Phimosis surgery, also called postectomy, aims to remove excess skin from the foreskin of the penis and is performed when other forms of treatment have not shown positive results in treating phimosis.
The surgery can be performed with general or local anesthesia and is a safe and simple method performed by a urologist or pediatric surgeon, and is commonly recommended for boys between 7 and 10 years of age, but it can also be performed in adolescence or adult, although recovery may be more painful.
Phimosis is excess skin on the head of the penis, which causes difficulty in exposing the glans and can disappear up to 1 year of age. However, phimosis can also appear in adulthood, in which case it is a consequence of infection or skin changes, for example. Learn more about phimosis.
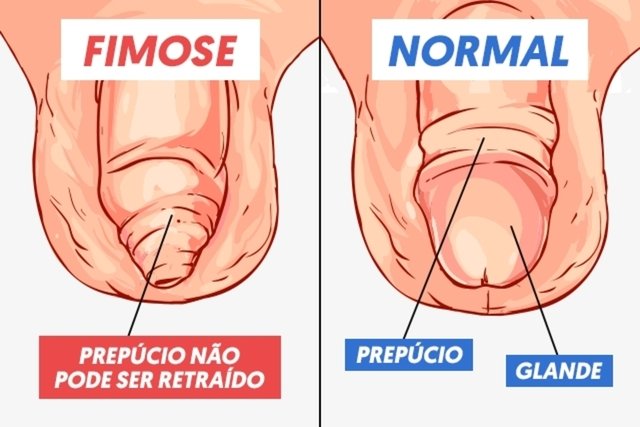
How it is made
Surgery for phimosis is performed by a urologist or pediatric surgeon, under sedation, local or general anesthesia depending on the person’s age. The surgery is considered simple and quick and consists of removing excess skin at the site, so that the glans can be exposed.
During the procedure, in addition to sedation or anesthesia, a penile nerve blocker is also administered, as this ensures that the person does not feel any discomfort during the procedure, only post-operatively.
Benefits of phimosis surgery
Postectomy is performed when other forms of treatment have not been effective in treating phimosis and, in these cases, it brings several benefits such as:
- Reduce the risk of genital infection;
- Reduce the risk of urinary infection;
- Prevent the appearance of penile cancer;
Furthermore, removing the foreskin also appears to reduce the risk of contracting sexually transmitted infections, such as HPV, gonorrhea or HIV, for example. However, undergoing surgery does not eliminate the need to use a condom during sexual intercourse.
Care during recovery
Recovery from phimosis surgery is relatively quick and in about 10 days there is no more pain or bleeding, but up to the 8th day there may be minor discomfort and bleeding resulting from erections that can occur during sleep and that is why it is recommended having this surgery during childhood, as it is an easier situation to control.
After surgery, the doctor may recommend changing the dressing the next morning, carefully removing the gauze and then washing the area with soap and water, taking care to avoid bleeding. At the end, the anesthetic ointment recommended by the doctor must be applied and covered with sterilized gauze, so that it is always dry. Stitches are normally removed on the 8th day.
To recover faster from circumcision, it is still recommended to take some precautions, such as:
- Avoid exertion in the first 3 days, resting;
- Place a bag of ice on the area to reduce swelling or when it hurts;
- Take painkillers prescribed by your doctor correctly;
Furthermore, in the case of adults or teenagers, it is advised not to have sexual intercourse for at least 1 month after surgery.
Possible risks of this surgery
This surgery, when performed in a hospital environment, has few health risks and is well tolerated and provides a quick recovery. However, although rare, complications such as bleeding, infection, narrowing of the urethral meatus, excessive or insufficient removal of the foreskin and preputial asymmetry may arise, possibly requiring further surgery.
Bibliography
- MINISTRY OF HEALTH. Phimosis. Available at: <http://portalms.saude.gov.br/saude-de-az/fimose>. Accessed on April 3, 2019

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13