The presence of high red blood cells in the urine is usually a sign of kidney problems, urinary infection or changes in the prostate. However, it can also be a consequence of very intense physical activity or due to the menstrual period. Therefore, the presence of red blood cells in the urine should always be evaluated by a doctor.
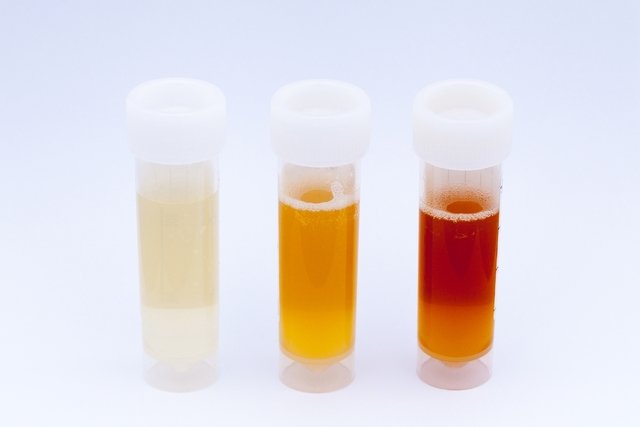
The existence of red blood cells in the urine, also known as hematuria, generally does not cause the appearance of symptoms, other than the change in color of the urine, which may become pinkish or reddish and, in some cases, cloudy. If you notice a change in the color of your urine, it is important to consult a urologist to identify the cause and begin appropriate treatment.
The value considered normal for red blood cells in urine is up to 15,000 per mL, which may vary according to the laboratory where the test was carried out.

What does red blood cells in urine mean?
The main causes of red blood cells in the urine are:
- Urinary infections;
- Inflammation of the kidneys;
- Changes in the prostate;
- Kidney diseases;
- Use of some medications, especially anticoagulants;
- Presence of kidney or bladder stones;
- Kidney cancer.
In the case of women, it is also possible to observe the presence of blood in the urine during the menstrual period and, therefore, it is not recommended that urine be collected during this period, as the test will indicate the presence of red blood cells. However, if the presence of blood is found outside the menstrual period, it is important that the woman consults the gynecologist so that more specific tests can be carried out.
Don’t ignore your symptoms!
Therefore, if any change is noticed in the urine, it is important that the person goes to the general practitioner or urologist so that tests can be carried out and appropriate treatment can be started.
Learn about other causes of blood in the urine.
How to identify high red blood cells in urine
The presence of red blood cells in urine is perceived mainly through the color of the urine, which is pink, bright red or dark depending on the amount of red blood cells. Furthermore, by viewing the urine microscopically, the presence of several or numerous intact red blood cells can be verified, as well as their degradation products, such as hemoglobin, which is identified through the strip test.
In this situation, it is also possible to identify the presence of hematic casts, which are structures formed by red blood cells, and, in some cases, the presence of numerous leukocytes and crystals.
Learn how to understand the urine test.
How the treatment should be carried out
Treatment for hematuria is indicated by the doctor according to the cause, that is, if high red blood cells in the urine are due to infections, the doctor may recommend the use of antibiotics to combat the infectious agent and thus reduce the amount of red blood cells present in urine.
If it happens due to the presence of a kidney or bladder stone, its removal is normally recommended, which is most often done through a small surgical procedure. After this procedure, it is normal for the person to continue to notice red urine, however, as recovery occurs, the urine returns to its normal color.
Bibliography
- LOPES, Marta Sofia C. et al. Microscopic hematuria: approach within primary health care. Portuguese Journal of General Family Medicine. Vol 34. 327-333, 2018
- NHS. Blood in urine. Disponível em: <https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/blood-in-urine/>. Acesso em 28 out 2019
- AMERICAN KIDNEY DISEASE. Blood in Urine. Disponível em: <https://www.kidneyfund.org/kidney-disease/kidney-problems/blood-in-urine.html>. Acesso em 28 out 2019
- STRASINGER, Susan K.; DI LORENZO, Marjorie S. Urianalysis and body fluids. 5 ed. United States: E. A Davis Company, 2008. 65-66.
- MCANINCH, Jack W.; LUE, Tom F. Smith and Tanagho General Urology. 18 ed. Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2014. 36-37.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13