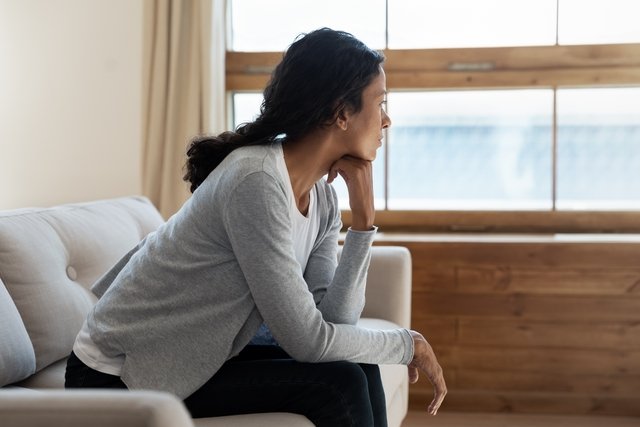
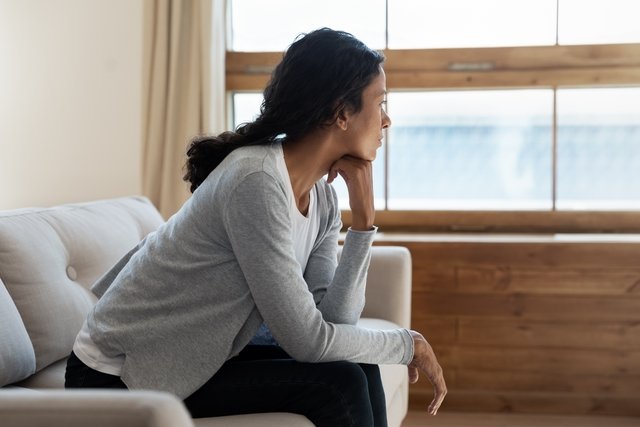
Schizoid personality disorder is characterized by a marked distancing from social relationships and preference for carrying out other activities alone, feeling little or no pleasure in carrying out these activities, in addition to a reduction in the change of expressions in social situations. Thus, it is common for people with this disorder to be described as distant and indifferent.
This type of disorder is rare, however it can be seen more frequently in men. It is important that it is identified by a psychologist and/or psychiatrist so that treatment can be started and, thus, it is possible to prevent the development of other psychological disorders, such as depression and anxiety.
Although there is no pre-defined treatment, it is recommended that people with schizoid personality disorder undergo behavioral therapy sessions so that their social skills can be stimulated. In some cases, the psychiatrist may also recommend the use of some medications.

Main symptoms
According to the DSM, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, the characteristic symptoms of a person with Schizoid Personality Disorder are:
- Lack of interest in establishing closer social bonds;
- Preference for carrying out solitary activities;
- Expression of little or no interest in having sexual experiences with the partner;
- Lack of pleasure in carrying out activities;
- Has no close friends or confidants other than first-degree relatives;
- Indifference when receiving praise or criticism;
- Demonstration of coldness and emotional detachment.
Based on the characteristics and symptoms presented, the psychologist and/or psychiatrist can diagnose the disorder, and it is important to make a differential diagnosis for schizophrenia, autism spectrum disorder and avoidant personality disorder, for example, as this way it is possible to begin the most appropriate treatment.
Possible causes
It is still not known for sure what causes this type of personality disorder originates, but it is thought that it may be related to hereditary factors and childhood experiences, since it is during the child’s development that he learns to interpret social cues and respond appropriately.
Some factors that can increase a person’s risk of suffering from this personality disorder are having a family member with a schizoid or schizotypal personality disorder or schizophrenia, as well as being a consequence of more treatment in childhood, especially when the person was raised by an emotionally distant and/or negligent person, for example.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for schizoid personality disorder must be guided by a psychotherapist, who usually performs cognitive-behavioral therapy with the aim of stimulating the development of social skills.
People with this type of disorder are at greater risk of developing other psychological disorders, such as depression or anxiety, for example, and, therefore, the use of medication may be recommended by a psychiatrist with the aim of reducing symptoms related to these disorders.
Bibliography
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5.ed. Portugal: Climepsi, 2013.
- MAZER, Angela K.; MACEDO, Brisa Burgos D. et al. Personality Disorders. Medicine (Ribeirão Preto, Online.). 50(Supl.1). 85-97, 2017
- MAYO CLINIC. Schizoid personality disorder. Disponível em: <https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/schizoid-personality-disorder/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20354419>. Acesso em 13 mar 2019

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13