Pain or stitching in the uterus can occur during the menstrual cycle, when there is an increase in the production of prostaglandin, which is responsible for the pain and which favors uterine contraction to release the endometrium, which is the wall of the uterus, characterizing menstruation.
However, when pain or stitching in the uterus occurs outside of the menstrual period and is accompanied by other symptoms, such as constant discharge, bleeding outside of menstruation, feeling of pressure in the belly, pain during sexual intercourse, enlarged abdomen and increased desire to urinate, it may be indicative of inflammation in the uterus, endometriosis, adenomyosis or uterine polyp, for example.
Therefore, if the pain in the uterus is constant, does not improve over time and is accompanied by other symptoms, it is important that the gynecologist is consulted so that tests can be carried out to help identify the cause and, thus, the most effective treatment can be initiated. adequate.

1. Menstruation
Pain or stitching in the uterus is common during menstruation, as during this period there is an increase in the production of prostaglandins, which are inflammatory substances capable of promoting uterine contraction and leading to the desquamation of the uterine wall, the endometrium, resulting in menstruation. .
What to do: Pain in the uterus due to menstruation is considered a normal situation, and it is not necessary to carry out any type of treatment. However, if the pain is very intense and makes daily activities difficult, it is important that the gynecologist is consulted so that the best medication to alleviate the pain can be indicated.
2. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, or PID, is an inflammation caused by microorganisms that normally begins in the vagina and extends to the uterus, causing symptoms such as pain, vaginal discharge, pain during sexual intercourse and bleeding outside the menstrual period. Know how to recognize the symptoms of PID.
What to do: Treatment for PID must be carried out according to the gynecologist’s guidance, and the use of antibiotics is normally indicated according to the infectious agent responsible for the inflammation.
3. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a situation in which there is abnormal growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, causing pain in the uterus, especially during the menstrual period, pain during sexual intercourse and increased menstrual flow, for example. Learn more about endometriosis.
What to do: It is important to follow the gynecologist’s instructions, who may recommend the use of anti-inflammatory medications to alleviate symptoms, hormonal medications or surgery in more serious cases.
4. Adenomiose
Adenomyosis is a change that occurs within the walls of the uterus itself, which become thicker, causing pain, which is usually more intense during menstruation, swelling in the belly, pain during sexual intercourse and increased menstrual flow, for example.
What to do: It is recommended that a gynecologist be consulted so that the diagnosis can be made and the most appropriate treatment can be initiated, which can be done with the use of medication to alleviate symptoms or, in more serious cases, surgery to remove the uterus. See more details on the treatment for adenomyosis.
5. Uterine fibroid
Uterine fibroids are a type of benign tumor that can form in the uterine muscle tissue and, in most cases, do not cause symptoms. However, when the fibroid is very large or several fibroids are identified, it is possible to have pain or stitching in the uterus, especially during sexual intercourse, constipation and a longer menstrual cycle.
What to do: The gynecologist may recommend the use of anti-inflammatory and hormonal medications, iron supplements or surgery to remove the fibroid.
6. Uterine polyp
The uterine polyp is a change, similar to a cyst, that can appear in the wall of the uterus, and that can cause pain in some women, in addition to irregular and heavy menstruation and vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse.
What to do: In most cases, it is not necessary to undergo treatment for uterine polyps, all that is necessary is regular follow-up with the gynecologist. In some cases, it may be necessary to use medication or undergo surgery to remove the polyp. Check out more details on uterine polyp treatment.
Recommended exams
Generally, to make an accurate diagnosis of the cause of pain or stitching in the uterus, the gynecologist may recommend carrying out some tests, the main ones being:
- Vaginal touch: the doctor inserts two gloved fingers into the woman’s vagina and, at the same time, places the other hand on the abdomen to evaluate the organs of the reproductive system, to diagnose endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease
- Speculum examination: a speculum is inserted into the vagina to assess the presence of discharge or bleeding;
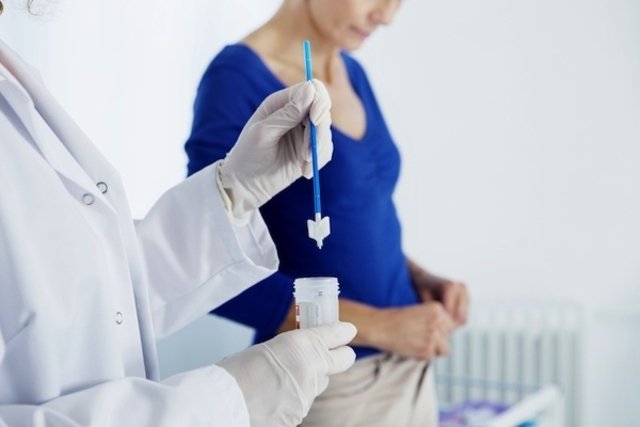
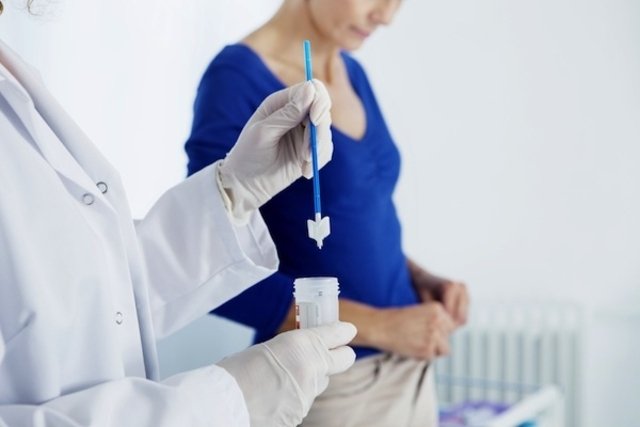
- Papanicolaou tests: also known as oncotic cytology, it is an exam used to detect the presence of uterine cancer and, to do this, a speculum must be inserted into the vagina and gently scrape the surface of the cervix to obtain cells for analysis. See how the exam is performed at: How the Pap smear is performed.
In addition to these tests, the doctor may recommend an ultrasound or an MRI, depending on the description of the woman’s symptoms and, in most cases, invasive tests should only be carried out after the start of sexual activity. Find out more about gynecological exams.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13