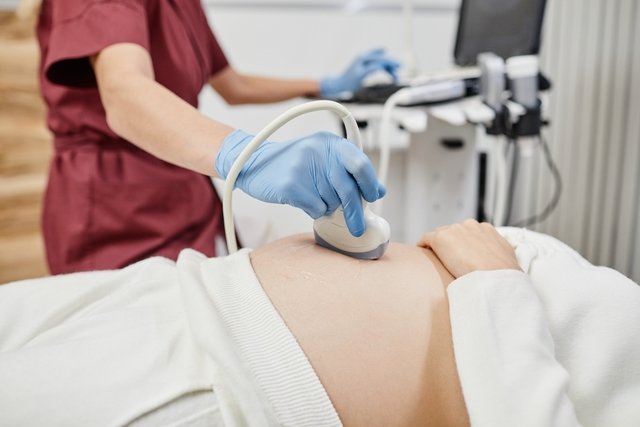
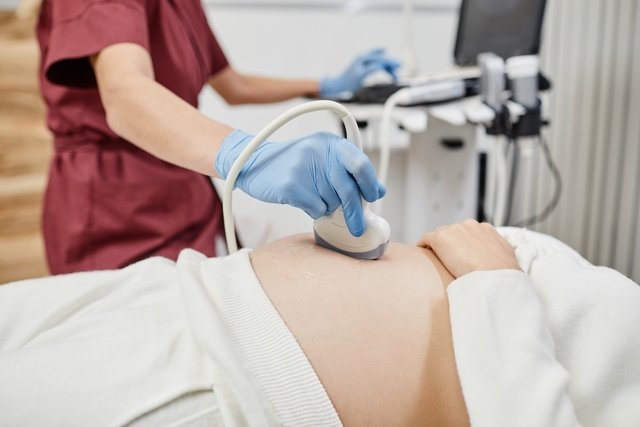
Psychological pregnancy is a psychological disorder that occurs when a woman believes she is pregnant and presents pregnancy symptoms, such as absence of menstruation, nausea or growth of her belly and breasts, but there is no fetus developing in her uterus.
Psychological pregnancy, known scientifically as pseudocyesis, mainly affects women who really want to get pregnant or those who are very afraid of getting pregnant, as happens during adolescence, for example.
Treatment for psychological pregnancy can be done with the use of hormonal medications to regularize menstruation, but it is also essential to consult a psychologist or psychiatrist to eliminate the causes that led to the development of this problem.
Psychological pregnancy symptoms
The main aspects of psychological pregnancy are:
- Absence of menstruation;
- Morning sickness;
- Somnolence;
- Food cravings or repulsion towards certain foods;
- Belly and breast growth;
- Weight gain and increased appetite;
- Sensation of feeling the fetus move;
- Breast milk production;
- Labor contractions.
These symptoms are the same as those of a normal pregnancy, but in a psychological pregnancy there is no baby being formed. Check out the main pregnancy symptoms.
It is not yet known for sure why these symptoms appear in cases of psychological pregnancy, however, it is possible that psychological stimuli generate an increase in the production of some pregnancy hormones, which results in symptoms similar to those of a true pregnancy.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of psychological pregnancy is made by the obstetrician, through the evaluation of symptoms, pelvic examination and tests, such as beta HCG in the blood or urine, which will always give a negative result due to the absence of the fetus in the woman’s uterus, which stimulates the production of hormones that indicate their presence.
Additionally, the doctor should order a transvaginal or abdominal ultrasound, which will show the absence of the gestational sac, fetal heartbeat and placenta.
Other tests that the doctor may order are the levels of the hormone prolactin in the blood, or a head tomography to rule out the presence of prolactinoma that may be causing milk production.
If you would like an evaluation by an obstetrician, schedule an appointment in the nearest region:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Possible causes
The causes of psychological pregnancy are not yet fully known, however, it is believed that it can be triggered by a combination of psychological and hormonal factors.
The main factors that can contribute to the development of psychological pregnancy are:
- Intense desire to become pregnant or difficulty getting pregnant;
- Great fear of getting pregnant;
- Infertility and sterility;
- Multiple miscarriages or loss of a child;
- Depression or anxiety;
- Emotional trauma or sexual abuse.
These factors can lead women to psychological disorders, resulting in an increase in body hormones and the development of pregnancy symptoms, but there is no fetus developing in the uterus.
Furthermore, psychological pregnancy can also be caused by tumors in the pituitary gland in the brain or tumor in the ovary, which cause changes in hormonal levels, absence of menstruation, milk production or belly growth, for example.
How the treatment is carried out
There is still no specific treatment for psychological pregnancy, however, the doctor can recommend treatments that help the woman deal with emotional factors, the main ones being:
1. Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy can be recommended by a doctor and should be carried out by a psychologist, as it helps women understand how their thoughts affect emotions and behaviors, reducing anxiety, depression or post-traumatic stress.
In these therapy sessions, the psychologist, in addition to discovering the reason behind the psychological pregnancy, will help the woman to deal better with the situation.
In some cases, the psychologist may refer the woman for an evaluation with a psychiatrist, who may recommend the use of medication to treat anxiety or depression.
2. Control anxiety and desire to get pregnant
Anxiety is one of the reasons that often leads to the emergence of a psychological pregnancy and in most cases it is caused by the intense desire to become pregnant or by the pressure caused by family or society.
Anxiety can be treated by a psychiatrist with antidepressant and/or anxiolytic medications, along with psychotherapy. Check out the main remedies recommended to treat anxiety.
Additionally, you can use natural remedies such as passion fruit tea, valerian, rosemary, chamomile or catnip, which are medicinal plants with calming and relaxing properties.
Watch the following video to see other tips from nutritionist Tatiana to help control anxiety:
3. Treat infertility and early menopause
Women who suffer from infertility or who go through menopause early can have a psychological pregnancy if they want to get pregnant and feel that their time is running out.
In these cases, hormone replacement therapy or assisted reproduction treatments, for example, may be recommended by the gynecologist.
Furthermore, if a woman has a tumor in the ovary or pituitary gland, the doctor may recommend the use of medication, surgery, chemotherapy or radiotherapy, for example.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13