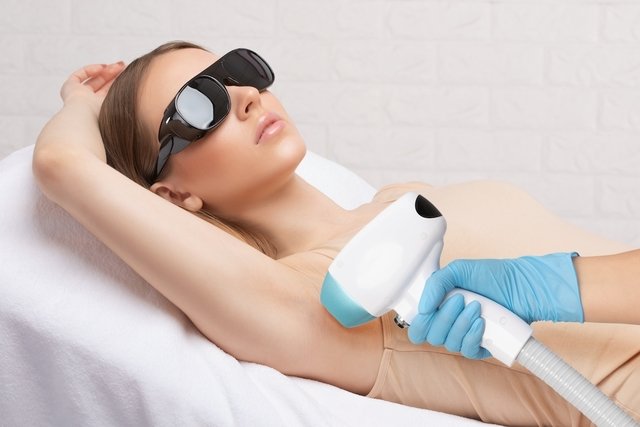
Photoepilation is a type of permanent hair removal that eliminates body hair using the intense pulsed light (IPL) technique, helping to slowly destroy the cells that produce hair, as the light is absorbed by the dark pigment of the hair.
This type of hair removal can be done on all skin types, by women or men who wish to eliminate hair from areas of the body, such as the groin, armpits, legs and beard, for example.
As photoepilation only works on hair that is directly connected to cells, which only happens in 20 to 40% of body hair, up to around 10 sessions may be necessary to obtain the result of permanent hair removal.
When is it indicated
Photoepilation is indicated for the permanent elimination of hair from areas of the body, and can be done by women or men.
The use of pulsed light can be used on all skin types, however, it presents better results on light skin with dark hair. See other indications of pulsed light.
If you wish to undergo photoepilation treatment, make an appointment with the dermatologist closest to your region:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
What areas can be waxed
Photoepilation can be used on almost all parts of the body, such as:
- Face;
- Axillas?
- Groin;
- Arms and legs;
- Stomach;
- Costas.
Other more sensitive areas, such as the intimate region or eyelids, should not be exposed to this type of hair removal.
How it works
Photoepilation works by emitting light in the form of pulses at different wavelengths, which are converted into heat and absorbed by the cells that produce hair, causing its destruction.
The interval between photoepilation sessions is 1 month, which is the time needed for the hair to be in the anagen phase, which is the hair growth phase, making it possible to obtain better results.
Difference between photoepilation and laser hair removal
Both pulsed light photoepilation and laser hair removal use beams of light that help eliminate hair.
However, they act differently. While photoepilation acts on the cells that produce hair, causing hair growth to weaken, laser hair removal acts directly on the pigment at the root of the hair, permanently destroying it.
Furthermore, the wavelengths of light from photoepilation and laser hair removal devices are different, and the results from photoepilation take longer to appear, whereas those from laser hair removal are faster.
To improve results in both cases, it is important to avoid waxing during treatment, as complete hair removal makes it difficult for light to pass to the cell that produces the hair or the hair root.
Watch the following video and learn more about how laser hair removal works:
How to prepare
To prepare for photoepilation, some precautions are important, such as:
- Inform your doctor about the use of medicinessuch as isotretinoin, corticosteroids, anticoagulants or photosensitizing medications;
- Inform if you are pregnant, suspected of being pregnant or breastfeeding;
- Inform if you have any health problemssuch as herpes, skin infections, skin cancer or heart disease;
- Inform your doctor about the use of anticoagulant medicationssuch as heparin, warfarin or acetylsalicylic acid, as it may be recommended to stop using them a few days before the session;
- Do not sunbathe or use artificial tanning for about 15 days before the session;
- Do not use wax, depilatory creams or electrolysis approximately 4 to 6 weeks before the procedure;
- Do not wear makeup on the day of the sessionif the photoepilation is on the face;
- Do not use oils, moisturizing lotions or perfumes in the area to be waxed, on the day of the session.
In addition, you should trim or shave your hair with a new razor about 3 to 5 days before the session.
How it is made
Photoepilation is carried out by a dermatologist or a professional specialized in aesthetics, using an intense pulsed light device, which emits pulse-shaped light with wavelengths from 590 nm to 1200 nm, which are absorbed by cells and present in the skin.
The pulsed light device is calibrated by the doctor before starting the procedure, according to the type of skin, color and thickness of the skin, as well as the area to be shaved.
During the session, both the person and the doctor must wear protective glasses to avoid damaging the retina of the eyes.
Each photoepilation session lasts around 30 minutes, which may vary according to the area of the body to be waxed, and the interval between sessions should be 4 weeks.
Main risks of photoepilation
The main risks of photoepilation are:
1. Spots or burns on the skin
Photoepilation can cause spots or burns on the skin, due to heating of the area to be treated, incorrect handling of the equipment or due to the use of too little gel during the procedure.
This risk can be reduced if the technique was performed by an experienced professional, who will know how to perform the technique correctly, handling the device appropriately and using the necessary amounts of gel.
2. Skin irritation and redness
After the sessions, the skin may become very red and irritated and there may even be some discomfort, pain and sensitivity in the treated area.
In these situations, it is possible to use calming moisturizing creams, with Aloe vera or chamomile in their composition or moisturizing and regenerating oils such as Bio Oil.
3. Scars on the skin
Although it is rare, photoepilation can cause scars or keloids on the skin, especially if the technique was not performed by an experienced professional, with adequate calibration of the device.
Normally, these risks can be avoided, and it is advisable to consult a dermatologist before starting photoepilation treatment.
Who shouldn’t do
Despite being considered a procedure with few risks, photoepilation is contraindicated in some specific cases, such as:
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding;
- Tanned skin;
- Acute or chronic skin diseases;
- Inflammations or active infectious diseases of the skin;
- Heart diseases, such as cardiac arrhythmia;
- such as isotretinoin, corticosteroids, anticoagulants or photosensitizing medications;
- Varicose veins in the region to be treated;
- Herpes labial ou genital.
Despite all these risks, photoepilation is considered a very safe aesthetic procedure and does not cause cancer, as it does not cause any type of change in skin cells.
However, it should not be performed on people who have already had a malignant tumor or during cancer treatment.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13