about the treatment options for skin cancer.
Bibliography
- PEREZ, M.; et al. Skin cancer: Primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. Part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 87. 2; 255-268, 2022
- AHMED, B.; et al. Malignant Melanoma: Skin Cancer-Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 30. 4; 291-297, 2020
- GRUBER, P.; ZITO, P. M. IN: STATPEARLS (INTERNET). TREASURE ISLAND (FL): STATPEARLS PUBLISHING. Skin Cancer. 2023. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441949/>. Accessed on October 27, 2023
- AMERICAN CANCER SOCIETY. Why you should know about melanoma. 2017. Disponível em: <http://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/cancer-control/en/booklets-flyers/why-you-should-know-about-melanoma-handout.pdf>. Acesso em 25 set 2019
- BRITISH ASSOCIATION OF DERMATOLOGISTS . MELANOMA IN SITU . 2018. Disponível em: <http://www.bad.org.uk/shared/get-file.ashx?id=2126&itemtype=document>. Acesso em 25 set 2019

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13