Otoscopy is an exam that serves to evaluate the structures of the ear, such as the ear canal and eardrum, in order to identify changes, infections or injuries.
This examination can be carried out in adults and children using a device called an otoscope, which has a magnifying lens and a light to help visualize the inside of the ear.
Otoscopy is generally performed when there are symptoms such as itching, redness, pain and discharge from the ear, or when there is a suspicion of a ruptured eardrum, for example.
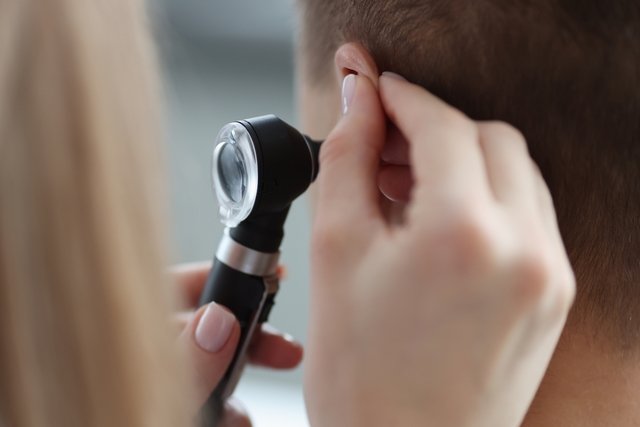
What is it for
Otoscopy is an exam that allows you to visualize the internal structures of the ear, which is why it allows you to identify problems such as:
To confirm the diagnosis of an ear disease, the doctor may also recommend other tests complementary to otoscopy, which may include pneumo-otoscopy, which is when a small rubber is attached to the otoscope to check the mobility of the eardrum, and audiometry, which assesses the mobility and pressure variations of the eardrum and ear canal.
Which doctor to consult
Otoscopy is normally performed by the otorhinolaryngologist in the office, when there are symptoms that may indicate a change in the ear. However, this examination can also be carried out by a general practitioner, for example.
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
How the exam is carried out
The otoscopy exam is used to examine the ear and is carried out according to the following steps:
- Before the exam, the person must be in a sitting position, which is the most common way to perform the exam;
- Firstly, the doctor assesses the structure of the external ear, observing whether the person has pain when pressing a specific area or whether there is any injury or wound in this region;
- If the doctor notices the presence of a lot of wax in the ear, he or she will clean it, as excess wax makes it difficult to see the inside of the ear;
- Next, the doctor will move the ear upwards and, if you are a child, pull the ear downwards and insert the tip of the otoscope into the ear hole;
- The doctor will analyze the structures of the ear, looking at the images in the otoscope, which works like a magnifying glass;
- If secretions or liquids are observed, the doctor may collect a sample to send to the laboratory;
- At the end of the exam, the doctor removes the otoscope and cleans the speculum, which is the tip of the otoscope that is inserted into the ear.
The doctor will do this process first in the ear without symptoms and then in the ear where the person complains of pain and itching, for example, so that if there is an infection it does not pass from one ear to the other.
This exam may also be indicated to identify a foreign object inside the ear and it may often be necessary to perform otoscopy with the aid of video, which allows the structures of the ear to be viewed in a much magnified way using a monitor.
How should the preparation be
To perform an otoscopy in an adult, no type of preparation needs to be done. In a child, it is necessary to keep the child hugged by the mother, so that it is possible to hold the arms with one hand and the other hand supports the child’s head, so she can be calm and relaxed. This position prevents the child from moving and hurting their ear during the exam.
Bibliography
- PIGNATARI, Shirley SN; ANSELM-LIMA, Wilma T. Textbook of Otorhinolaryngology. 3rd ed. Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier, 2018. 49-65.
- INTERAMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF PEDIATRIC OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY. Child’s ear examination. Available at: <http://www.iapo.org.br/novo/secao.asp?s=69>. Accessed on February 7, 2020
- RIBEIRÃO PRETO MEDICINE. Otorhinolaryngology semiology. Available at: <http://revista.fmrp.usp.br/1996/vol29n1/semiologia_otorrinolaringologica.pdf>. Accessed on February 7, 2020
- ENDO, Luiza H.; STEAL, Silvia B. Otoscopy and tympanometry in the diagnosis of secretory otitis media. Journal of Pediatrics. Vol.74, n.5. 353-354, 1998

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13