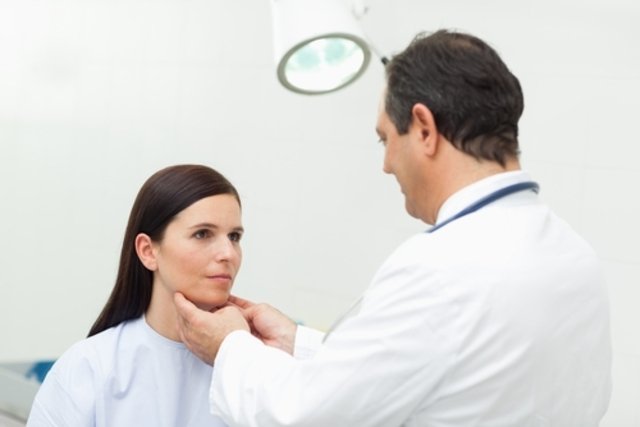
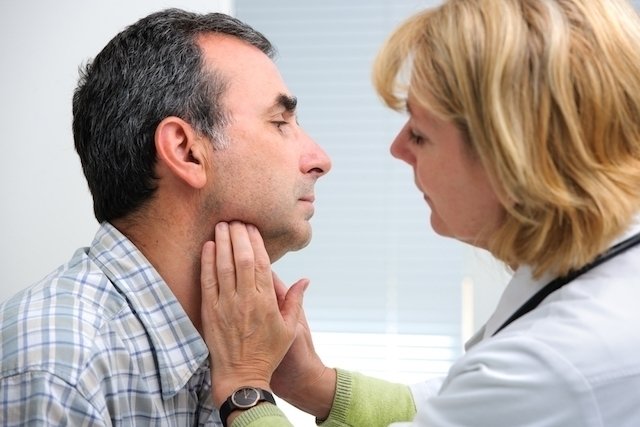
A lump in the neck can be caused by a contracture in the neck or inflammation of a lymph node due to an ear infection, throat infection or the flu, and can also be a sign of more serious situations, such as cancer, infectious parotitis or a thyroid nodule. , for example.
The lump or nodule in the neck should be evaluated by a doctor, especially when it does not decrease in size over time and when other symptoms appear, such as excessive tiredness, difficulty swallowing, general malaise or weight loss without an apparent cause.
It is important that the cause of the lump in the neck is identified so that the most appropriate treatment can be initiated according to the cause, which may include rest, use of antibiotics, use of anti-inflammatory or thyroid-regulating medications, or surgery.
Main causes
The main causes of a lump on the neck are:
1. Inflamed lymph nodes
When lymph nodes become inflamed, they form lumps that appear in the form of a lump. These lumps can appear on the back of the neck or on the side behind the ear, depending on the lymph node that is inflamed, causing pain and discomfort when touched.
Lumps in the neck can be caused by infections or inflammations such as inflammation in a tooth, flu, tonsillitis or otitis, forming nodules in the neck, disappearing after a few days, or being a sign of Hodgkin’s lymphoma, especially when the lump does not decrease in size and other symptoms appear.
What to do: Rest and hydration are recommended, in addition to identifying and eliminating the cause that caused the swelling, as it is not necessary to take any specific medication to treat it. However, the doctor may recommend analgesic or anti-inflammatory medications to relieve pain or sensitivity in the area. Additionally, you can drink eucalyptus tea and use clay compresses, as they help reduce inflammation and strengthen the body’s defenses.
Don’t ignore your symptoms!
A thyroid nodule is characterized by the appearance of a lump in the throat, in front of the neck, which must be evaluated by an endocrinologist. Generally, thyroid nodules do not cause symptoms, however, in some cases, they can cause a sore throat, swelling in the neck or difficulty breathing and swallowing.
When these nodules appear, it is necessary to consult an endocrinologist so that the person’s signs and symptoms can be evaluated, in addition to recommending diagnostic tests such as a biopsy, which identify whether the nodule is benign or whether there is a risk of cancer. Learn how to identify a thyroid nodule.
What to do: If the nodule is benign and there are no symptoms or changes in the hormones of this gland, monitoring is recommended, through annual ultrasounds and blood tests. On the other hand, if you present symptoms, changes in hormonal levels or if there is a risk of cancer, the doctor will recommend the most appropriate treatment, which may include medicines such as levothyroxine or radioactive iodine, or surgery may be necessary to remove the nodule.
3. Neck contracture
Neck contractures can generate a painful lump in the back of the neck and arise when the muscle contracts incorrectly and is unable to return to its normal state when at rest.
Generally, these types of lumps are hard and are accompanied by pain and discomfort in the affected region, and there is also a limitation in movement. See how to identify a muscle contracture.
What to do: To treat a muscle contracture in the neck region, it is recommended to take a very hot water bath, apply hot compresses to the painful area, massage the region with anti-inflammatory ointments, such as Cataflam, and stretch the neck muscles. Furthermore, the use of muscle relaxing medications, such as Miosan, may be recommended by the doctor to relieve the discomfort caused by the contracture.
When contractures do not go away, worsen or cause persistent pain for more than 7 days, it is recommended to consult a doctor or physiotherapist to evaluate other ways of treating the problem.
4. Sebaceous cyst
Another possible cause that can lead to the appearance of a lump in the throat are sebaceous cysts, which form on the skin due to the accumulation of sebum, which is an oily substance produced in the skin to lubricate and protect hair.
These types of lumps or cysts are small, soft and do not cause pain, but when they are inflamed they cause redness, pain and an increase in temperature in the region where they appear.
What to do: The treatment of these lumps requires evaluation by a dermatologist, who may recommend minor surgery to remove the cyst. Learn more about the treatment of sebaceous cysts.
5. Cancer
In more serious cases, the appearance of a lump in the neck may indicate the presence of cancer and, in these cases, the lump is accompanied by other symptoms, such as hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, feeling of a lump in the throat, frequent choking, loss of weight without apparent cause and general malaise.
Tumors that arise in the neck can be from local structures, such as muscles, lymph nodes, skin, or from organs that are in this region, such as the thyroid, or they can be a metastasis.
What to do: In the presence of a nodule associated with the aforementioned symptoms, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible, so that a diagnosis can be made and the best treatment can be indicated.
6. Infectious parotitis
Infectious parotitis, better known as mumps or mumps, appears as a lump between the ear and chin due to inflammation of the parotid glands, which are saliva-producing glands, when they are affected by the family virus. Paramyxoviridae.
In addition to the lump or nodule in the neck, the person may have a fever and pain in that region.
What to do: Mumps treatment is done in order to alleviate the symptoms of the disease and, therefore, the general practitioner or pediatrician may recommend the use of analgesics, such as paracetamol, to reduce discomfort, in addition to rest, drinking water and soft food. which are also important for improving symptoms until the body is able to eliminate the mumps virus. See details of mumps treatment.
7. Lipoma
Lipoma is a type of cyst that can appear in various parts of the body, such as the neck, shoulders, arms, back, abdomen and thighs, and is made up of fat cells.
The lipoma grows over time without causing symptoms, with only a lump or nodule being identified under the skin. However, when it increases in size and causes compression or obstruction in some tissue, it can cause symptoms such as local pain and signs of inflammation, such as redness and increased local temperature.
What to do: Treatment for lipoma consists of performing a small surgery to remove it, which can be done in the dermatologist’s office, under local anesthesia, leaving a small scar at the site. See more details about lipoma treatment.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13