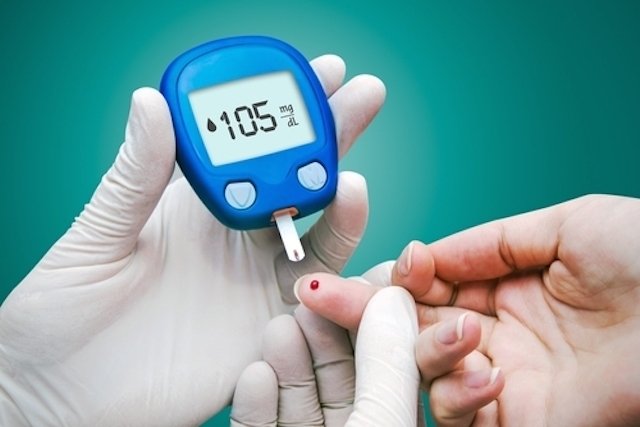
Pre-diabetes is a condition that precedes diabetes and serves as a warning to prevent the progression of the disease. A person can know that they are pre-diabetic through a simple blood test, where blood glucose levels can be observed, even when fasting.
It is considered pre-diabetes when fasting blood glucose is between 100 and 125 mg/dl and diabetes when the value is greater than 125 mg/dl, while the value considered normal for fasting glucose is up to 99 mg/dl.
Therefore, when a person has fasting blood glucose levels above 100 mg/dl, it is important that they are monitored regularly by a doctor to check whether the levels are regularized or whether diabetes is developing.
Diabetes risk test
If, in addition to increased blood glucose levels, there is an accumulation of fat in the belly, enter your data in this test to find out your risk of developing diabetes:
Symptoms of prediabetes
Pre-diabetes does not have any symptoms and this phase can last from 3 to 5 years. If a person does not take care of themselves during this period, they are very likely to develop diabetes, a disease that has no cure and that requires daily control.
The only way to know if a person has diabetes is through testing. Normal fasting blood glucose is up to 99 mg/dl, so when the value is between 100 and 125, the person already has pre-diabetes. Other tests that also serve to diagnose diabetes are the glycemic curve and the glycated hemoglobin test. Values between 6.0% and 6.4% are indicative of pre-diabetes. Learn more about tests to confirm prediabetes and diabetes.
These tests can be carried out when the doctor suspects diabetes, when there is a history in the family or in a check-up annual, for example.
Glucose test calculator
To find out if the glucose test is normal and if there is a risk of pre-diabetes, select the test carried out in the calculator below and enter your result:
How to treat prediabetes and avoid diabetes
To treat pre-diabetes and prevent the progression of the disease, you must control your diet, reducing your intake of fats, sugar and salt, and increasing your consumption of foods rich in fiber and proteins, such as brown rice and dark leafy vegetables. and beans, for example, as they help combat excess blood sugar. Check out other foods that help prevent diabetes.
In addition to diet, it is important to practice physical activity regularly, as this way excess sugar in the blood can be used to provide energy for exercise, helping to prevent diabetes.
It is also important that blood glucose levels are measured regularly, as this makes it possible to check whether blood sugar levels are as expected and whether pre-diabetes is controlled, in addition to being able to assess the risk of developing diabetes. diabetes and the need to start treatment with medication. See how to measure blood glucose at home.
Is prediabetes curable?
People who follow all medical advice and adapt their diet and regular physical activity can normalize their blood glucose levels, preventing progression to diabetes. But after reaching this goal, it is important to maintain this new healthy lifestyle so that your blood sugar levels do not rise again.
Bibliography
- GUIDELINES OF THE BRAZILIAN DIABETES SOCIETY 2021. Pharmacological treatment of prediabetes. Available at: <https://diretriz.diabetes.org.br/tratamento-farmacologico-do-pre-diabetes/>. Accessed on 24 Dec 2021

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13